TL;DR
|
“If your virtual care platform still relies on human staff for intake, triage, follow-ups, and reminders, you’re already behind.”
In a market where scale, speed, and personalization define patient experience, AI voice agents are no longer essential; they’re your frontline differentiator.
Telehealth has entered a new phase. It is about making it sustainable, scalable, and seamless. Industry data indicate that more than 80% of patients now prefer digital-first interactions, and provider networks are facing increasing pressure to deliver faster, 24/7 care with limited resources.
At the same time, virtual care models are strained by rising volumes, limited staff, and the growing demand for personalized outreach. Manual workflows are no longer enough.
That’s where AI voice agents come in, offloading repetitive tasks, reducing call center load, automating documentation, and creating intelligent, always-on patient touchpoints.
In this blog, we’ll break down how AI voice agents function in clinical workflows, explore strategic use cases across the virtual care journey, and highlight how they drive efficiency, improve patient engagement, and reduce operational burden for telehealth providers.”
From Voice to Virtual Care: How AI Voice Agents Automate Patient Interactions
AI voice agents are software systems that can communicate with users through spoken language. In the context of healthcare, they are used to automate and support patient interactions—such as collecting symptoms, confirming appointments, or following up after treatment—without requiring human intervention. These agents rely on several core components:
| Component | Function |
| ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition) | Converts the patient’s spoken words into text. Example: “I have a sore throat” becomes a text input. |
| NLU (Natural Language Understanding) | Interprets the meaning behind the transcribed text. It identifies intent (e.g., report symptoms, book appointment) and relevant entities (e.g., “sore throat”, “two days”). |
| Dialog Management | Determines the next action or response based on the conversation context. It handles the flow of dialogue, including follow-up questions or decision-making steps. |
| TTS (Text-to-Speech) | Converts the system’s response (in text) back into spoken words. This allows the AI agent to “talk” to the patient naturally. |
For example, A patient calls a clinic’s helpline with flu-like symptoms.
- Patient: “Hi, I’ve been feeling feverish and coughing a lot since yesterday.”
- ASR: Transcribes this into: “Hi, I’ve been feeling feverish and coughing a lot since yesterday.”
- NLU: Detects:
- Intent: Report symptoms
- Entities: “feverish”, “coughing”, “since yesterday”
- Intent: Report symptoms
