TL;DR
|
Your data protection strategy speaks louder than your product features.
Today, protecting sensitive data is a direct driver of customer trust, brand reputation, and business continuity. According to the Cisco Consumer Privacy Report, 68% of consumers say they would stop doing business with a company after a data breach has occurred. This means privacy and trust are now central to the customer experience.
Modern teams rely on data to build products, run tests, generate insights, and make decisions. Developers need test environments. Analysts need real datasets. Customer support teams need access to operational systems. In all of this, realistic data is essential, but exposing real sensitive data is a risk you can’t afford to take.
So, how do you ensure teams can work efficiently, without compromising security?
The answer lies in Data Masking, but choosing the right approach is critical. Should you permanently mask data for development and testing? Or do you need to dynamically mask sensitive information in real-time, based on who’s accessing it?
This blog simplifies the choice by comparing two types of data masking, Static Data Masking
(SDM) and Dynamic Data Masking (DDM). We will explain where each method fits into your data lifecycle and how to align it with compliance requirements and customer trust.
Static Data Masking Explained: Secure Test Data Without Compromising Privacy
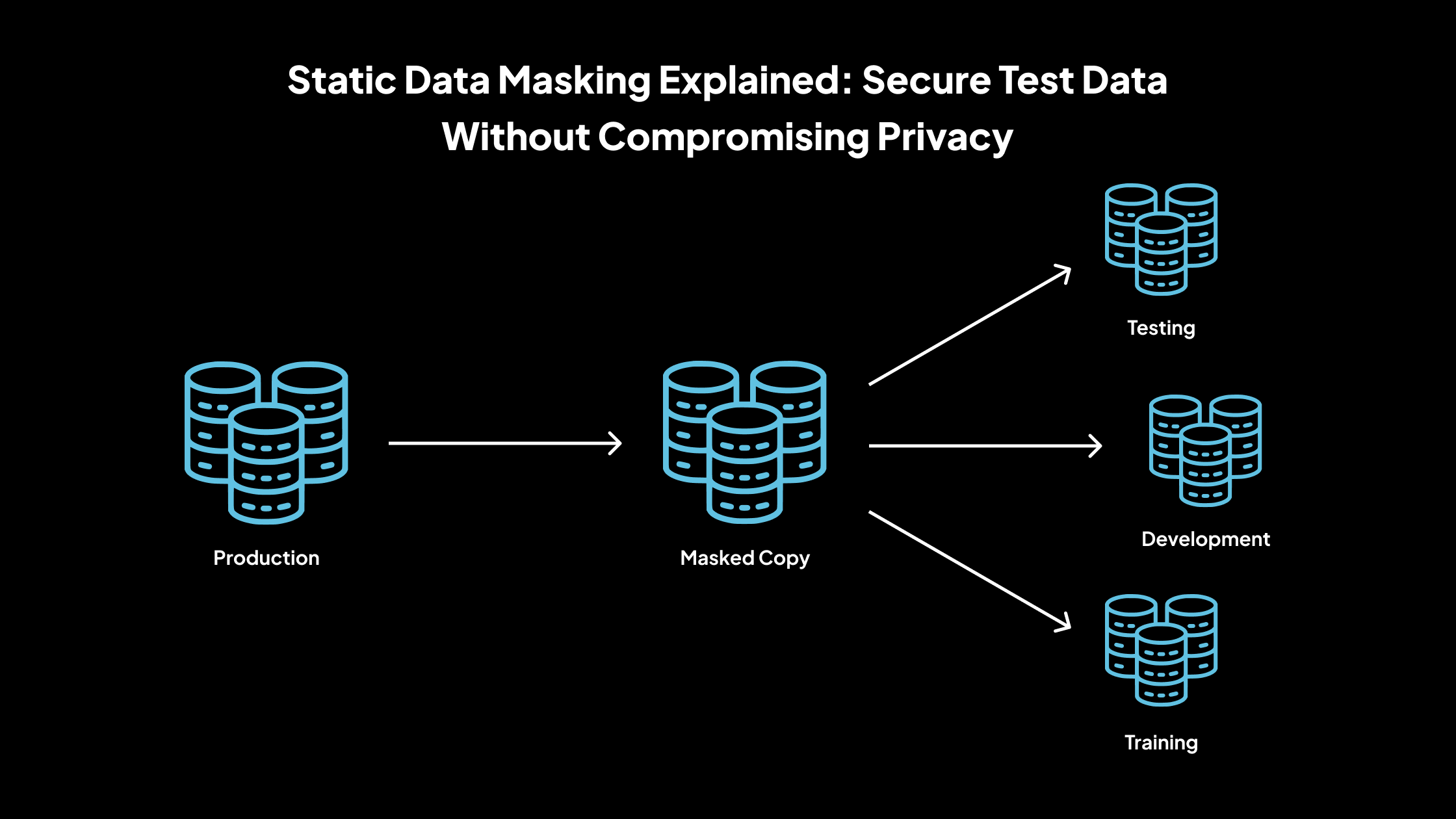
Static Data Masking is a data protection technique where sensitive information in a dataset is permanently replaced with fictitious yet realistic values. This transformation occurs in non-production environments, ensuring that the original sensitive data is never exposed during development, testing, or training activities.
How It Works
1. Data Identification
The first step involves scanning the dataset to identify sensitive fields, such as personally identifiable information (PII) or financial data.
For example, columns containing Social Security Numbers, email addresses, or credit card details are flagged for masking.
2. Masking Process
