TL;DR
|
Screening is no longer a small step in hiring. It’s the part that decides whether you hire fast, fairly, and at scale or lose good candidates before they even reach a manager.
Right now, the front end of the funnel is getting heavier. A recent analysis of 31 million applications across 95,000 jobs from 2021 to 2024 shows that applicant volume keeps rising, while recruiter capacity has not grown fast enough to match it. This means early-stage screening is where delays and drop-offs start.
Candidates feel those delays immediately. A global Sterling survey found 71% of job seekers have dropped out or considered dropping out of a hiring process because it took too long or felt too complex. When screening drags, strong candidates leave first.
But adoption isn’t automatic. Voice AI recruiters bring scale and consistency, while human screeners bring judgment, empathy, and context. The right choice depends on role type, hiring volume, and risk tolerance.
This blog lays out those differences clearly and helps you decide when an AI voice recruiter should handle early screening, when human screeners should lead, and when a hybrid approach makes the most sense.
Current State of Screening and Early‑Stage Hiring
Hiring teams are under pressure to move fast, handle large volumes, and still find the right candidates. The early stages of recruitment, especially screening, are where most challenges begin.
Regular Screening
Most companies still rely on manual steps in the early phases of hiring.
- Phone screenings are conducted by recruiters who call each candidate individually.
- Scheduling is often back-and-forth over email or through tools that still need human input.
- Assessment is subjective; recruiters rely on gut feeling, experience, and limited call notes.
This process works for low-volume hiring but quickly breaks down as application volume rises.
Early-Funnel Screening Problems Hiring Teams Face
You’re trying to move candidates through the funnel quickly, but the first step, screening, often slows everything down.
Time To Hire Stretches Out Early
Screening is still a manual task in most teams. Even a short 5–10-minute call multiplies quickly at scale, and missed calls or reschedules add more delay. Rootle notes that screening time stacks up to dozens of recruiter hours per role in volume hiring.
High Applicant Volume Creates A Backlog
Many roles attract hundreds or thousands of applicants. Recruiters can’t call everyone, so screening becomes a triage process. That means good candidates may wait too long or get filtered out before a real conversation. High-volume recruiting tools are now built specifically to handle this load.
