TL;DR
|
In healthcare, missing a patient’s symptom isn’t just a delay; it can be the difference between prevention and crisis. This simple truth is driving a massive shift toward smarter, more proactive care, especially in how we monitor patients beyond hospital walls.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is no longer a futuristic concept; it has become a growing standard of care. A recent study predicts that by 2029, 65% of providers will expand their use of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM).
But monitoring vital signs alone isn’t enough.
What about symptoms that devices can’t detect? What about the millions of patients who forget to enter their data or don’t understand how to use an app?
This is where AI voice agents play a significant role. These intelligent, voice-driven systems collect data, interact with patients, understand their needs, and help clinicians take action when it matters most.
In this blog, we’ll explore how AI voice agents are being integrated into RPM programs to improve patient engagement, streamline care delivery, and enable earlier intervention, especially for those who need it most.
What Are AI Voice Agents in the Context of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)?
AI voice agents are intelligent, voice-enabled software systems designed to communicate with patients using natural, two-way speech. These systems utilize technologies such as speech recognition, natural language understanding (NLU), and text-to-speech (TTS) to facilitate interactive conversations. In a Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) setup, these agents can:
- Ask health-related questions
- Understand and record patient responses.
- Provide reminders and instructions
- Transfer relevant data to healthcare providers in real time.
These interactions are not limited to fixed scripts. The voice agent can adapt based on patient responses, clinical data, or predefined care protocols.
Modern Voice Agents vs. Conventional IVR: Enhancing Patient Communication
Below is a side-by-side comparison highlighting the key differences between AI voice agents and conventional IVR systems in remote patient monitoring.
| Feature | Conventional IVR Systems | AI Voice Agents |
| Interaction Style | Menu-driven, limited options (“Press 1 for…”) | Conversational, natural speech-based |
| Response Capability | Fixed responses only | Contextual understanding and dynamic response generation |
| Personalization | One-size-fits-all | Adjusts conversation based on patient history or profile |
| Error Handling | Often fails on unexpected inputs | Can handle diverse phrasing and rephrase for clarity |
| Use of AI | No | Yes. NLP, machine learning, and real-time processing |
AI voice agents do not rely on rigid scripts. Instead, they understand patient speech in real time and respond appropriately, much like speaking to a human. This leads to better patient engagement, especially for those who may be uncomfortable with complex menu systems or non-human interactions.
Types of RPM Devices and How Voice Agents Enhance Their Use
Remote Patient Monitoring relies on a variety of medical devices to collect health data from patients in real time. These devices are used in the home setting and transmit data back to healthcare providers for review and intervention. Below is an overview of common remote patient monitoring devices, along with an explanation of how AI voice agents complement and enhance their functionality.
1. Blood Pressure Monitors
These devices measure a patient’s systolic and diastolic pressure. They’re often used for patients with hypertension or cardiovascular conditions. Data is sent to clinicians to monitor trends and adjust medications.
2. Blood Glucose Monitors
Primarily used by diabetic patients, these devices monitor blood sugar levels. They help healthcare providers assess how well glucose is being managed and detect dangerous highs or lows.
3. Smart Thermometers
These thermometers record and transmit body temperature data. They help detect fevers related to infections, including postoperative complications or flare-ups of chronic diseases.
4. Pulse Oximeters
These non-invasive devices measure blood oxygen saturation and heart rate. They are vital for patients with respiratory conditions such as COPD, asthma, or COVID-19.
5. ECG Monitors
Portable or wearable ECG devices monitor heart rhythm and detect abnormalities, such as arrhythmias. Data is shared with cardiologists for diagnosis and timely intervention.
6. Wearables (e.g., Smartwatches, Biosensors)
These devices collect continuous data, including steps, heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. Some also include fall detection and emergency alert features, making them useful for elderly care.