Predefined masking algorithms or transformation rules are applied to replace original values with fictitious but realistic alternatives.
For example, a real email like alex.claire@example.com may be masked as user123@demo.com.
3. Data Duplication
Once the data is masked, a new copy of the dataset is generated for use in non-production environments like development or testing.
This ensures that the original sensitive data stays protected while still providing usable data for internal processes.
4. No Reversibility
Masked data is irreversible, meaning it cannot be transformed back into its original state. This ensures strong data privacy and compliance.
Even if someone gains access to the masked dataset, they cannot retrieve the original values, eliminating the risk of re-identification.
Common Use Cases for Static Data Masking
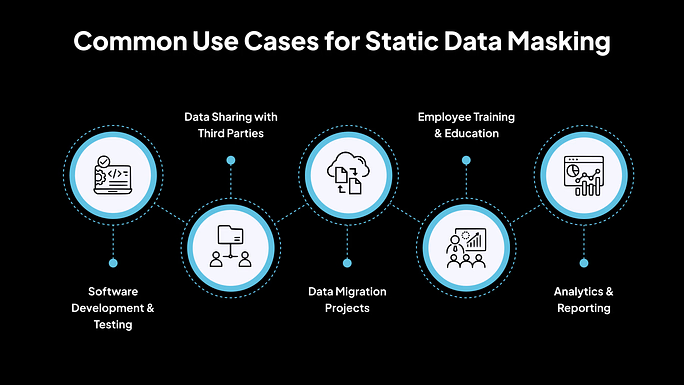
1. Software Development & Testing
SDM allows developers and QA teams to work with realistic test data without risking exposure of real sensitive information. This ensures secure development and debugging in safe, non-production environments.
2. Data Sharing with Third Parties
When organizations need to collaborate with vendors or external consultants, SDM enables them to share data that mimics production sets. This helps maintain compliance while preventing leakage of sensitive or regulated data.
3. Data Migration Projects
During system upgrades or migrations, sensitive data can be masked before being transferred between environments. This ensures data remains protected throughout the migration lifecycle and reduces the risk of exposure.
4. Employee Training & Education
SDM provides trainees with hands-on experience using realistic, anonymized data in training platforms. This builds operational understanding without compromising the confidentiality of actual users or customers.
5. Analytics & Reporting
By anonymizing sensitive data fields, SDM enables analysts to derive insights without breaching privacy standards. This ensures secure use of business intelligence tools while maintaining data integrity.