- Dialog Manager: Decides to ask:
- “Do you also have a sore throat or difficulty breathing?”
- “Do you also have a sore throat or difficulty breathing?”
- TTS: Converts this response into natural voice output and delivers it to the patient.
This interaction continues until the system collects enough data for triage or hands it off to a human provider.
AI Voice Agent Use Cases That Improve Virtual Care Delivery
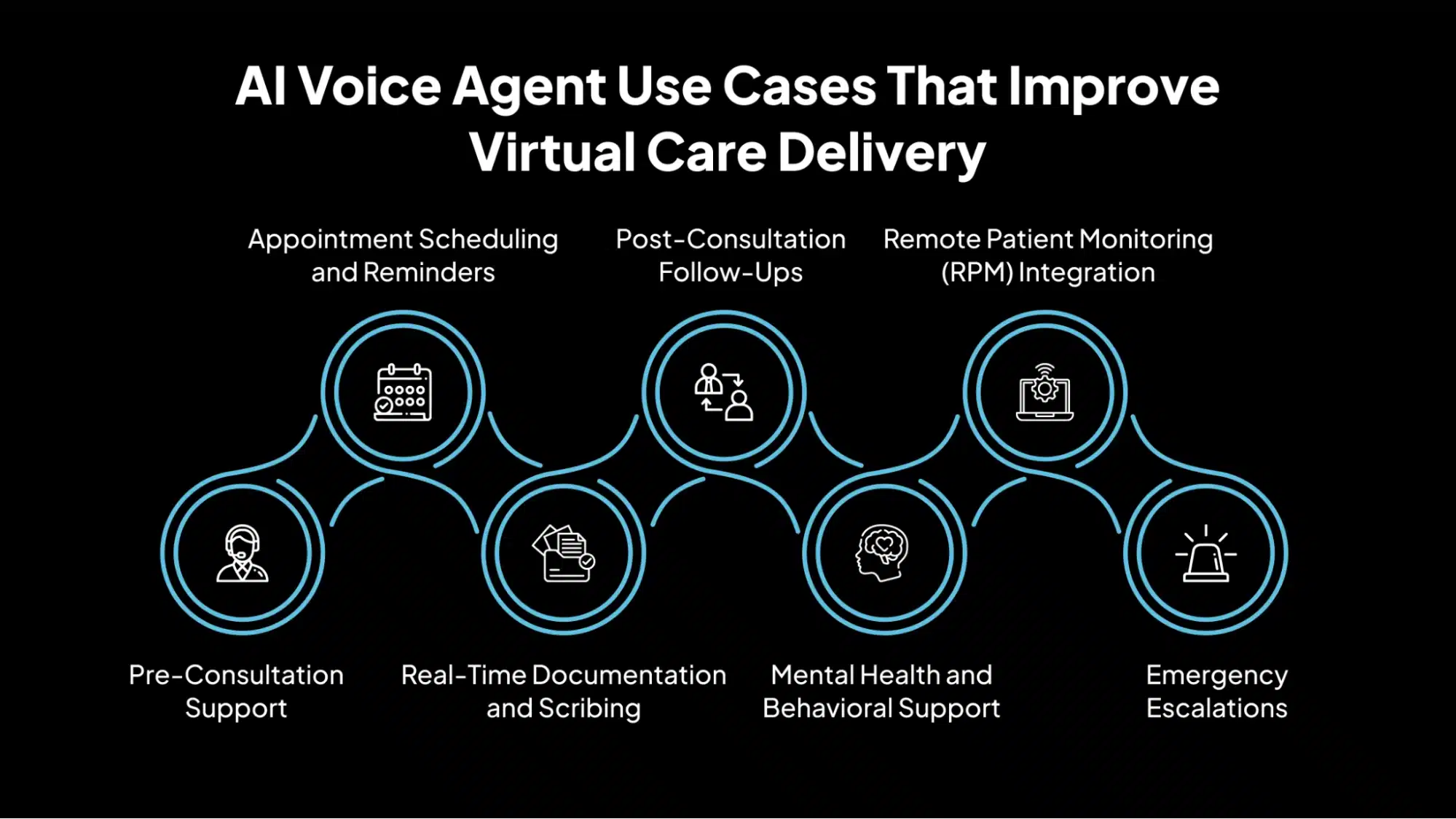
AI voice agents are being integrated across multiple stages of the virtual care journey. From patient intake to follow-up, these agents support routine tasks, improve care accessibility, and reduce the burden on clinical staff.
1. Pre-Consultation Support
AI voice agents can collect important patient information before a telehealth appointment, enabling clinicians to prepare and prioritize care effectively.
Voice agents can guide patients through a series of structured questions to gather information about symptoms, medical history, and current medications. This data can be summarized and passed to the provider before the virtual consultation, ensuring better-informed clinical decisions.
Based on the responses, the system can evaluate the urgency of the case and determine the appropriate type of provider or service. For instance, a patient reporting mild seasonal allergies may be routed to a nurse practitioner, while someone describing chest pain may be prioritized for immediate review by a physician.
2. Appointment Scheduling and Reminders
Scheduling and confirming appointments through voice agents simplifies the process for both patients and staff. Patients can use voice commands to check provider availability, schedule appointments, or modify existing bookings. This eliminates the need to wait on hold or navigate complex phone menus.
AI voice agents can place reminder calls prior to appointments, confirm attendance, and allow patients to reschedule if necessary. For example, a voice agent might say: “You have an appointment tomorrow at 10:00 AM with Dr. Smith. Press 1 to confirm or 2 to reschedule.” This simple interaction helps reduce the number of missed appointments.
3. Real-Time Documentation and Scribing
During a virtual visit, voice agents can assist by capturing the conversation and generating clinical notes. With patient consent, the voice agent can listen to the conversation between the clinician and patient, transcribing it in real-time. This helps reduce the need for manual note-taking.
The system can analyze the transcript and generate structured summaries, such as SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan) notes. This allows clinicians to focus on patient care instead of documentation and reduces after-hours administrative work.