Scheduling Block Progress
The back-and-forth to set up a call is a hidden cost. It can take days to align a 10-minute screening window across time zones, work shifts, or candidate availability. Voice AI screening platforms reduce this by letting candidates complete screening at a time that works for them.
Human Judgment Varies More Than Teams Expect
Two recruiters may rate the same candidate differently because of experience, fatigue, or interpretation. In high-volume processes, this inconsistency makes it harder to defend and improve hiring outcomes. Voice AI systems address this by asking the same questions in the same way and producing structured outputs.
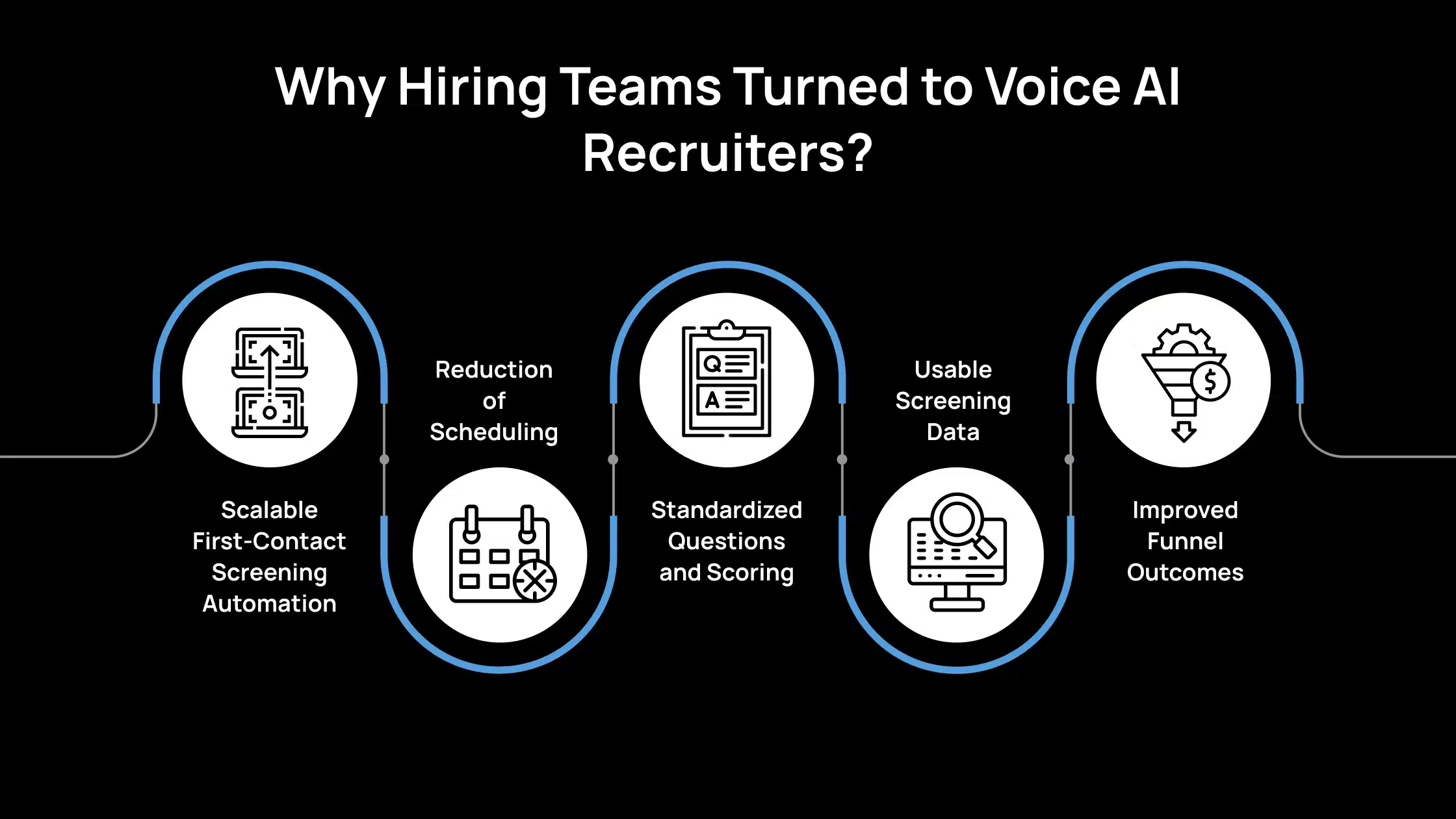
Why Hiring Teams Turned to Voice AI Recruiters?
Voice AI recruiters exist because early-stage screening is repetitive, time-heavy, and easy to standardize.
Scalable First-Contact Screening Automation
A voice AI recruiter can run hundreds of screening calls in parallel, without waiting for recruiter availability. The goal isn’t “better conversation.” The goal is to achieve faster throughput while maintaining the same baseline quality.
Reduction of Scheduling
Instead of coordinating live calls, candidates complete screening on demand. This directly reduces idle time between the application and the shortlist. Voice AI recruiters highlight that this shifts screening from “days” to “hours” for many teams.
Standardized Questions and Scoring
Every candidate gets the same structured questions. Responses are recorded, transcribed, and scored against defined criteria. This makes screening more consistent and easier to audit.
Usable Screening Data
Instead of scattered call notes, you get transcripts, audio, flagged answers, and summary scores pushed into your ATS. That helps recruiters compare candidates quickly and justifies screening decisions to hiring managers.
Improved Funnel Outcomes
A large field experiment in entry-level hiring found that AI-interviewed candidates were more likely to receive offers, start roles, and stay past 30 days, while humans still made final decisions. This suggests structured AI screenings can capture better early-stage signals at scale.
Voice AI can introduce new risks, such as accent- or speech-pattern bias, if models aren’t trained to account for diversity. Recent research warns about transcription errors affecting non-native speakers and people with speech disabilities. Automation only works well when these risks are tested and managed.