Advantages of SDM
1. Enhanced Data Security
Since the data is irreversibly masked before leaving production, there’s no chance of sensitive information being leaked in test or development environments. This reduces insider threats and enforces a strict boundary between real and simulated data use.
2. Compliance with Regulations
Helps organizations adhere to data protection laws, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA, by ensuring that sensitive information remains inaccessible during testing or development. This helps reduce audit risks and ensures legal obligations are met consistently.
3. No Performance Overhead
Since the data is masked before use, no additional processing is required during data access, resulting in consistent performance. This maintains high system performance and user productivity in test environments.
4. Data Integrity Preservation
The structure and relationships within the data are maintained, allowing for realistic testing scenarios. This ensures the masked data behaves like real data for application testing, debugging, and validation.
5. Simplified Data Management
With data already anonymized, teams can reduce the complexity of implementing access control measures for non-production environments. This lowers administrative overhead while enhancing governance.
Disadvantages of SDM
1. Additional Storage Requirements
SDM creates new masked versions of datasets, increasing the overall storage footprint across environments. This can lead to added infrastructure costs, especially in data-heavy organizations.
2. Irreversibility
Once data is masked using SDM, it cannot be converted back to its original form.
This limits flexibility when real data is later required for specific non-production use cases.
3. Not Suitable for Real-Time Data Access
SDM works on static copies of data; it’s ineffective for real-time applications or systems that require live access to frequently updated data. Organizations needing instant data masking must look to dynamic alternatives.
4. Complex Masking Rules
Designing accurate and meaningful masking rules to preserve usability while hiding sensitive values can be time-consuming and complex. This often requires domain expertise and ongoing updates to keep rules aligned with evolving data models.
5. Potential for Data Inconsistencies
If not properly implemented, SDM can lead to discrepancies between masked and original datasets, affecting the reliability of testing outcomes. This can affect test results, data accuracy, or even mislead analytics if relational integrity is not preserved.
Dynamic Data Masking (DDM): Role-Based Protection Without Data Duplication
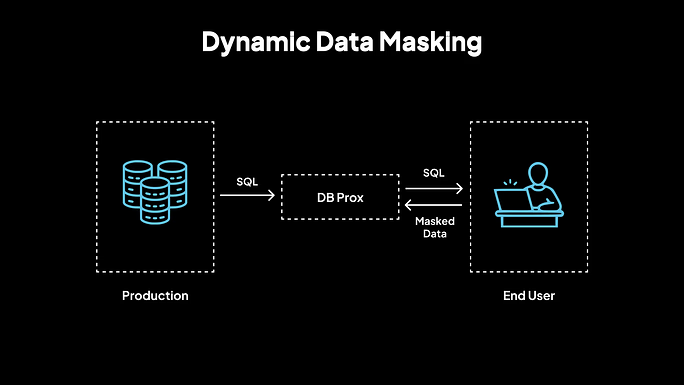
Dynamic Data Masking (DDM) is a data protection technique that applies masking rules to sensitive data in real time as it is accessed.
Unlike static data masking, which alters the data permanently, DDM does not change the underlying data. Instead, it ensures that sensitive information is hidden or masked only when it is being queried or accessed by a user, based on their role and permissions. This allows for data security without modifying or duplicating the original data.
How It Works
1. User Queries and Data Access
When a user submits a query or requests access to data, the system processes the request as usual. However, before the data is displayed, DDM rules come into effect. The system checks the user’s credentials, permissions, and role to determine what data can be shown.
2. Real-Time Masking Process
Depending on the defined masking rules, the sensitive fields (e.g., Social Security numbers, credit card information) in the requested data are masked (e.g., replaced with asterisks or pseudonyms) before being presented to the user.
For instance, a user with limited access may only see a masked version of sensitive data,, such as a truncated credit card number (1234****5678) instead of the full number.