4. Post-Consultation Follow-Ups
Voice agents play an important role in ensuring continuity of care after a virtual visit. After a telehealth session, a voice agent can check in on the patient’s condition through automated calls.
For example: “Are your symptoms improving since your last visit?” Based on the response, the system can escalate to a human provider if needed. The agent can remind patients to take prescribed medications and provide instructions or health tips. For instance, it might explain how to take an antibiotic or the importance of completing the full course.
5. Mental Health and Behavioral Support
Conversational voice agents can help monitor and support mental wellness between clinical visits. Patients experiencing anxiety, depression, or stress can engage in guided conversations with voice agents that follow therapeutic frameworks like CBT (Cognitive Behavioral Therapy). These interactions help patients reflect on their experiences, manage triggers, and access support resources.
AI voice agents can perform mood check-ins and offer coping strategies or breathing exercises. For example, a voice agent might ask: “On a scale from 1 to 5, how are you feeling today?” and respond accordingly based on the answer.
6. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Integration
AI voice agents enhance the utility of home monitoring devices by making interactions more conversational and responsive, thereby improving user experience. Instead of requiring patients to log into apps or manually upload data, voice agents can ask about or retrieve readings from connected devices.
For instance, “I noticed your blood pressure reading today was higher than usual. Are you experiencing any headaches?”
The system can analyze changes in vital signs and, if necessary, notify care teams or prompt the patient to take action. This is especially useful in managing chronic conditions such as diabetes or heart failure.
7. Emergency Escalations
Voice agents can detect signs of medical emergencies and act quickly to ensure appropriate care escalation. If a patient mentions terms like “chest pain,” “shortness of breath,” or “I can’t breathe,” the system can flag the urgency based on keyword detection and tone analysis.
In high-risk cases, the voice agent can immediately connect the call to a live healthcare professional or alert emergency services. For example, if a patient reports signs of a stroke, the system could say, “Your symptoms may indicate a medical emergency. Connecting you to help now,” and initiate a direct escalation.
The Strategic Advantage of AI Voice Agents in Telehealth Workflows
Below are the essential ways AI voice agents in telehealth deliver measurable value across telehealth workflows, improving efficiency, patient engagement, and care outcomes.
1. For Patients
24/7 Access and Immediate Support
AI voice agents operate around the clock, enabling patients to access basic healthcare services or information at any time, even outside of clinic hours. This ensures timely responses for needs such as symptom triage, appointment booking, or medication guidance without waiting for office availability.
Reduced Digital Literacy Barriers
Voice interfaces remove the need for navigating complex apps or typing on screens. Patients only need to speak naturally, which benefits elderly individuals, people with disabilities, and those who may not be comfortable using digital devices or written communication.
Hands-Free, Natural Conversations
Unlike chat-based systems, voice agents allow patients to interact without needing to touch a screen or keyboard. This is especially helpful for individuals with physical limitations, during recovery, or in moments when hands are occupied, such as caregiving or multitasking at home.
2. For Providers and Clinicians
Reduced Cognitive and Documentation Workload
Voice agents can assist with real-time documentation during virtual consultations, capturing notes and generating structured summaries to support effective communication. This reduces the manual entry burden on clinicians, allowing them to focus more on the patient during the call.
Scalability with Fewer Resources
Clinics can handle higher volumes of routine patient interactions, such as intake, follow-ups, and reminders, without increasing staffing levels. Voice agents automate these tasks, enabling practices to expand their service reach without scaling operations linearly.
Better Use of Clinician Time
By automating repetitive or low-complexity interactions, voice agents allow providers to concentrate on higher-priority clinical tasks. This improves appointment quality, reduces burnout, and ensures that human expertise is focused where it is most needed.
3. For Health Systems and Payers
Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
Automating voice-based interactions reduces the need for large call centers or administrative staff. This leads to significant cost reductions in patient engagement, appointment handling, and post-visit communications.
Reduced Administrative Burden
Tasks such as appointment confirmation, symptom intake, and medication follow-up can be managed by voice agents, freeing up staff from routine phone work and paperwork. This streamlines operations and minimizes delays in service delivery.
