TL;DR
|
Every 39 seconds, a healthcare data breach occurs. In 2024 alone, over 275 million records were compromised, putting sensitive patient information at risk.
As the healthcare industry faces an increasing number of cyberattacks and data leaks, the urgency to protect Protected Health Information (PHI) has never been higher. For healthcare organizations, safeguarding patient data is a matter of trust, security, and legal obligation.
Data masking helps protect healthcare data by masking sensitive information, allowing organizations to ensure that data is protected even when used in non-production environments, such as testing, development, or analytics.
The technique involves obfuscating real patient data with fictitious but realistic values, thereby reducing the risk of exposing sensitive details. This blog examines the crucial role of data masking in achieving HIPAA compliance, outlines best practices for its implementation, and highlights the challenges that healthcare organizations must overcome to safeguard patient privacy.
Understanding HIPAA and Its Relevance to Healthcare Data
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)is a U.S. federal law enacted in 1996 to protect sensitive patient health information from unauthorized disclosure, fraud, and theft.
HIPAA mandates secure handling of health data by healthcare providers, insurers, and their business partners. It comprises several rules, including the Privacy Rule, Security Rule, and Breach Notification Rule, each designed to safeguard health information in different contexts.
Covered Entities and Business Associates
Under HIPAA, a “Covered Entity” refers to healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses that electronically transmit health information for certain transactions. These entities are directly responsible for complying with HIPAA’s privacy and security provisions.
A “Business Associate” is an individual or organization that performs certain functions or activities on behalf of, or provides services to, a Covered Entity that involves access to Protected Health Information (PHI). Business Associates must adhere to HIPAA regulations through contractual agreements, ensuring the confidentiality and security of PHI.
Protected Health Information (PHI)
PHI includes any health information that can identify an individual and is created, received, maintained, or transmitted by a Covered Entity or Business Associate. This includes information related to an individual’s physical or mental health condition, healthcare services provided, or payment for healthcare services.
To qualify as PHI, the information must be individually identifiable. This means it includes personal identifiers such as names, addresses, birth dates, Social Security numbers, and other unique identifiers. Even if health information is de-identified, it is no longer considered PHI and is not subject to HIPAA regulations.
HIPAA’s Privacy Rule permits the use and disclosure of PHI for treatment, payment, and healthcare operations without patient authorization. However, for other purposes, such as marketing or research, explicit patient consent is generally required.
What Is Data Masking and Why Is It Essential for Healthcare Security
Data masking is a data security technique that involves obscuring sensitive information within a database to prevent unauthorized access, while maintaining the data’s usability for authorized purposes.
This process ensures that sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) or protected health information (PHI), is not exposed during activities like testing, development, or analytics. In the healthcare industry, data masking is crucial for several reasons:
Compliance with Regulations
It helps healthcare organizations comply with data protection regulations, such as HIPAA, by safeguarding sensitive patient information.
Protection Against Data Breaches
By masking data, healthcare providers reduce the risk of exposing sensitive information during system migrations, third-party collaborations, or internal testing.
Maintaining Data Integrity
Masked data retains its original structure and format, enabling realistic testing and analysis without compromising patient privacy.