3. Data Integrity Remains Intact
The advantage of DDM is that the underlying data remains unaltered in the system. The original sensitive information is stored as-is in the database, but it is only visible in its masked form to those who do not have the necessary permissions to view it.
This makes DDM particularly valuable for compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, where sensitive information must be protected from unauthorized access.
Common Use Cases for Dynamic Data Masking
1. Customer Support Portals
Customer service representatives may need access to customer details to resolve issues or answer questions. DDM ensures that agents can access non-sensitive data (such as customer names and order histories) without exposing sensitive information, like credit card numbers or Social Security numbers.
2. Analytics Platforms
Data analysts frequently work with large datasets to gain valuable insights and produce reports. With DDM, analysts can access the data they need for analysis while ensuring that sensitive information, such as health records or financial data, remains protected and masked.
3. Access Control in Production Environments
DDM can be used in live, production systems to control who can see what data. For example, database administrators or application developers may need to interact with live systems, but they do not need access to sensitive customer data. DDM ensures that they can perform their jobs without viewing protected information.
The system dynamically masks the sensitive fields depending on the user’s role, ensuring compliance with data access policies.
Advantages of Dynamic Data Masking
1. No Need for Data Duplication
Since masking occurs in real-time, there is no need to store multiple copies of data (one for production and one for testing or development). This can significantly save on operational costs and simplify data management.
2. Real-Time Data Protection
DDM offers real-time protection of sensitive data. As soon as a user queries or accesses data, the system applies the masking rules based on the user’s permissions.
This ensures that sensitive data is never exposed, even in live environments where real-time access is required. This ability to mask data on the fly is crucial for environments that require both high performance and data security simultaneously.
3. Granular Control Over Data Visibility
DDM enables organizations to define specific rules governing which users can access sensitive data and to what extent. The system utilizes role-based access control (RBAC), which dynamically masks data based on the user’s role, department, or level of clearance.
For example, HR staff may need to see employee names and salaries, but not personal bank account information, while managers may have access to complete employee records.
Disadvantages of Dynamic Data Masking
1. Potential Performance Overhead Due to Real-Time Processing
Since DDM works by intercepting user queries and applying masking rules in real time, it can introduce some performance overhead, particularly in high-traffic systems.
Each query may need to be processed through a masking engine, which can slow down response times if the system is not optimized. This overhead can be especially noticeable in large-scale databases with complex queries, so it’s essential to balance security with system performance to ensure minimal impact on the user experience.
2. Complex Configuration and Maintenance of Masking Rules
Setting up DDM requires careful configuration of masking rules to ensure that sensitive data is appropriately protected across all user roles and scenarios.
The system must be configured to recognize which data fields should be masked and which users should have access to unmasked data. This can be particularly complex, especially for organizations with large and dynamic user bases or highly sensitive data.
3. Risk of Exposure if Masking Policies Are Not Properly Implemented
If DDM rules are not correctly configured or enforced, there is a risk of exposing sensitive information to unauthorized users.
For example, a misconfigured user role may allow an employee access to unmasked data they shouldn’t be able to see. Additionally, errors in the masking algorithms or flaws in the system’s implementation could inadvertently allow sensitive data to be displayed in an unmasked form.
Static Dynamic Masking vs Dynamic Data Masking: Essential Differences You Need to Know
While both Static and Dynamic Data Masking aim to protect sensitive information, they differ significantly in how, when, and where data is masked, making it essential to understand their unique roles and applications. Below is a detailed of comparison of each type of data masking:
1. Data Modification
Static Dynamic Masking
Static Data Masking permanently alters the original data. Once the data is masked, it is no longer in its original form, and this change is irreversible.
SDM creates a new copy of the data, where sensitive fields are replaced with masked values that look realistic but are not the actual data. This process is useful in non-production environments where data doesn’t need to be updated or accessed in real-time.
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic Data Masking, on the other hand, masks data in real-time when it is accessed. The original data remains intact in the database, and only the masked version is displayed to users based on their roles and permissions.