Insights from Voice Analytics for Population Health
AI voice agents can gather and analyze large volumes of conversational data. When de-identified and aggregated, this data provides trends and insights that help healthcare organizations monitor population health, identify care gaps, and plan interventions more effectively.
Essential Considerations for Integrating AI Voice Agents into Virtual Care
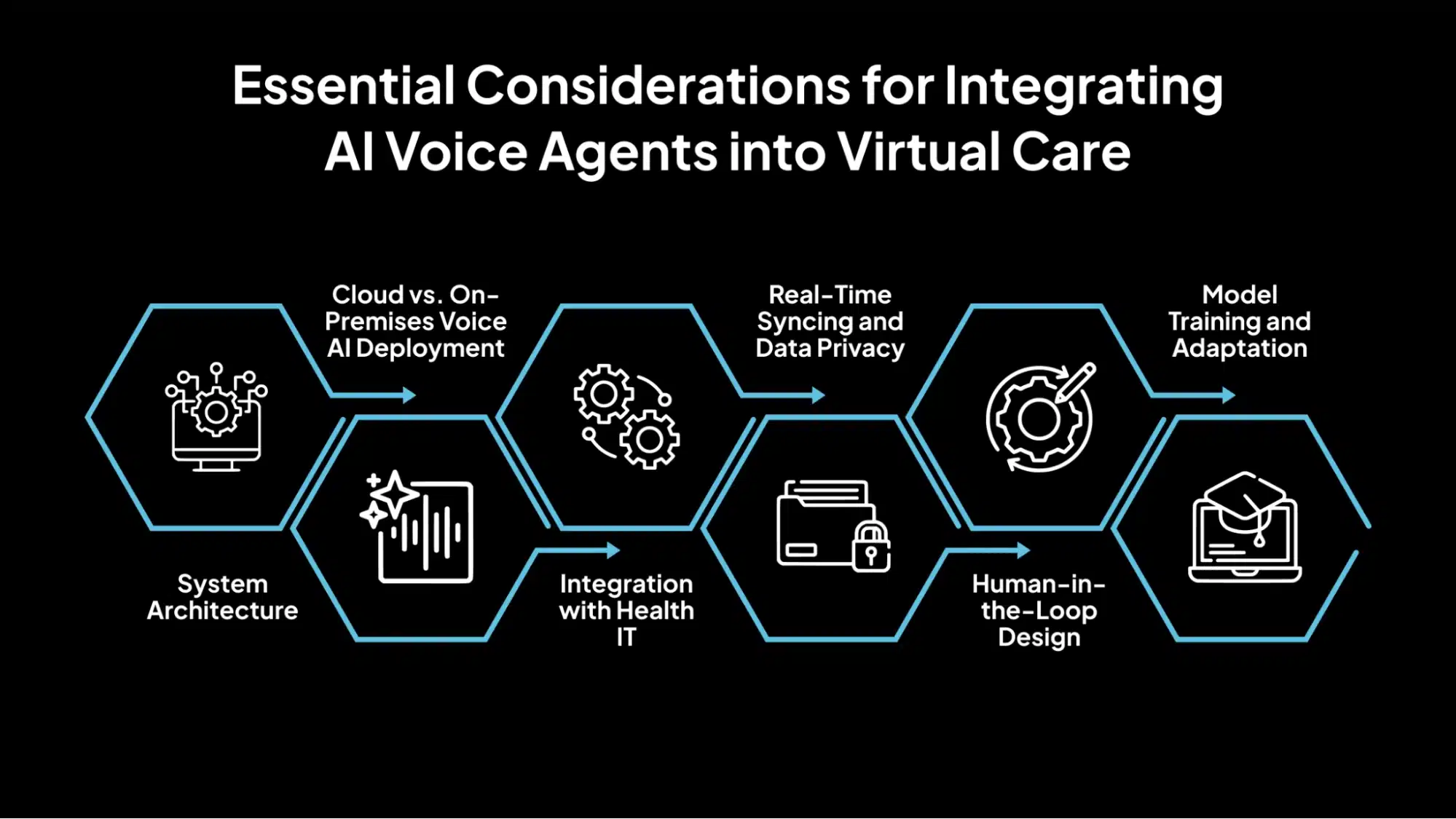
Deploying AI voice agents in telehealth requires careful planning across technical, clinical, and operational areas. Below are the key considerations for a successful and safe implementation.