| Types of Data Masking Techniques | ||
|---|---|---|
| Technique | Description | Use Cases |
| Static Data Masking (SDM) | Creates a masked copy of data, replacing sensitive info with realistic data for non-production use. | Software development, testing, and data analysis without accessing sensitive data. |
| Dynamic Data Masking (DDM) | Mask data in real-time without altering the original data based on user roles. | Role-based access control, real-time protection during data retrieval. |
| Tokenization | Replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens, mapped back to the original data. | Payment processing, storing tokens instead of sensitive data. |
| Data Redaction | Removes or obscures sensitive information in documents to prevent exposure. | Document sharing, ensuring sensitive data is not exposed in publications. |
How Data Masking Supports HIPAA Compliance
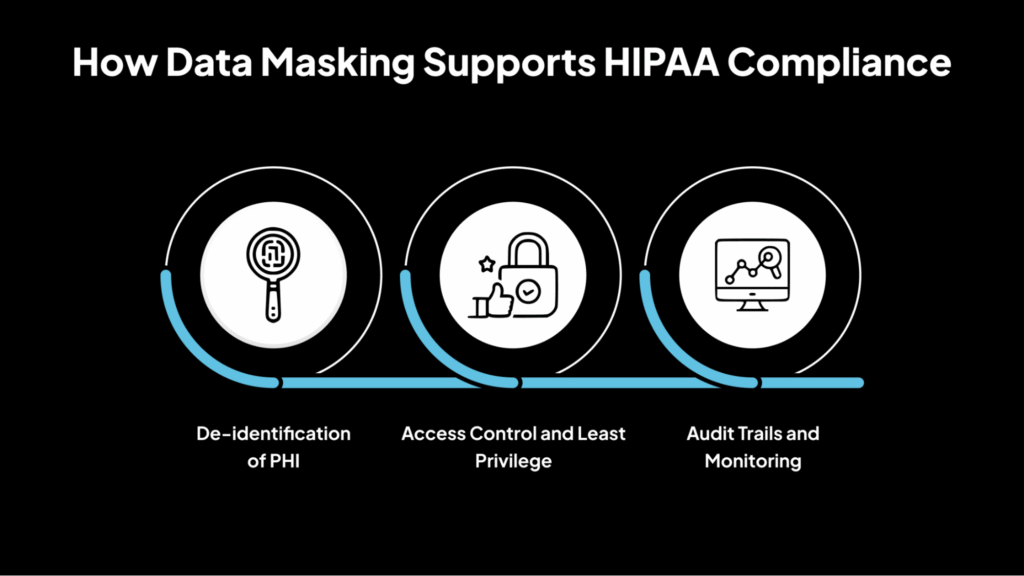
Below is an explanation of how data masking plays a crucial role in supporting HIPAA compliance by safeguarding sensitive healthcare information.
1. De-identification of PHI
Data masking plays a crucial role in de-identifying Protected Health Information (PHI), aligning with the HIPAA Privacy Rule. By transforming sensitive data into non-sensitive equivalents, data masking ensures that the information cannot be traced back to an individual without additional information.
This process is crucial for enabling the use of health data in research, analytics, and testing without compromising patient privacy. According to the HIPAA Privacy Rule, de-identified data is not subject to the same restrictions as identifiable health information, thus facilitating broader data utilization while maintaining compliance.
2. Access Control and Least Privilege
Implementing data masking enforces strict access controls by ensuring that only authorized personnel can view sensitive information. This aligns with the HIPAA Security Rule’s requirement for the implementation of access controls to protect electronic PHI.
Data masking techniques, such as dynamic data masking, allow organizations to display only the necessary data to users based on their roles and responsibilities, thereby adhering to the principle of least privilege. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
3. Audit Trails and Monitoring
By logging all access and modifications to sensitive data, organizations can track who accessed what information and when. This capability is essential for detecting and responding to unauthorized access or potential breaches.
HIPAA mandates that covered entities and business associates implement audit controls to record and examine activity in systems containing electronic PHI. Regular monitoring and analysis of these audit trails help ensure compliance and provide documentation in case of audits by regulatory bodies.
Essential Benefits of Data Masking in Ensuring HIPAA Compliance
Data masking offers several benefits that not only protect sensitive patient information but also ensure healthcare organizations remain fully compliant with HIPAA regulations. Below are the essential advantages of implementing data masking in healthcare settings.
1. Data Minimization
Data masking aligns with HIPAA’s principle of data minimization by ensuring that only masked data is accessible during non-production activities. This reduces the exposure of Protected Health Information (PHI), thereby mitigating the risk of unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
By limiting access to sensitive information, organizations can comply with the HIPAA Privacy Rule, which mandates that only the minimum necessary information be used or disclosed.
2. Secure Testing and Development
Data masking enables development and testing teams to work with realistic datasets without exposing actual PHI.
By replacing sensitive information with anonymized data, organizations can conduct thorough testing and development processes while maintaining compliance with HIPAA regulations. This practice ensures that sensitive data is not inadvertently exposed during the software development lifecycle.
3. Enhanced Access Controls
Implementing data masking provides an additional layer of security by enforcing access controls. Only authorized personnel with the necessary permissions can view unmasked data, ensuring that sensitive information is protected.
This practice supports HIPAA’s Security Rule, which requires covered entities to implement access controls to protect electronic PHI.
4. Audit and Compliance Reporting
Data masking facilitates auditing and compliance reporting by ensuring that only masked data is stored and shared, thereby protecting sensitive information. This simplifies the process of demonstrating compliance with HIPAA regulations during audits.