Operational Workflow of AI Voice Agents in Remote Patient Monitoring
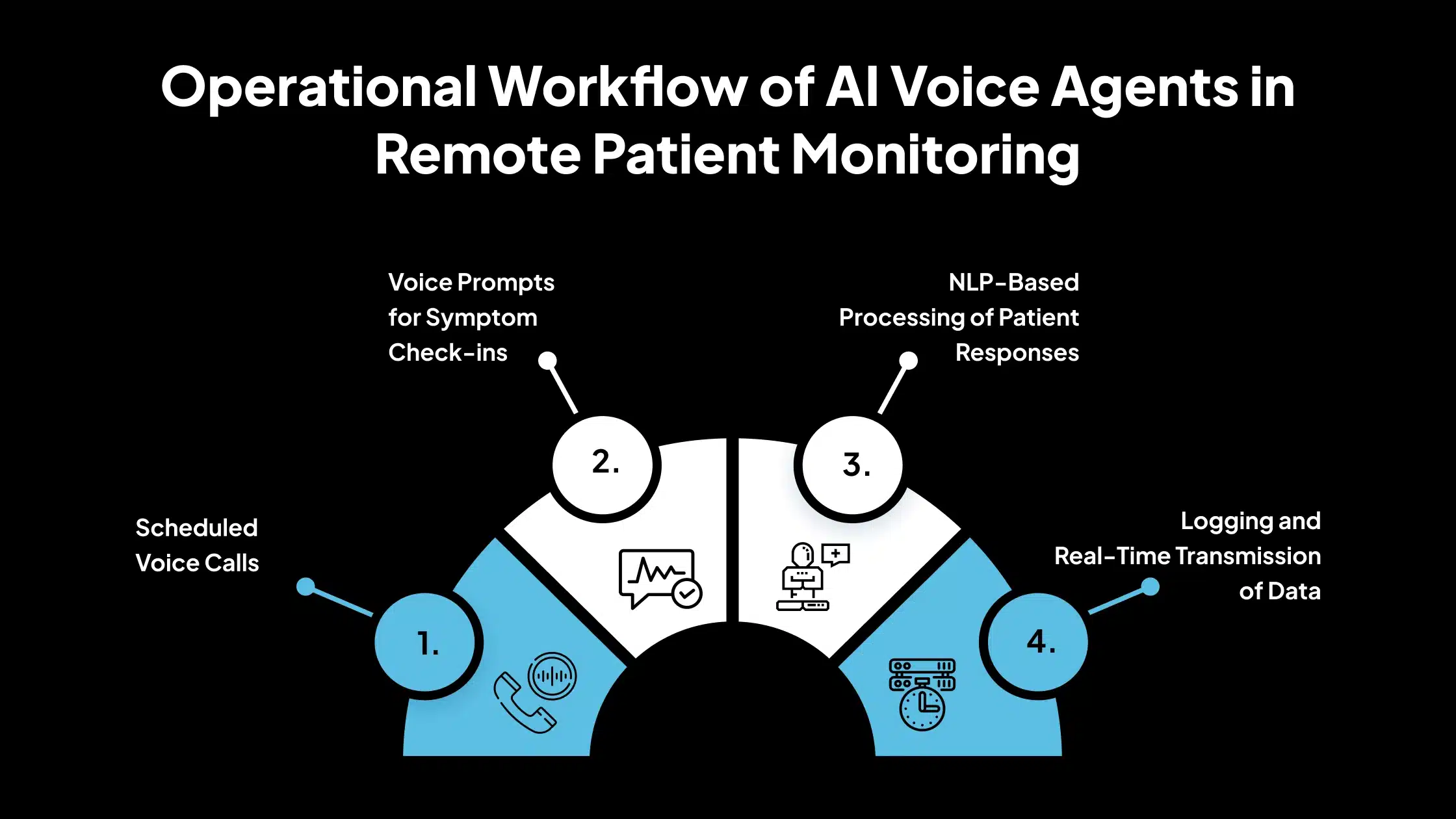
AI voice agents operate as the patient-facing interface in RPM programs. Their goal is to guide patients through regular check-ins and collect health data using voice communication.
1. Scheduled Voice Calls
Voice agents can be programmed to call patients at specific times, daily, weekly, or as needed. Patients may also initiate contact at their discretion. This ensures routine monitoring and immediate communication when concerns arise.
2. Voice Prompts for Symptom Check-ins
During interactions, the agent asks structured questions about symptoms, including pain, fatigue, and breathing issues. It can also guide patients through the process of reporting device readings, such as “Please tell me your blood pressure reading from today.”