1. System Architecture
The core architecture of a voice AI system begins with ASR (Automatic Speech Recognition), which converts spoken words into text. Next, an LLM or NLU (Natural Language Understanding) module interprets the meaning and identifies the intent behind the text. The Dialog Manager decides the appropriate response based on the conversation flow and system logic. Finally, TTS (Text-to-Speech) converts the system’s response into voice output. Each of these components must work together in real time for a smooth and responsive user experience.
2. Cloud vs. On-Premises Voice AI Deployment
Voice agents can be deployed in the cloud or on-premises, depending on regulatory, privacy, and scalability needs.
Cloud-based systems are faster to implement and easier to scale, while on-premises deployments may be required for strict data control or compliance in certain regions. Healthcare organizations must evaluate security, latency, and integration requirements when choosing between the two.
3. Integration with Health IT
For voice agents to deliver real clinical value, they must connect with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems. This allows them to access patient history, medications, and appointment data, and update records based on interactions. Proper integration reduces duplicate data entry and keeps patient records consistent.
4. Real-Time Syncing and Data Privacy
Data collected by voice agents should synchronize with backend systems in real-time to ensure care teams always have the latest information. At the same time, data transmission must comply with healthcare privacy regulations, such as HIPAA or GDPR, which include secure encryption, access control, and audit logging.
5. Human-in-the-Loop Design
AI voice agents should be designed with clear rules for when to escalate a call to a human. This could include detecting uncertainty, receiving an unclear response, or identifying symptoms that require clinical judgment. Escalation ensures patient safety and prevents frustrating experiences when the AI is unable to provide effective assistance.
6. Model Training and Adaptation
AI voice agents must be trained on medical language to accurately understand and process clinical terms. They should also be tested with real patient voice samples representing different age groups, accents, and languages to ensure they respond appropriately across diverse populations.Performance should be monitored regularly, and the system should be improved over time based on real-world feedback. This includes reviewing errors, updating responses, and refining models to handle edge cases. Continuous learning helps the voice agent become more accurate, reliable, and valuable in day-to-day healthcare settings.
Real-World Applications of AI Voice Agents in Telehealth
AI voice agents are already being utilized in real-world healthcare settings to automate tasks, enhance efficiency, and improve patient care. The following examples illustrate how various organizations have effectively applied voice technology in real-world scenarios.
1. IBM Agent PULSE with Cleveland Clinic
IBM partnered with the Cleveland Clinic to pilot an AI voice agent called Agent PULSE, specifically designed for patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD). The voice agent conducted routine check-ins with patients, asking about symptoms, medication adherence, and overall well-being.
Based on patient responses, the system could flag potential issues and escalate them to care teams for review. This helped clinicians prioritize patients who needed attention and reduced the time spent on manual follow-ups.
2. Voice-Based Stroke Assessment (VOICE Project)
The VOICE Project developed and evaluated a voice agent designed to detect early signs of stroke during emergency calls. The system used real-time speech processing to analyze patient responses and speech patterns, such as slurring or confusion, during triage conversations.
Clinical trials demonstrated that the voice agent could facilitate rapid screening and enable emergency teams to assess stroke risk more effectively. This type of system is especially valuable in situations where every minute counts.
3. Healthcare Call Centers with AI Voice Deflection
Some hospital networks have implemented AI voice agents in their call centers to handle high volumes of routine inquiries. These include tasks like appointment confirmations, test result updates, and medication refill requests. This helped reduce wait times for patients and allowed human staff to focus on more complex or urgent calls.
4. Scribing in Primary Care Clinics
AI voice agents are being used as ambient scribes in primary care settings to assist with clinical documentation. During virtual or in-person visits, the system listens in and generates structured clinical notes in formats like SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan). In real-world use, this approach has saved approximately 5 hours per week per physician, reducing after-hours paperwork and helping clinicians spend more time on patient care.