This means that DDM does not alter the actual data in the system but instead applies masking rules at the point of access, making it a more flexible solution for real-time operations.
2. Performance Impact
Static Dynamic Masking
Static Data Masking does not introduce any performance overhead during data access because the masking occurs at the time of data creation.
Once the data is masked, it does not require any additional processing when accessed. This makes SDM ideal for scenarios where performance is critical, and the data will not be queried or updated in real-time.
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic Data Masking can introduce performance overhead because it requires real-time processing of data requests. Every time a query is executed, the system must apply the masking rules dynamically before returning the results.
Depending on the size of the database and the complexity of the masking rules, real-time processing can lead to slower response times, especially in systems with high query volumes or complex datasets. Therefore, DDM needs to be carefully optimized to strike a balance between security and system performance.
3. Compliance and Security
Static Dynamic Masking
SDM is easier to manage in terms of compliance with data protection regulations because it permanently alters sensitive data before it is accessed or shared. T
This means that even if data is exposed in non-production environments, the sensitive information is already masked, ensuring that the organization complies with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA. Since the data is never exposed in its original form, SDM is a straightforward solution for meeting compliance requirements.
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic Data Masking provides real-time data protection, but it requires strict configuration to ensure compliance. Because DDM only masks data during access and leaves the original data unchanged, it must be carefully implemented to ensure that unauthorized users cannot bypass the system.
Configuring DDM requires defining appropriate roles, access levels, and masking rules to ensure that only authorized personnel can view unmasked data. If not correctly configured, there is a risk of non-compliance, especially in environments with complex data access needs.
Making the Right Choice: When to Use Static vs Dynamic Data Masking
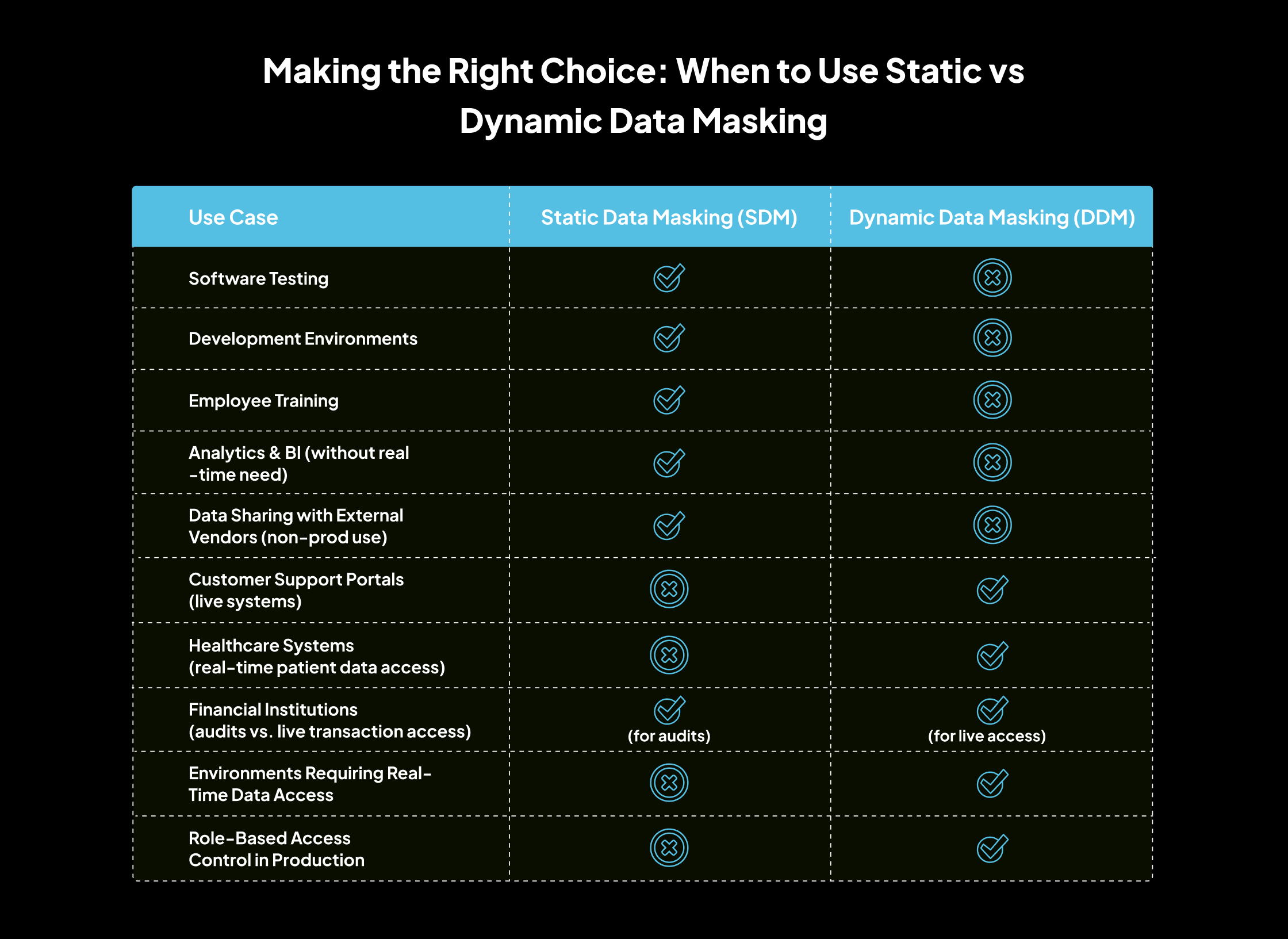
When deciding between Static Data Masking (SDM) and Dynamic Data Masking (DDM), it is essential to carefully consider various factors that influence which technique is best suited for your needs. Let’s explore these factors:
Factors to Consider
1. Nature of the Data
The type of data you are handling plays a crucial role in choosing the right data masking method.