3. NLP-Based Processing of Patient Responses
The agent uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand and interpret spoken responses. It can recognize medical terms, assess symptom severity, and respond accordingly, even if patients use varied language or sentence structures.
4. Logging and Real-Time Transmission of Data
All collected information is securely logged and transmitted in real time to the provider’s dashboard or integrated Electronic Health Record (EHR) system. This enables clinicians to view and act on the data without delay.
System Architecture and Multichannel Capabilities of AI Voice Agents in Remote Monitoring
Behind the voice agent is a technical framework that enables secure, accurate, and scalable operations.
1. Cloud-Based AI Engines for Natural Language Understanding
Voice agents operate through cloud-hosted AI engines that manage language comprehension and response generation. This enables real-time processing and facilitates easy updates to enhance system performance.
2. Integration with RPM Platforms and Data Management Systems
The voice agent connects directly to RPM platforms to ensure all patient data is synchronized. Integration allows seamless transfer of voice-collected data into the same system that handles device-collected metrics.
3. Secure APIs to Synchronize with EHRs and Alert Systems
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) allow voice agents to communicate securely with hospital systems. This enables real-time updates to patient records and can trigger automated alerts for care teams when critical symptoms are reported.
4. Fallback to SMS, Mobile Apps, or Email
If voice interaction fails, due to poor network conditions, technical issues, or patient preference, the system can switch to alternative modes, such as SMS, mobile app notifications, or email, to continue the interaction.
5. Bilingual or Multilingual Capabilities for Accessibility
Voice agents are often equipped to communicate in multiple languages. This ensures patients from diverse linguistic backgrounds can engage comfortably, improving overall response rates and reducing health disparities.
Essential Features of AI Voice Agents for Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
