TL;DR
|
Agentic AI systems do not fail quietly. When they fail, they act.
Unlike traditional AI, agentic AI tools can make decisions, call tools, and execute actions independently. In production environments, this means a single error is not just a wrong answer. It can trigger incorrect workflows, unintended actions, or policy violations at scale.
Recent industry reports show that model accuracy issues account for only a small share of AI-related production incidents; rather, decision logic failures, tool misuse, and poor monitoring in autonomous systems are the main causes. As organizations move from prompt-based AI to agent-driven systems, these risks increase, not decrease.
If you are building or deploying agentic AI tools, you are no longer evaluating a model. You are evaluating a system that plans, acts, and adapts over time.
This shift changes what “quality” means. Accuracy alone is not enough. You need to know whether the system behaves safely, predictably, and reliably under real conditions.
This blog focuses on how you evaluate agentic AI tools for production-grade systems and breaks down the core challenges, practical evaluation frameworks, and the metrics that matter when autonomy is involved.
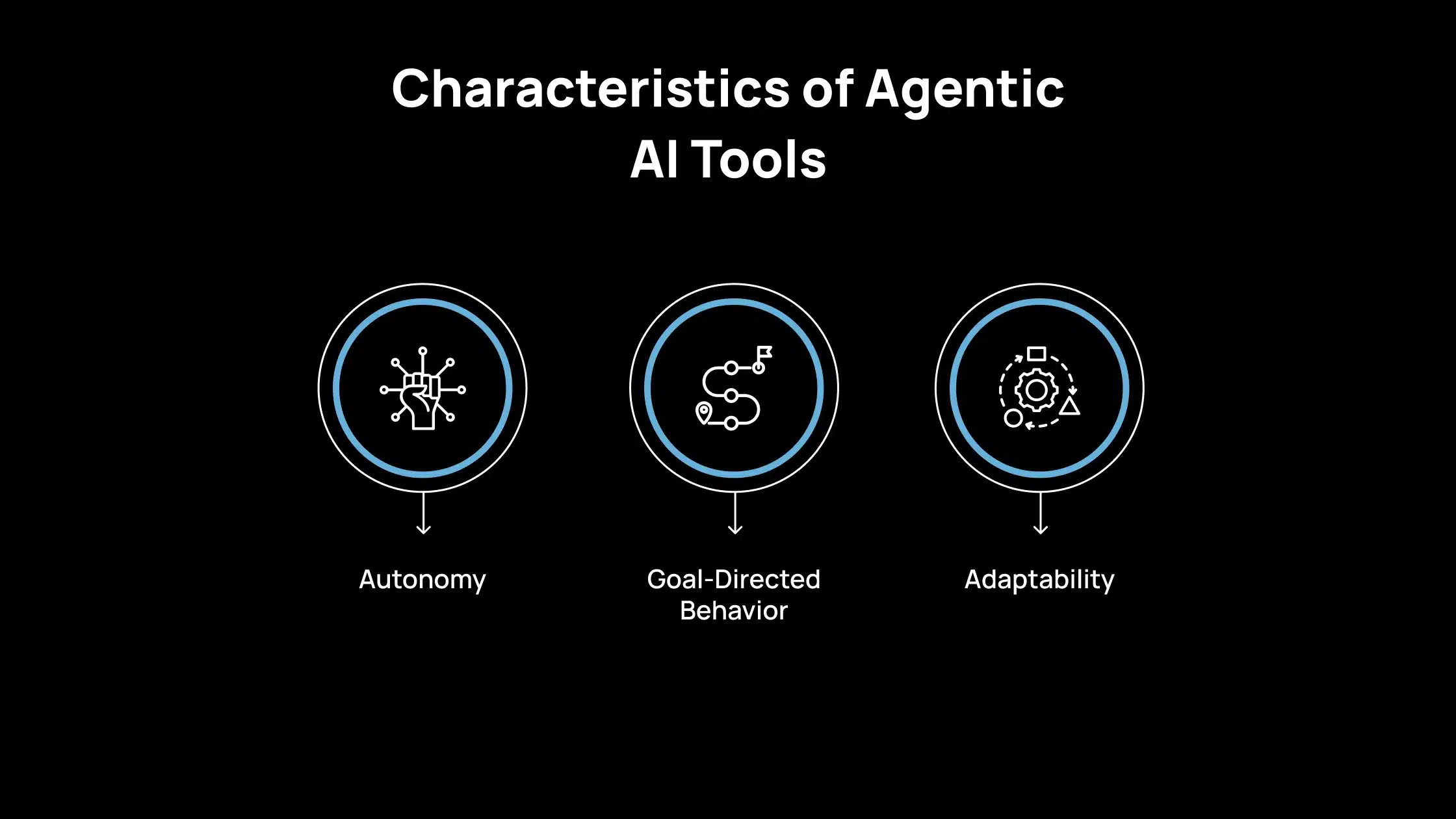
Characteristics of Agentic AI Tools
If you are evaluating agentic AI tools for real systems, the first challenge is understanding what makes them different from standard AI models. Agentic tools are not just models that respond to prompts. They are systems built to act, decide, and adjust over time while working toward a defined goal. Here is the list of core characteristics of Agentic AI tools:
1. Autonomy
You give the system a high-level goal, not step-by-step instructions. The agent breaks that goal into smaller actions and decides when and how to execute them. Your role shifts from directing every step to setting boundaries and success criteria.