By maintaining masked datasets, organizations can provide auditors with the necessary information without exposing sensitive PHI.
Essential Strategies for Implementing Data Masking to Ensure HIPAA Compliance
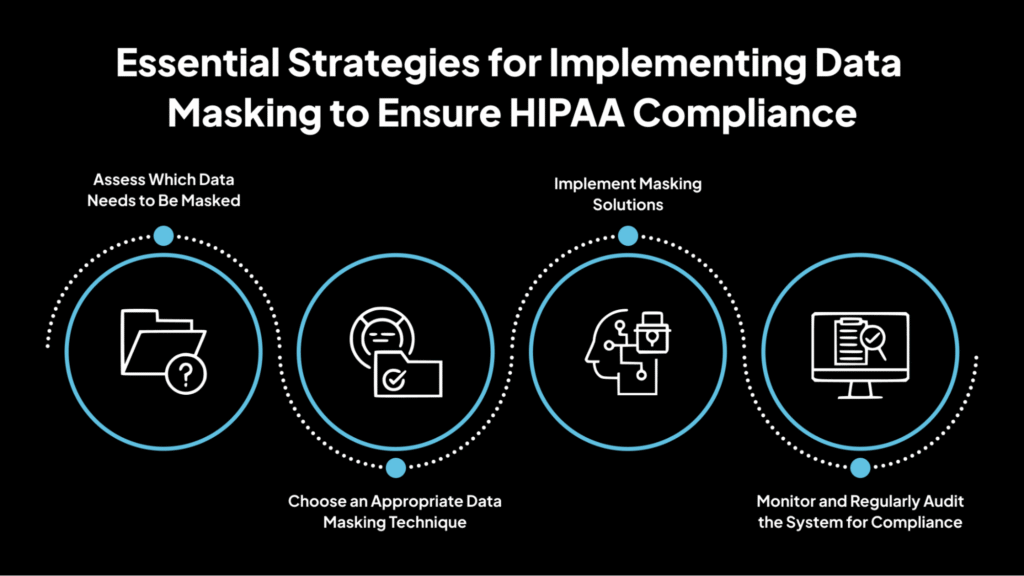
Below is a detailed explanation of how to effectively implement data masking in healthcare organizations.
1. Assess Which Data Needs to Be Masked
Begin by identifying and classifying sensitive data within your systems. This includes:
- Patient Identifiers: Names, Social Security numbers, medical record numbers.
- Medical Information: Diagnoses, treatment plans, lab results.
- Financial Data: Insurance details, billing information.
Utilize automated data discovery tools to scan databases and pinpoint PHI across structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data sources.
2. Choose an Appropriate Data Masking Technique
Select a data masking method that aligns with your organization’s needs:
- Static Data Masking (SDM): Creates a masked copy of the database for use in non-production environments. Ideal for application testing and analytics.
- Dynamic Data Masking (DDM): Masks data in real-time during access, ensuring that unauthorized users see only masked data. Suitable for production environments where data access needs to be controlled.
- Tokenization: Replaces sensitive data with unique tokens that can be mapped back to the original data through a secure tokenization system. Helpful in protecting sensitive data in transactional systems.
- Data Redaction: Removes or obscures sensitive information within documents, ensuring that only authorized users can view the original data.
3. Implement Masking Solutions
Deploy data masking solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing healthcare systems. Choose tools that automate the data masking process to reduce manual errors and ensure consistency.
Ensure the solution supports HIPAA compliance by providing features like audit trails, role-based access controls, and encryption. Select tools that can scale with your organization’s data growth and evolving compliance requirements.
Regularly update and maintain the masking solutions to adapt to changes in data sources and compliance regulations.
4. Monitor and Regularly Audit the System for Compliance
Establish continuous monitoring and auditing mechanisms. Maintain logs of all data access and masking activities to detect and respond to unauthorized access promptly.
Generate reports to demonstrate adherence to HIPAA requirements during audits and other regulatory reviews. Conduct periodic reviews of data masking policies and practices to ensure ongoing compliance and address emerging risks.
Challenges in Implementing Data Masking for HIPAA Compliance and How to Overcome Them
While data masking is a powerful tool for ensuring HIPAA compliance, implementing it effectively comes with its own set of challenges. Below, we explore these challenges and offer insights on how to overcome them.