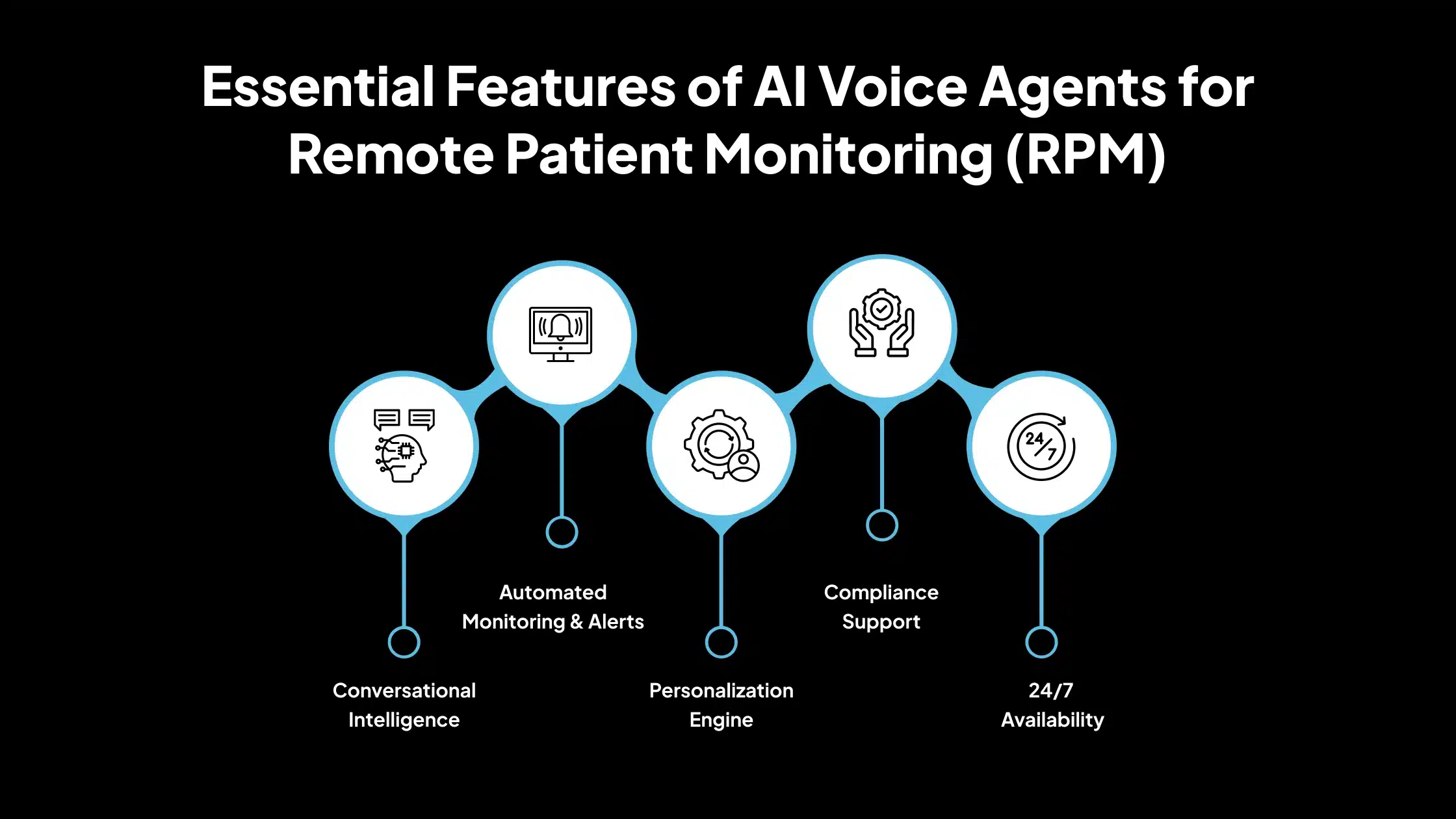
Below are the essential features that enable AI voice agents to effectively support remote patient monitoring and enhance care delivery.
1. Conversational Intelligence
AI voice agents utilize advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) to facilitate seamless, two-way conversations with patients. They can manage dynamic dialogues, adjust their tone to match the context (e.g., urgency or reassurance), and remember previous interactions.
This enables more natural and human-like engagement, thereby improving patient comfort and compliance.
2. Automated Monitoring & Alerts
The system can automatically monitor incoming responses for signs of health deterioration. If a patient reports a critical symptom or fails to respond within a certain timeframe, the voice agent can trigger an alert. These alerts are sent to care teams in real time, helping them act quickly when intervention is needed.
3. Personalization Engine
Voice agents can tailor interactions based on each patient’s unique profile. This includes factors such as medical history, current treatment plans, preferred language, and past interaction patterns. Personalization makes communication more relevant, which increases the likelihood of patient engagement and adherence.
4. Compliance Support
Data privacy and security are critical in healthcare. AI voice agents are designed to comply with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States and GDPR in the European Union. All communication is encrypted, and sensitive data is stored and transmitted securely, ensuring the protection of patient information at every step.
5. 24/7 Availability
Unlike human staff, voice agents can operate continuously without breaks. This allows patients to engage with the system at any time, including outside business hours or during emergencies. It is especially useful for chronic care management, post-surgical monitoring, and reporting of late-night symptoms.
Benefits of AI Voice Agents in Remote Monitoring Programs
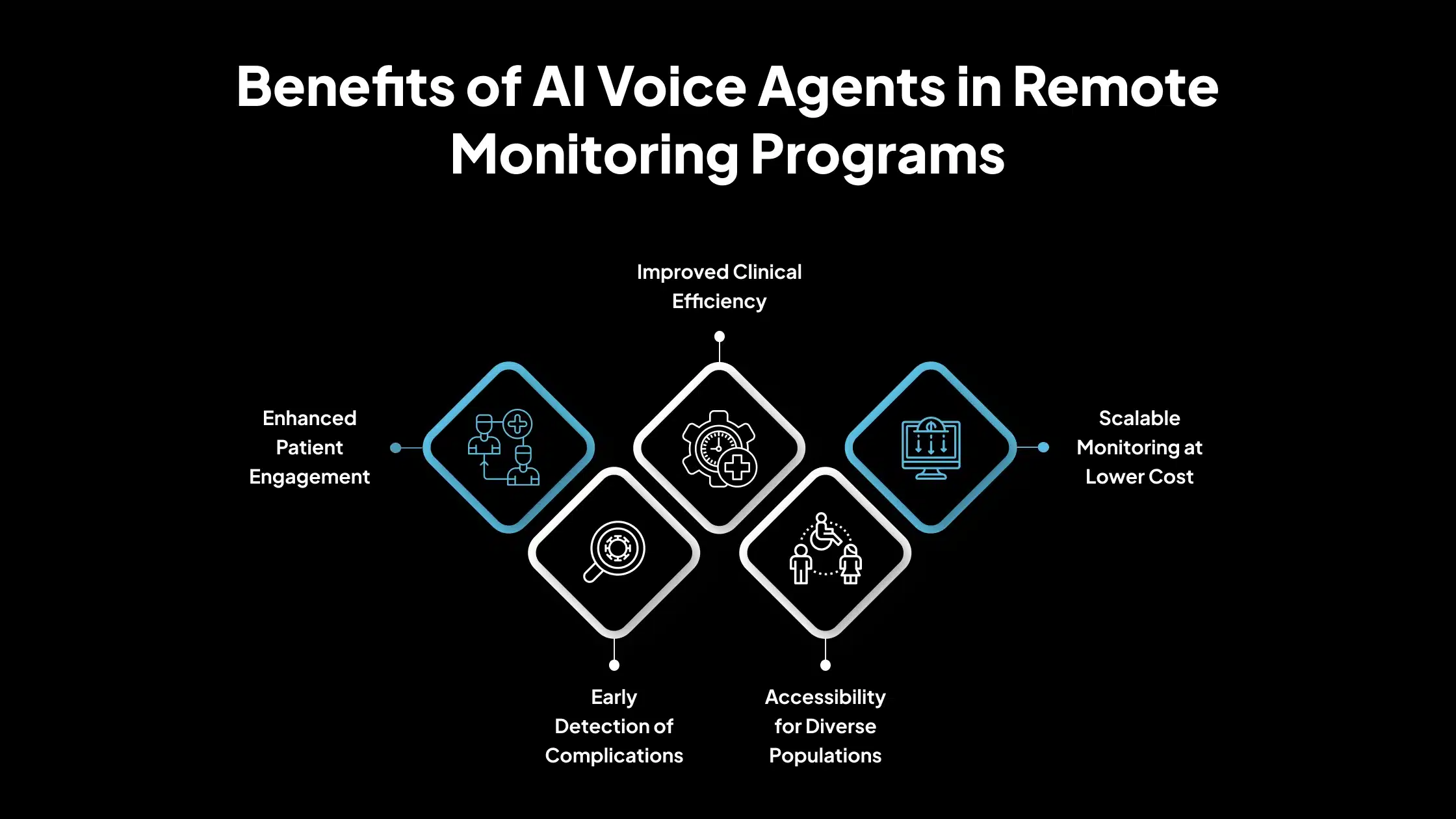