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
If your data contains PII (such as names, addresses, or phone numbers), it is vital to ensure this data is masked or protected in both production and non-production environments. SDM may be more suitable in cases where sensitive data is used outside of production, such as in testing or development.
Protected Health Information (PHI)
PHI, which includes sensitive medical information, is subject to strict regulations like HIPAA. DDM might be needed in production environments where real-time access to PHI is required for authorized users, while maintaining compliance by masking data for unauthorized personnel.
Financial Data
Financial data, including credit card numbers, account information, and transaction details, requires robust protection. If the data is being shared with external vendors or used for non-production purposes, SDM may be preferable to ensure sensitive data is never exposed in an unprotected form.
2. Regulatory Requirements
Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA requires the protection of sensitive data. Depending on the industry you are in, your data protection strategy must align with the relevant laws.
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation)
GDPR requires data controllers and processors to ensure the confidentiality and security of personal data. DDM might be necessary to ensure data is protected in real-time while in production, particularly if personal data needs to be accessed for operational purposes.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
HIPAA mandates strict protections for healthcare data. Organizations working with PHI may use DDM in production environments to restrict access based on roles, ensuring only authorized users can view sensitive health information.
CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act)
The CCPA emphasizes consumer privacy rights in California. DDM can help ensure that only authorized personnel have access to personal information, thereby assisting businesses to comply with this regulation.
3. Operational Needs
The choice between SDM and DDM should align with your specific workflows and operational requirements.
Real-Time Access
If your operations require real-time data access, such as customer support or transaction processing, DDM is the most appropriate option. DDM allows you to access live data without exposing sensitive information, ensuring compliance and security during production use.
Batch Processing and Testing
For environments where data is processed in batches or used for testing and development (such as software development or analytics), SDM is a better fit. SDM permanently masks data, which is suitable when real-time data access is not required and performance needs are not as high.