1. Maintaining Data Integrity
Ensuring that data masking does not compromise the usability or integrity of data is paramount, especially in clinical decision-making contexts. Masked data must retain its structure and format to ensure that applications and systems function correctly.
For instance, if patient names are replaced with pseudonyms, the masked data should still align with other datasets, such as billing or appointment records, to maintain relational integrity. Failure to do so can result in errors in data processing and analysis, which may impact patient care and organizational operations.
2. Balancing Privacy and Usability
Striking a balance between protecting sensitive information and ensuring that data remains usable for authorized professionals is a significant challenge. Over-masking can render data unusable for analysis, testing, or reporting purposes, while under-masking can leave sensitive information exposed.
For example, in a healthcare setting, if diagnostic codes are masked but the associated patient identifiers are not, the data may still be re-identifiable. Therefore, it’s crucial to apply masking techniques that preserve data utility without compromising privacy.
3. Compliance and Regulation Variability
Ensuring that data masking solutions comply with HIPAA, as well as other local or international data protection laws, adds complexity to the implementation process. HIPAA provides specific guidelines for de-identifying Protected Health Information (PHI).
Still, other regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, may have different requirements for data anonymization and pseudonymization.
For instance, GDPR emphasizes the need for data protection by design and by default, which may necessitate additional measures beyond those required by HIPAA. Organizations operating internationally must ensure that their data masking practices align with all applicable regulations to avoid legal repercussions.
Best Practices for Implementing Data Masking in Healthcare
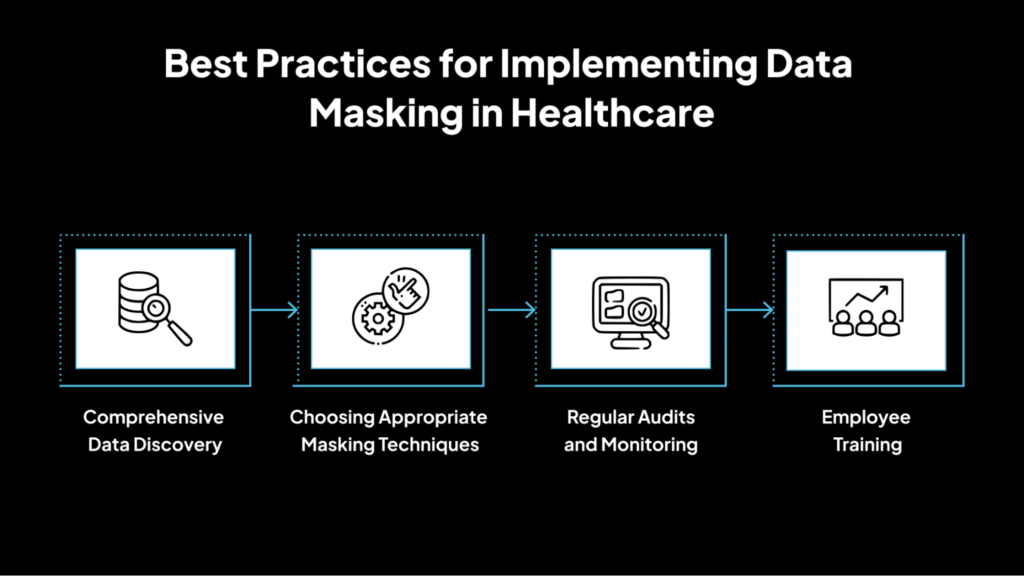
Implementing data masking in healthcare requires careful planning and best practices to ensure patient privacy, regulatory compliance, and data security. Here are the essential strategies for successful implementation.
1. Comprehensive Data Discovery
Before implementing data masking, it’s crucial to identify and classify all sensitive data within your systems. This includes:
- Protected Health Information (PHI): Such as patient names, Social Security numbers, medical records, and billing information.
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII): Including addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Financial Data: Like credit card numbers and bank account details.
Utilizing automated data discovery tools can help scan databases and pinpoint sensitive information across structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data sources. This step ensures that all sensitive data is identified before applying masking techniques.
2. Choosing Appropriate Masking Techniques
Selecting the correct data masking method is crucial for striking a balance between data protection and usability. The choice of technique should align with the specific use case and regulatory requirements.
For instance, SDM is suitable for testing environments, whereas DDM is more suitable for production systems that require real-time data access.