Future Outlook: The Next Evolution of AI Voice in Virtual Care
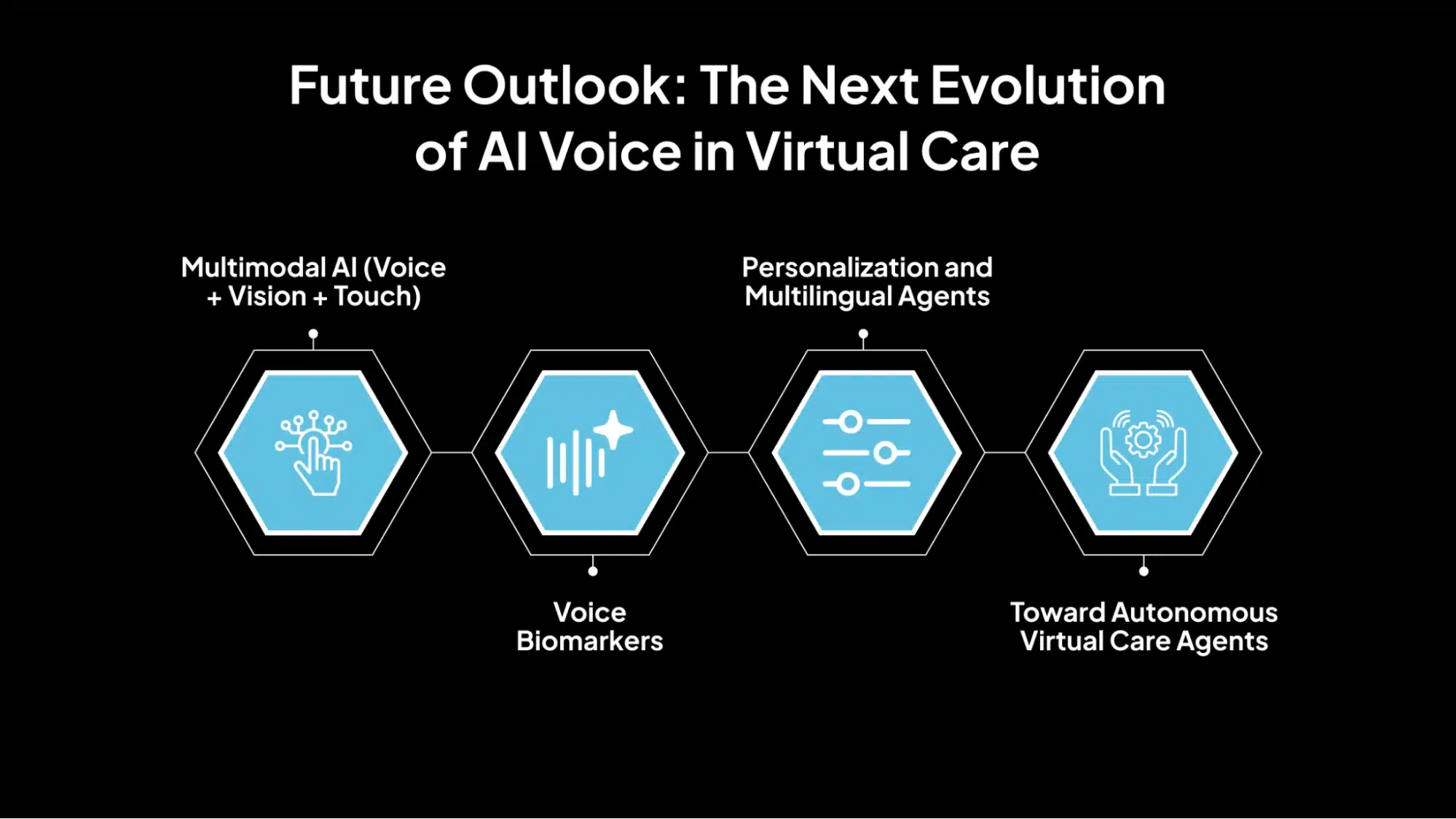
AI voice agents are evolving rapidly. As technologies advance, voice-enabled systems are expected to play an even more integral role in delivering accessible, scalable, and intelligent virtual care. Below are essential trends that will shape the future of this field.
1. Multimodal AI (Voice + Vision + Touch)
Future systems will not rely solely on voice. Multimodal AI integrates multiple data inputs, including facial expressions, gesture recognition, and sensor feedback, to build a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s condition.