Below are the essential benefits of integrating AI voice agents into remote monitoring programs, highlighting their impact on both patient care and clinical efficiency.
1. Enhanced Patient Engagement
AI voice agents provide a conversational experience that feels more natural than interacting with buttons or forms. This human-like interface encourages patients to respond regularly and share more accurate information.
According to a recent study, over 60% of patients prefer voice interactions over typed responses for routine health check-ins, especially when managing chronic conditions. Improved engagement often leads to better adherence to care plans and more consistent health monitoring.
2. Improved Clinical Efficiency
Routine tasks, such as symptom surveys, medication adherence checks, and appointment reminders, can be fully automated through voice agents. This reduces the burden on clinical staff, allowing healthcare providers to allocate more time to complex or high-risk patients.
For example, a 2022 McKinsey report found that up to 40% of healthcare tasks can be automated, which directly improves operational efficiency without compromising care quality.
3. Scalable Monitoring at Lower Cost
AI voice agents can handle thousands of simultaneous conversations without trequiringadditional human staff. This scalability makes them ideal for large healthcare systems or population health initiatives. They also eliminate costs associated with manual outreach, such as call center staffing and personnel expenses.
4. Early Detection of Complications
By collecting patient-reported symptoms on a daily or regular basis, voice agents can identify early warning signs of clinical deterioration.
These real-time insights allow providers to intervene before conditions escalate, potentially reducing emergency room visits or hospitalizations. A recent study found that early alerts from digital RPM tools reduced hospitalization rates by 25% in heart failure patients.
5. Accessibility for Diverse Populations
Not all patients are comfortable using mobile apps or navigating digital portals. Voice-based systems provide a simpler and more inclusive option, especially for elderly patients, individuals with visual impairments, or those with limited digital literacy.