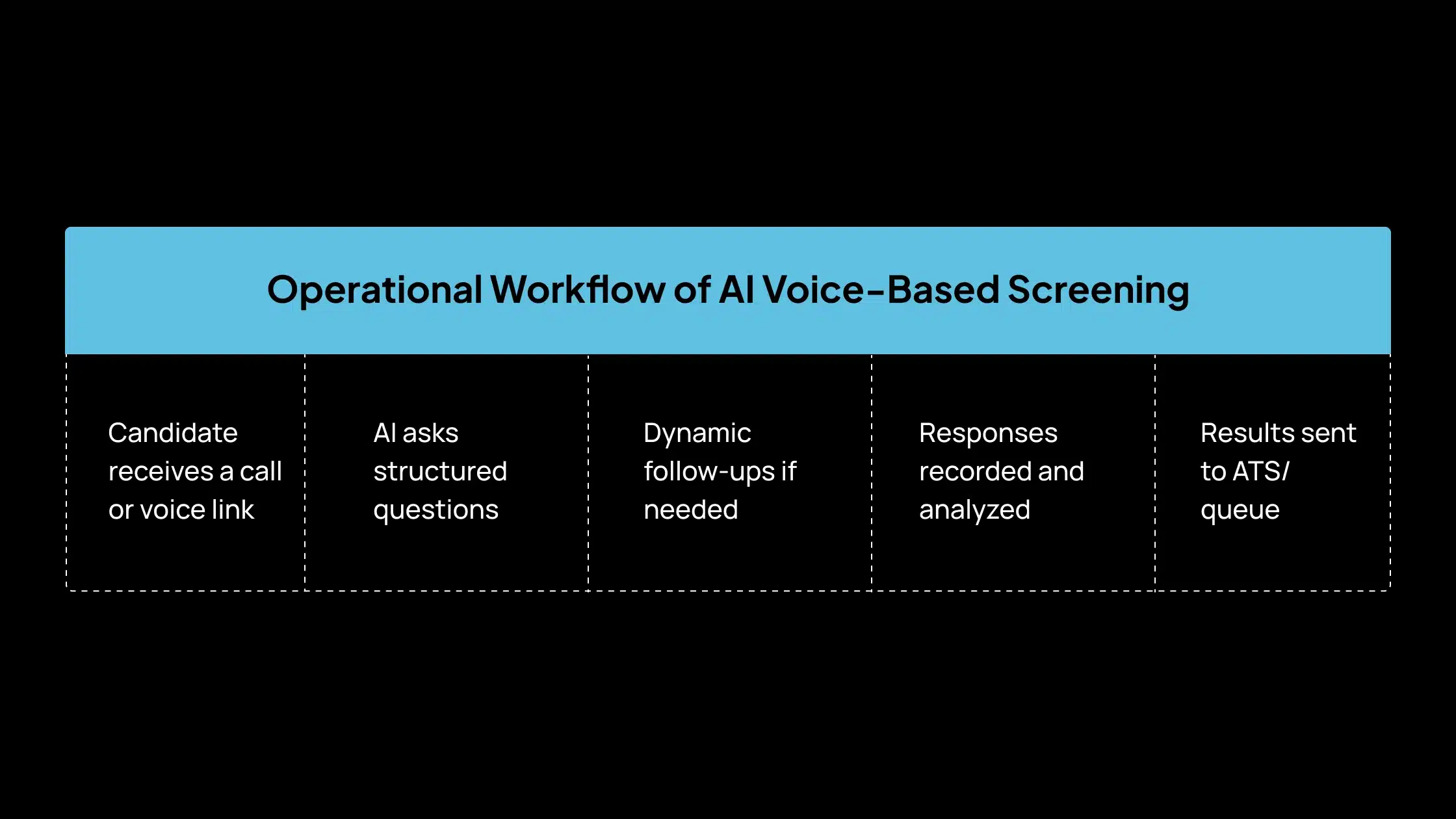
Operational Workflow of AI Voice-Based Screening
A voice AI recruiter (also called a voice AI recruiter or AI interviewer) is a system that conducts screening calls with candidates using conversational voice technology. It handles first-round questions, records answers, and sends structured results back to your hiring workflow.