For example, during a video consult, a voice agent might analyze tone of voice, facial tension, and oxygen levels from a wearable to assess both physical and emotional health. This combination allows for more accurate assessments and timely interventions.
2. Voice Biomarkers
Voice can serve as a biomarker for health conditions. Research indicates that changes in pitch, speed, or articulation may signal issues such as neurological disorders, respiratory illnesses, or mental health decline.
For example, a sudden reduction in speech clarity might indicate early signs of Parkinson’s disease. As voice biomarker detection becomes more reliable, AI voice agents may support early screening and diagnosis, especially in remote care settings.
3. Personalization and Multilingual Agents
AI voice agents are becoming more personalized, adapting to a patient’s medical history, preferences, and even communication style. They can recall previous interactions and tailor responses to meet the patient’s specific needs.
Additionally, support for multiple languages and dialects will enable voice agents to serve diverse populations more effectively. This is particularly important in regions with varied language preferences or limited access to bilingual providers.
4. Toward Autonomous Virtual Care Agents
Can AI Voice Agents become your first-line “Virtual Doctor”? One long-term possibility is the development of autonomous virtual care agents that can handle most routine patient interactions without human intervention.
These systems could manage triage, diagnostics, prescription renewals, and patient education, acting as a digital front line for healthcare systems. While they won’t replace doctors, they can significantly reduce the load on human staff by managing high-volume, low-complexity tasks efficiently. The challenge lies in ensuring safety, trust, and oversight as these systems become more capable.
How Avahi AI Voice Agents Optimize Call Center Operations for Providers
Managing high call volumes is one of the most time-consuming and resource-draining tasks in healthcare today. For practices seeking to reduce operational stress and enhance patient experience without increasing staff, Avahi AI Voice Agents provide a practical and scalable solution.
Explicitly designed for high-demand care environments like dental, specialty, primary, and urgent care, Avahi automates patient communication through innovative, conversational voice technology, available 24/7.
Here’s What Avahi AI Voice Agents Can Do for Your Practice:
- Instantly Answer Common Patient Questions
Patients can get immediate answers to frequently asked questions—like office hours, directions, and service availability—without waiting on hold.
- Automate Appointment Scheduling
Let patients book, reschedule, or cancel appointments in real time, without requiring staff involvement. Reduce friction and missed care opportunities.
- Send Reminders and Post-Visit Follow-Ups
Reduce no-shows and maintain care continuity with automated alerts that keep patients informed about their upcoming or recent visits.
- Intelligently Route Urgent Calls
Calls involving time-sensitive or critical symptoms are automatically escalated to the appropriate clinical team, ensuring prompt intervention.
- Support Insurance and Referral Questions
Streamline administrative workflows by automating responses to insurance coverage, referral tracking, and call triage.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are AI voice agents in telehealth, and how do they work?
AI voice agents in telehealth are software systems that use speech recognition, natural language processing, and automated responses to interact with patients through voice. They help handle tasks like symptom triage, appointment scheduling, and post-consultation follow-ups, freeing up clinical staff for higher-value care.
2. How do AI voice agents in telehealth improve patient experience?
AI voice agents in telehealth provide 24/7 access, reduce wait times, and support hands-free, natural conversations. Patients receive immediate support and consistent communication, even outside of business hours, making the care process more accessible and engaging.
3. Can AI voice agents in telehealth integrate with EHR and other health IT systems?
Yes, most AI voice agents in telehealth are designed to integrate with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and other digital platforms. This enables the real-time syncing of patient data, automated documentation, and seamless workflow automation for healthcare providers.
4. Are AI voice agents in telehealth compliant with data privacy regulations?
AI voice agents in telehealth must adhere to healthcare privacy laws, such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. They use encrypted communication, secure storage, and strict access controls to ensure patient data is protected throughout the interaction.
5.What are the most common use cases for AI voice agents in telehealth today?
Everyday use cases for AI voice agents in telehealth include automated symptom intake, appointment reminders, virtual triage, medication adherence follow-ups, and real-time scribing. These applications help telehealth providers reduce costs and increase operational efficiency.