Consider a Hybrid Approach for Comprehensive Data Protection
In many cases, organizations may benefit from a hybrid approach that combines both SDM and DDM to achieve comprehensive data protection. A hybrid model allows organizations to use SDM for non-production environments (where data can be permanently masked for security) and DDM for production environments (where data must be dynamically masked based on user roles). This combination ensures that sensitive data is protected throughout its entire lifecycle, whether in development, testing, or live operations.
For example, a healthcare organization may use SDM for testing and training environments, where real-time access to medical data is not required, and DDM in production for live patient records. A financial institution may use SDM for data used in audits and DDM for staff accessing real-time transaction information.
Avahi’s Data Masker: A Smart Solution for Protecting Confidential Information
As part of its commitment to secure and compliant data operations, Avahi’s AI platform provides tools that enable organizations to manage sensitive information precisely and accurately. One of its standout features is the Data Masker, designed to protect financial and personally identifiable data while supporting operational efficiency.
Overview of Avahi’s Data Masker
Avahi’s Data Masker is a versatile data protection tool designed to help organizations securely handle sensitive information across various industries, including healthcare, finance, retail, and insurance.
Why Choose Avahi’s Intelligent Data Masking Tool?
- Protects Sensitive Information Across Industries
Designed to secure financial, healthcare, retail, and insurance data, without interrupting daily operations.
- Supports Regulatory Compliance
Helps meet GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS requirements by anonymizing and masking personal and transactional data.
- Enables Safe Data Sharing
Ensures only authorized users, internal or external, can access real data through role-based access controls.
- Preserves Operational Efficiency
Allows development, analytics, and fraud detection teams to work with realistic, non-sensitive data formats.
- Reduces Risk of Data Breaches
Minimizes exposure of real data in test environments, vendor interactions, and cross-department workflows.
- Integrates Seamlessly with Enterprise Workflows
Applies masking without disrupting backend processes, ensuring business continuity and productivity.
Simplify Data Protection with Avahi’s AI-Powered Data Masking Solution
At Avahi, we recognize the crucial importance of safeguarding sensitive information while maintaining seamless operational workflows.
With Avahi’s Data Masker, your organization can easily protect confidential data, from healthcare to finance, while maintaining regulatory compliance with standards like HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR.
Our data masking solution combines advanced AI-driven techniques with role-based access control to keep your data safe and usable for development, analytics, and fraud detection.
Whether you need to anonymize patient records, financial transactions, or personal identifiers, Avahi’s Data Masker offers an intuitive and secure approach to data protection.
Ready to secure your data while ensuring compliance? Get Started with Avahi’s Data Masker!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the main types of data masking techniques?
The two primary types of data masking techniques are Static Data Masking (SDM) and Dynamic Data Masking (DDM). SDM permanently replaces sensitive data in non-production environments, while DDM applies real-time masking based on user roles without altering the underlying data. Both help in securing sensitive information and complying with privacy regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
2. When should I use Static Data Masking over Dynamic Data Masking?
Use Static Data Masking (SDM) when working in non-production environments like development, testing, or employee training. It’s ideal for scenarios where real-time access is not needed, but permanent data obfuscation is required to maintain privacy and PII security.
3. What are the benefits of Dynamic Data Masking in production environments?
Dynamic Data Masking (DDM) provides real-time data protection by masking sensitive information on the fly based on user permissions. It’s ideal for production systems where data access control and minimal performance impact are essential. DDM is especially useful in industries like finance, healthcare, and customer service.
4. Does data masking help with compliance requirements like GDPR or HIPAA?
Yes. Both SDM and DDM help organizations meet compliance requirements under laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA by ensuring that personally identifiable information (PII) and protected health information (PHI) remain inaccessible to unauthorized users, even in internal environments.
5. Is data masking reversible?
In Static Data Masking, the masking is irreversible, meaning original data cannot be recovered once masked, enhancing data privacy. In contrast, Dynamic Data Masking is non-destructive, meaning the underlying data remains unchanged and only appears masked during access.