Here’s how it usually runs in real hiring teams:
- Candidate receives a call or voice link: The invite is triggered right after the application or after the resume filtering. No recruiter has to schedule it manually.
- AI asks structured screening questions: Questions are based on your role template, experience checks, availability, certifications, and basic competency prompts.
- Dynamic follow-ups happen when needed: If a candidate gives a vague or partial answer, the system can ask a follow-up. Some platforms use branching logic to probe deeper into key requirements.
- Candidate responses are recorded and analyzed: The system captures the call, converts speech to text, and tags role-relevant information.
- Results flow into your ATS or screening queue: Recruiters receive transcripts, scores, and a short summary inside the ATS, so they can review fast and move candidates forward
How Human Screeners Evaluate Candidates?
Human screeners are still central to hiring because it also involves interpreting context, building trust, and making judgment calls that don’t fit neat rules. Here is what human screeners typically do:
At the screening stage, recruiters do more than ask standard questions.
- Hold a real conversation: A human screener can adjust their tone, pace, and style based on the candidate. This helps people open up and share details they might not give in a rigid format.
- Probe beyond the first answer: If a response is unclear, a human can ask follow-ups that fit the moment. They can also spot when a candidate is skipping over something important.
- Read context and intent: Humans can detect hesitation, confusion, or enthusiasm and ask questions that help clarify fit. This is useful when the role needs judgment, teamwork, or customer handling.
- Assess soft skills early: Screening often includes checks on communication style, attitude, and professionalism. Humans can evaluate these more naturally in conversation.
Challenges And Constraints Of Human Screening
These strengths come with real limits, especially at scale. Every screening depends on recruiter availability. Even short delays early on can stretch time-to-hire by days.
After many calls in a day, attention tends to drop. This affects consistency and can lead to weaker decisions late in the pipeline. Even with a script, humans phrase questions differently, skip areas, or emphasize personal preferences. This makes candidate comparison harder.
High-volume screening requires more recruiter hours, which raises cost per hire in roles where margins are already tight. To screen twice as many candidates, you need more recruiters. There’s no easy way to expand screening capacity overnight.
AI Voice Recruiter vs. Human Screener: Detailed Comparison
| Stage | AI Voice Recruiter | Human Screener |
| Speed & Throughput | Screens candidates 24/7 with no scheduling delays. | Limited by calendar availability and daily call capacity. |
| Consistency & Structure | Asks the same questions and applies the same rubric every time. | Interview style and scoring can vary by recruiter or day. |
| Quality of Signal | Strong for clear, structured criteria and knock-out checks. | Strong for nuance, soft skills, and potential assessment. |
| Candidate Experience | Offers on-demand interviews and faster movement in the funnel. | Builds rapport and feels more personal for many candidates. |
| Fairness & Bias | Reduces human drift but may struggle with accents or speech differences without audits. | Can adapt to context but may introduce unconscious bias. |
| Cost & ROI | Low marginal cost per screen and scales instantly. | Cost rises linearly with volume and requires more headcount. |
Early screening is where hiring teams feel the most pressure: thousands of applicants, tight timelines, and the need to stay fair and consistent. An AI voice recruiter can take over the most repeatable parts of first-round screening, while human screeners remain essential in areas needing judgment, empathy, and context. Below is a practical comparison across core stages.
1. Speed and Throughput
A voice AI recruiter can interview candidates back-to-back, 24/7, without waiting for recruiter availability. This removes the biggest delay in early hiring and scheduling. In markets with high hiring volume, AI screening can sharply reduce time-to-hire by delivering an initial shortlist within hours, not days. Surveys in 2024–2025 show many recruiters already use AI mainly for speed and scale, and adoption continues to rise year over year.