2. Goal-Directed Behavior
The agent plans a sequence of actions instead of generating a single response. Each step is chosen based on progress toward the goal, not just the immediate input. You evaluate whether the plan and execution align with the intended outcome, not just the final result.
3. Adaptability
The agent changes its actions when inputs, tools, or context change. If a tool fails or returns unexpected results, the agent adjusts its plan rather than stopping. You must assess how well it recovers, not just how often it succeeds.
How Agentic AI Tools Differ From Conventional AI Systems?
Understanding this difference helps you avoid using the wrong evaluation methods.
| Aspect | Conventional AI Systems | Agentic AI Tools |
| Primary Interaction | You provide an input and receive a single output, such as text, a label, or a score. | The system takes actions using external tools, APIs, or execution environments. |
| State Handling | Does not retain a long-term state across interactions. | Maintains state across steps and uses past decisions to guide future actions. |
| Decision Scope | Responds to the current input only. | Plans and executes multi-step actions toward a goal. |
| Evaluation Focus | Output accuracy, relevance, or similarity to expected results. | Decision paths, tool usage, recovery behavior, and goal alignment. |
| Error Impact | Errors usually affect a single response. | Errors can propagate across steps and affect the entire workflow. |
| System Behavior | Reactive. | Autonomous and goal-driven. |
Challenges in Evaluating Agentic AI
When evaluating agentic AI for production systems, the difficulty lies not solely in model quality. The challenge comes from how these systems act, adapt, and evolve. Each challenge below explains what you need to account for before trusting an agent in a real environment.
1. Complex Input and Action Space
Agentic AI systems often have multiple valid ways to reach the same goal. The same input can lead to different actions depending on context, state, or tool availability.
You cannot rely on a single expected output. Your evaluation must cover a wide range of inputs, actions, and decision paths to understand real behavior.
2. Multi-Step Decision Processes
Agentic systems make decisions across a sequence of steps rather than in isolation. A correct outcome can still hide poor reasoning, risky actions, or inefficient paths. You need to evaluate intermediate decisions, tool calls, and state changes, not just the result.
3. Component Interdependencies
An agent’s behavior depends on how planning logic, memory, tools, and decision rules interact. A failure in a single component can alter the entire system’s behavior.
You must test each component individually, then evaluate how they work together as a complete workflow.
4. Evolution Over Time
Agentic AI systems change as models are updated, tools evolve, and data patterns shift. Behavior that was safe or effective during testing can drift in production.
You need ongoing evaluation and monitoring to detect changes in performance, behavior, and risk.
5. Safety and Alignment Risks
Autonomy increases the impact of errors and misalignment. An agent can take unintended actions, misuse tools, or violate policies without direct oversight.
Your evaluation must include safety checks, policy enforcement tests, and failure scenarios, not just performance metrics.