3. Regular Audits and Monitoring
Continuous oversight is vital to ensure that data masking practices remain effective and compliant with regulations. Maintain logs of all data access and masking activities to detect and respond to unauthorized access promptly.
Generate reports to demonstrate adherence to HIPAA and other relevant regulations during audits and other compliance reviews. Conduct periodic reviews of data masking policies and practices to ensure ongoing compliance and address emerging risks.
Regular audits and monitoring help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure that data masking strategies are effectively protecting sensitive information.
4. Employee Training
Educating staff on data protection practices is essential for maintaining a secure environment. Provide training on:
- Data Handling Procedures: Guidelines on how to manage sensitive information securely.
- Regulatory Requirements: Understanding of HIPAA and other relevant data protection laws.
- Incident Response: Procedures to Follow in Case of a Data Breach or Security Incident
Regular training sessions help reinforce the importance of data security and ensure that employees are adequately equipped to handle sensitive information.
Why Choose Avahi Data Masker: Streamlined, Scalable, and Secure Data Masking
As part of its commitment to secure and compliant data operations, Avahi’s AI platform provides tools that enable organizations to manage sensitive information precisely and accurately. One of its standout features is the Data Masker, designed to protect financial and personally identifiable data while supporting operational efficiency.
Avahi Data Masker is designed for organizations that need to handle sensitive information while maintaining operational efficiency securely. It offers a structured, AI-powered approach to data masking, ensuring that confidential fields, such as personal identifiers, financial records, and health data, are protected while remaining usable for internal processes like analytics, development, and testing. Here are the reasons to choose Avahi Data Masker:
- Cross-Industry Compliance Support: Enables secure data handling across healthcare (HIPAA), finance (PCI DSS), retail, and other regulated sectors.
- Role-Based Access Control: Restricts data visibility to authorized users, ensuring sensitive data is protected when accessed by multiple teams or vendors.
- AI-Powered Masking Logic: Uses intelligent algorithms to identify and mask sensitive fields without altering data structure or usability.
- Simple, Guided Workflow: A user-friendly interface streamlines the process from file upload to secure output.
- Data Usability Post-Masking: Masked data retains its format, supporting downstream tasks such as reporting, fraud detection, or test environments.
This functionality ensures data security, regulatory compliance, and operational continuity in a single solution.
Simplify Data Protection with Avahi’s AI-Powered Data Masking Solution
At Avahi, we recognize the crucial importance of safeguarding sensitive information while maintaining seamless operational workflows.
With Avahi’s Data Masker, your organization can easily protect confidential data, from healthcare to finance, while maintaining regulatory compliance with standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Our data masking solution combines advanced AI-driven techniques with role-based access control to keep your data safe and usable for development, analytics, and fraud detection.
Whether you need to anonymize patient records, financial transactions, or personal identifiers, Avahi’s Data Masker offers an intuitive and secure approach to data protection.
Ready to secure your data while ensuring compliance? Get Started with Avahi’s Data Masker!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is HIPAA data masking, and why is it important?
HIPAA data masking involves replacing sensitive patient information with fictional data to prevent unauthorized access while maintaining usability for non-production tasks, such as testing and development. It is essential for safeguarding Protected Health Information (PHI) and ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
2. How does HIPAA data masking help in compliance with healthcare regulations?
HIPAA data masking ensures that healthcare organizations meet the Privacy and Security Rules of HIPAA by de-identifying PHI during non-production use. This reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, while helping organizations stay compliant with federal healthcare regulations.
3. What types of data can be protected using HIPAA data masking?
HIPAA data masking can protect various types of PHI, including patient names, Social Security numbers, medical records, insurance details, and billing information. By masking these sensitive data elements, organizations can maintain privacy and reduce the risk of exposure during testing or development processes.
4. What are the benefits of using data masking in healthcare for HIPAA compliance?
The benefits of HIPAA data masking in healthcare include enhanced data security, minimized risk of data breaches, secure testing and development environments, and simplified compliance reporting. It ensures that sensitive data is only accessible to authorized users, mitigating risks associated with non-compliance.
5. How do healthcare organizations implement HIPAA data masking effectively?
To implement HIPAA data masking effectively, healthcare organizations should first assess which sensitive data needs masking, choose the appropriate masking technique (e.g., static or dynamic), and regularly monitor systems for compliance. Ensuring integration with existing systems and ongoing audits is crucial for maintaining data privacy and compliance with HIPAA.