Humans can only run a limited number of screens per day. Even strong recruiters hit a throughput ceiling because each call takes time and follow-up admin. When pipelines are large, this creates backlogs, slower candidate movement, and higher drop-off, especially for hourly and frontline roles where candidates expect fast responses.
2. Consistency and Structure
An AI voice recruiter runs a structured interview every time: the same questions, the same order, the same scoring rubric. That consistency helps reduce “interviewer drift” and makes results easier to compare across hundreds of applicants. It’s one reason regulated or high-risk hiring environments are moving toward more structured, technology-supported screening.
Humans naturally vary. Two recruiters may interpret the same answer differently, or the same recruiter may score differently depending on fatigue, mood, or context. Humans can be trained to use structured scorecards, but maintaining perfect consistency at scale is hard.
3. Quality of Signal
Voice AI is strongest when questions have clear, job-linked scoring: eligibility, experience thresholds, role-specific scenarios, language proficiency, availability, or compliance checks. Because it turns answers into structured data and summaries, recruiters get a cleaner, faster first-pass ranking. Some 2025 market analyses report measurable improvements in early-funnel conversion and shortlist accuracy when AI handles structured first-round screens.
Humans are better at reading nuance. They can probe unexpected but promising answers, notice context behind career gaps, and evaluate interpersonal signals in real time. This matters for roles where “potential” or situational judgment outweighs checklist criteria, such as leadership, complex sales, or specialist positions.
4. Candidate Experience
A voice AI recruiter can improve the experience by letting candidates interview at a time that suits them, without waiting days for a slot. That speed and convenience can reduce anxiety for some applicants. At the same time, perception varies: a 2024 survey found that about 43% of candidates felt uncomfortable with AI-led interviews, showing that acceptance is significant but not universal.
Humans tend to create stronger rapport and allow a more conversational flow. Candidates who value a “real person” early on, especially for senior or relationship-heavy roles, often respond better to human screens. Humans also handle emotional or sensitive conversations more naturally, which can shape an employer brand.
5. Fairness and Bias Considerations
Standardization can reduce human biases, such as snap judgments and halo effects. But voice systems depend on speech recognition, and research shows accuracy can drop for certain accents or dialects. A 2025 study and report found that error rates among some non-native speakers can reach around 22%, which could unfairly hurt candidates if left uncorrected. That’s why responsible use requires: accent-robust models, bias audits, clear opt-outs, and human review for edge cases.
Humans bring their own biases, conscious or not, based on background, speaking style, or familiarity. Structured scorecards help, but bias can still creep in. Humans, however, can adapt in real time when a candidate has a disability or communication difference, where AI might misinterpret signals.
6. Cost and ROI
Once set up, an AI interviewer can run thousands of screens with little added cost per interview. Industry statistics in the 2024–2025 report major efficiency gains from AI adoption, including large reductions in cost-to-hire and recruiter admin time.
The strongest ROI usually comes from letting AI do first-pass screening while recruiters focus on high-value steps like final interviews, selling the role, and closing candidates.
Human screening scales with headcount. More applicants mean more recruiter hours, more scheduling overhead, and higher costs. For fast-moving pipelines, that linear scaling becomes expensive, and delays can cause good candidates to drop out.
Primary Criteria for Automating Screening with an AI Voice Recruiter
You should automate with an AI voice recruiter:
- When the role attracts a high volume of applicants and needs rapid early-stage screening.
- Can be standardized with a clear script, rubric, and objective pass/fail criteria.
- When speed and scalability are critical because delays directly increase drop-offs or business risk.
- When you need consistent, structured interview data to compare candidates reliably and track funnel metrics.
- When human screening capacity is limited or the cost per screen is too high to sustain at scale.
- When your hiring stack supports it, including ATS integration and a stable voice AI interviewing system.
- When candidates must be able to complete screening 24/7 across multiple time zones or geographies.
Decision Criteria for Human-Led First-Round Screening
You should rely on human screeners when :
- Hiring for senior, strategic, or highly specialized roles where context and leadership judgment matter.
- The role requires nuanced evaluation of cultural fit, potential, or ambiguous competencies.