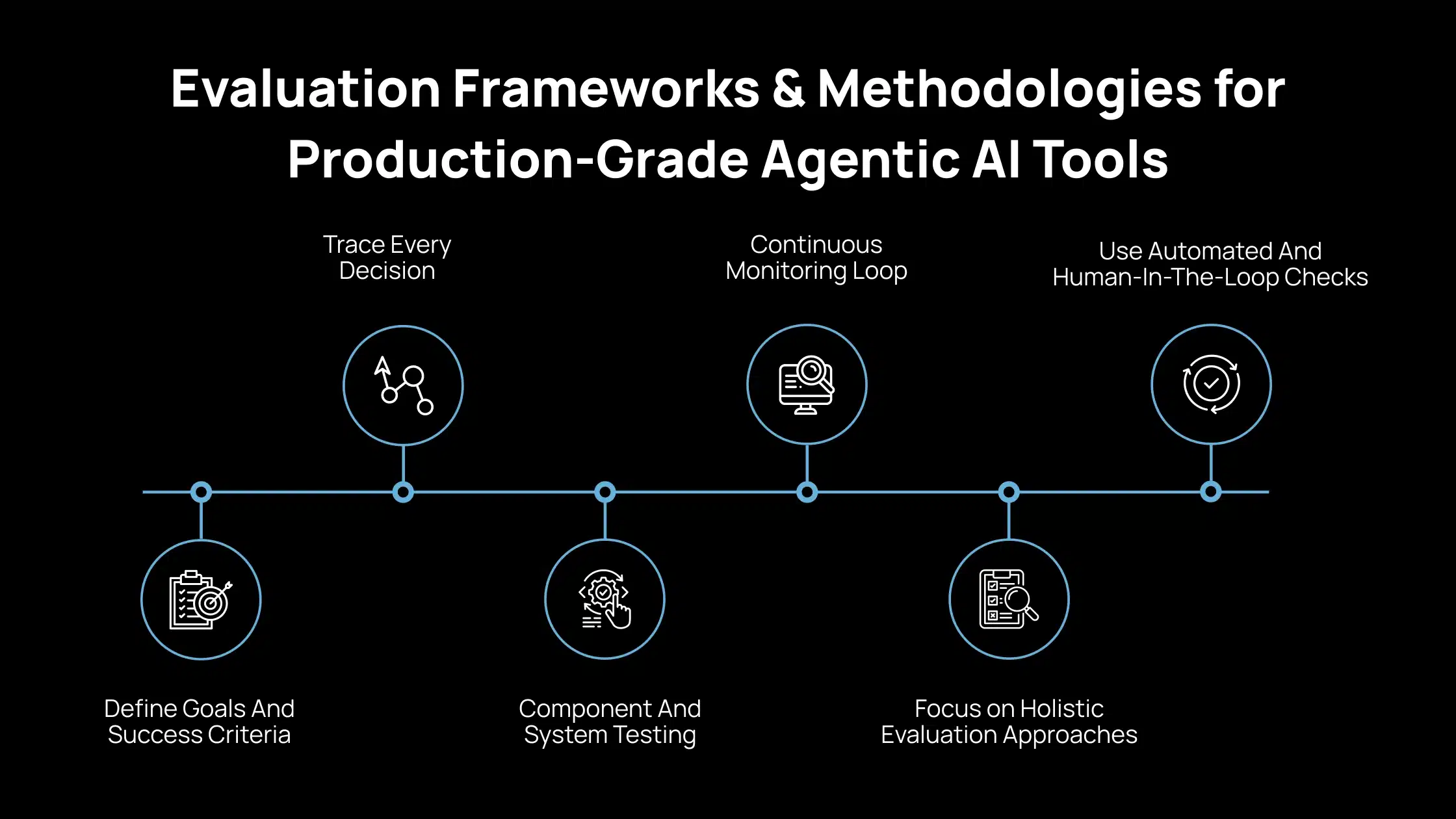
Evaluation Frameworks & Methodologies for Production-Grade Agentic AI Tools
When you evaluate agentic AI tools for production, ad hoc testing is not enough. You need a structured framework that reflects how these systems plan, act, and change over time. This section outlines a practical evaluation approach you can apply directly to real deployments.
1. Define Goals And Success Criteria
Start by defining what success means at the system level. Focus on end-to-end outcomes, not individual model responses. You should be able to state, in simple terms, what the agent must achieve and what failure looks like.
2. Trace Every Decision
Instrument the system to record plans, tool selections, sub-tasks, and default behaviors. This trace lets you understand why the agent acted in a certain way. Without decision traces, you cannot reliably debug or improve agent behavior.
3. Component And System Testing
Test each component independently, including planning logic, memory handling, and tool interfaces. Then evaluate the full workflow to see how components interact under real conditions. This helps you identify failures that only appear at the system level.
4. Continuous Monitoring Loop
Evaluation does not stop after deployment. You need ongoing checks to detect performance changes, new failure patterns, and unexpected behaviors. Monitoring closes the gap between testing and real-world usage.
5. Focus on Holistic Evaluation Approaches
You should assess technical accuracy, reliability, and latency alongside safety and decision quality. This includes how the agent handles uncertainty, errors, and ambiguous inputs. A narrow focus on output quality misses critical system risks.
6. Use Automated And Human-In-The-Loop Checks
Use automated tests to cover scale, regressions, and known failure cases. Include human review for alignment, safety judgment, and edge cases that automation cannot fully capture. This combination helps you balance efficiency with responsible oversight.
Evaluating Agentic AI Tools Using Production-Focused Metrics
To evaluate agentic AI tools in production, you need metrics that reflect how the system performs, behaves under load, and aligns with real-world constraints. The categories below help you measure what actually matters when an agent operates without constant supervision.