- Candidate volume is low and a high-touch, relationship-driven approach is appropriate.
- Employer branding is sensitive and candidates strongly expect early human interaction.
- Automation risk is high, such as diversity-sensitive roles, empathy-heavy jobs, or cases with language and accent concerns.
- Automation infrastructure is not mature yet or when you are running a small pilot before scaling.
When to Shift to a Hybrid Voice AI and Human Workflow
You should use a hybrid approach when :
- A voice AI recruiter can handle the first-touch, high-volume screening, and humans can step in after clear thresholds are met.
- A practical hybrid workflow is to run AI voice recruiter screens first, filter and score candidates, then route shortlisted profiles to a human screener before the hiring manager interview.
- The hybrid model works well because it combines early-stage efficiency with human judgment where nuance and context matter.
- You should design a smooth hand-off by aligning AI outputs to recruiter needs and keeping messaging consistent with your employer brand.
- You should be transparent with candidates by clearly stating when they are speaking to AI and when they will speak to a human.
- You should govern the system by monitoring AI screening outcomes, checking for bias, and running regular audits.
- You should train recruiters to interpret AI-generated transcripts, scores, and summaries so they can make better and faster decisions.
Why Avahi Is the Perfect Fit for Modern Talent Acquisition Teams?
For HR and talent acquisition teams, speed, consistency, and trust are everything. Whether you’re coordinating interviews across time zones or handling a surge of candidate inquiries, your systems must not only move fast but also operate securely and in line with your organization’s compliance standards.
This is where Avahi’s AI Voice Agent becomes a valuable tool for talent acquisition teams. Here’s how this supports modern HR and Talent Acquisition teams:
- Always-on responsiveness
No missed calls or delayed replies. Candidates receive instant, human-like support, which is critical for fast-moving hiring pipelines that rely on secure and reliable service availability. - Secure handling of candidate data
With compliance-aligned processes, the AI agent ensures candidate information flows through your ATS/CRM safely and consistently, reducing the risk of data mishandling. - Reduced administrative workload
Repetitive tasks like scheduling, reminders, and initial screening are automated—helping teams meet recruitment SLAs without sacrificing data governance. - Improved audit readiness
Every interaction is logged, traceable, and aligned with the security controls required by modern compliance frameworks. - Better candidate experience, powered by secure automation
Candidates receive timely answers, while your team stays focused on meaningful conversations, rather than paperwork or coordination.
For HR leaders operating in competitive hiring markets, pairing AI automation with strong compliance foundations (such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2) ensures both speed and trust, so your team delivers great candidate experiences without creating new security risks.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it legal to use an AI voice recruiter for screening?
In most regions, yes, but rules are evolving fast. There is no single U.S. federal law for AI hiring, yet several states and cities require disclosure, consent, or bias audits when automated tools affect hiring decisions. So legality depends on where you hire and how the tool is used.
2. Do candidates accept AI voice screening?
Acceptance is mixed. Many candidates are fine with AI in early rounds if it speeds things up, but trust is not universal. For example, a 2025 Gartner survey found only about a quarter of candidates trust AI to evaluate them fairly, and most want employers to be transparent about AI use.
3. What kinds of roles are the best fit for an AI voice recruiter?
AI voice recruiters work best for high-volume roles with clear eligibility checks and structured questions, like frontline, support, sales development, or seasonal hiring. If the role can be screened using a consistent rubric, AI usually adds value by speeding up first-round filtering.
4. What are the biggest risks of AI voice screening?
The main risks are fairness and accuracy. Voice systems can mis-transcribe or mis-score candidates with certain accents, dialects, or speech disabilities if the model is not tested properly. That’s why bias monitoring, audit trails, and human override options are important.
5. How do we avoid bias when using a voice AI recruiter?
Start with job-relevant, structured questions, then run regular bias audits on outcomes (pass rates by group where lawful). Offer candidates an accommodation or human alternative, and review edge cases manually. Many current regulations and guidance emphasize disclosure plus documented fairness checks.