1. Technical Performance Metrics
Task Success
This measures whether the agent achieves the intended goal in accordance with the predefined requirements. You should define success criteria clearly so results are consistent and comparable. A completed task that violates constraints or skips required steps should count as a failure.
Tool Call Accuracy
This evaluates whether the agent selects the correct tools and uses them with valid parameters.
Incorrect or unnecessary tool calls increase cost and risk. You should track tool usage patterns and flag repeated misuse or retries.
Plan Coherence
This measures whether the agent follows a logical and consistent sequence of steps. A coherent plan shows that decisions are connected and aligned with the goal. Incoherent planning often signals hidden errors, weak reasoning, or missing safeguards.
2. Operational and Reliability Metrics
Latency and Throughput
Latency is the time it takes the agent to complete tasks. Throughput measures how many tasks it can handle under load. You need both to understand whether the system can meet production performance requirements.
Failure Rates
This tracks how often the agent hits timeouts, retries, or fallback paths. High failure rates indicate instability, tool issues, or weak planning logic. You should measure failures per task, not just per request.
Trace Coverage
This measures how much of the agent’s behavior is visible through logs and traces. Full trace coverage allows you to diagnose errors and understand decision paths. Low coverage limits your ability to debug and improve the system.
3. Safety and Alignment Metrics
Policy Adherence
This evaluates whether the agent consistently follows defined rules and constraints. Policies may include data access limits, action boundaries, or content restrictions. Any policy violation should be treated as a high-severity issue.
Risk Escalation Frequency
This measures how often the agent requires human review or intervention. Frequent escalation can indicate poor decision-making confidence or unsafe behavior. Tracking this helps you decide where automation is appropriate and where controls are needed.
4. Human and Economic Dimensions
User Trust Scores
These scores reflect how human reviewers assess the agent’s decisions and actions. Trust is built through consistency, clarity, and predictable behavior. Low trust often points to explainability or alignment gaps.
Cost Per Success
This measures the total cost required for each completed task. You should include model usage, tool calls, retries, and infrastructure costs. This metric helps you assess whether the agent delivers practical value at scale.
Pre-Deployment & Monitoring Checklist to Validate Agentic AI Tools in Production
Use this checklist to validate agentic AI tools before deployment and to keep control once the system is live. Each item focuses on reducing risk and increasing visibility in real production conditions.
1. Pre-Deployment Tests
|
2. Continuous Production Monitoring
|
How Avahi Helps You Turn AI Into Real Business Results?
If your goal is to apply AI in practical ways that deliver measurable business impact, Avahi offers solutions designed specifically for real-world challenges. Avahi enables organizations to quickly and securely adopt advanced AI capabilities, supported by a strong cloud foundation and deep AWS expertise.
Avahi AI solutions deliver business benefits such as:
- Round-the-Clock Customer Engagement
- Automated Lead Capture and Call Management
- Faster Content Creation
- Quick Conversion of Documents Into Usable Data
- Smarter Planning Through Predictive Insights
- Deeper Understanding of Visual Content
- Effortless Data Access Through Natural Language Queries
- Built-In Data Protection and Regulatory Compliance
- Seamless Global Communication Through Advanced Translation and Localization
By partnering with Avahi, organizations gain access to a team with extensive AI and cloud experience committed to delivering tailored solutions. The focus remains on measurable outcomes, from automation that saves time and reduces costs to analytics that improve strategic decision-making to AI-driven interactions that elevate the customer experience.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation, all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency?
Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What makes evaluating agentic AI tools harder than evaluating traditional AI models?
Agentic AI tools do more than generate outputs. They plan, call tools, maintain state, and adapt over time. Because actions compound across steps, a single mistake can affect the entire workflow. This means you must evaluate behavior, decisions, and recovery paths, not just accuracy.
2. Can I rely on offline testing to validate agentic AI tools?
No. Offline testing is necessary but not sufficient. Agentic AI behavior changes under real traffic, real data, and real tool failures. Production validation requires continuous monitoring, tracing, and drift detection to catch issues that do not appear during testing.
3. What is the most important metric when evaluating agentic AI tools?
There is no single metric. Task success, tool call accuracy, safety compliance, and cost per success must be evaluated together. Focusing on a single metric often masks critical risks, especially in autonomous systems.
4. How do I know if an agentic AI tool is safe for production use?
You need evidence from safety simulations, policy enforcement tests, and real-world monitoring. A production-ready agent should demonstrate consistent policy adherence, controlled escalation to humans, and predictable behavior under edge cases.
5. When should human-in-the-loop review be required?
Human review is essential for high-risk decisions, ambiguous inputs, and policy-sensitive actions. If an agent frequently escalates or produces low-trust decisions, that signals gaps in alignment, confidence, or system design that need attention.