Speaking is intuitive and doesn’t require internet access or complex device handling. As a result, voice agents can help bridge the digital divide in healthcare access.
Use Cases of AI Voice Agents in Remote Monitoring Programs
Here are several real‑world use cases illustrating the impact of AI voice agents in remote monitoring programs in patient care.
1. Chronic Disease Management
For patients with long‑term conditions like diabetes, hypertension, COPD, or heart failure, voice agents help with regular symptom check‑ins, medication reminders, and lifestyle guidance (diet, activity).
They can prompt patients to report their vitals (e.g.,, blood pressure, glucose) or subjective symptoms on a daily or at set intervals. They often escalate to clinicians when thresholds are exceeded or warning signs appear.
Chronic diseases require continuous monitoring; small changes, if undetected, can lead to complications. Many patients struggle with adherence or forget to self‑report; voice agents reduce these gaps.
A study presented at the American Heart Association’s 2025 Hypertension Scientific Sessions investigated the use of AI voice agents in older chronic‑care patients to improve blood pressure control. Early results showed improved engagement and outcome metrics in the participant group compared to usual care.
2. Post‑Acute Care and Discharge Follow‑Up
After a patient leaves the hospital (following surgery or an acute event), voice agents conduct regular check-ups via phone calls or voice prompts. They monitor medication adherence, wound healing (via symptom reporting, including pain and swelling), rehabilitation tasks, and symptoms that may indicate complications or readmission risk.
The period after discharge is high risk: patients often misunderstand instructions, miss medications, or experience complications. Early detection and support can reduce readmission.
The Geisinger Monitoring Program (GMP) used an interactive voice response (IVR) protocol as a telemonitoring adjunct for Medicare patients under primary care, following hospital discharge. The program demonstrated a 44% reduction in 30-day hospital readmissions compared to the control group in a case-managed population.
Another study in older adults demonstrated that automated post-discharge follow-up phone calls and structured discharge phone call protocols reduced readmissions in postoperative patients.
3. Geriatric and Palliative Care
Regular wellness checks via voice (e.g., asking about general well‑being, pain, mobility, feeding, sleep) for elderly or home‑bound patients. Voice agents can assess mood, feelings, and loneliness, and escalate to human providers if needed. Reminders for medications, assistance with daily routines.
Many older patients have limited mobility, reduced technical literacy, or sensory issues (such as vision or dexterity). Voice interfaces are easier. Emotional and social support are often overlooked, yet they are crucial in maintaining a high quality of life.
The AHA hypertension study (from Emory,, etc.) previously utilized voice agents,, including those for older adults, with an emphasis on multilingual support and cultural competency.
4. Mental Health Monitoring
Agents prompt regular mood check-ins (“How are you feeling today?” and “Have you felt anxious/depressed?”). Behavioral health screening questions; tracking sleep, appetite, and stress.
Conversational triage: if a patient reports severe symptoms (e.g., suicidal ideation), escalate to mental health professionals.
Mental health conditions often fluctuate; regular self‑reporting helps catch deterioration.
Some patients may prefer speaking over typing or app forms, reducing the barrier to expressiveness.
Many voice‑agent applications primarily combine symptom check‑ins that include mental health elements (mood, depression), especially in chronic disease or post‑discharge contexts. One systematic review noted that conversational agents, including voicebots,, can serve as caregivers for non-communicable diseases that involve mental health aspects.
5. Pandemic and Infectious Disease Monitoring
During infectious disease outbreaks (e.g., COVID‑19), voice agents screen patients for symptoms (fever, cough, breathlessness), provide information,and monitor quarantine compliance. Post‑infection follow‑ups to track recovery and long‑COVID symptoms.
Infectious diseases often require rapid scaling of monitoring, particularly when health systems are already overburdened. Voice agents can relieve load, reach more people, and provide consistent screening.
Best Practices for Deploying AI Voice Agents in RPM Systems
Successful integration of AI voice agents into Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) requires a structured approach. The following elements are essential for effective deployment and long-term impact.
1. Platform Selection Criteria
Select platforms with healthcare-optimized natural language processing (NLP) that can accurately understand and respond to standard medical terms and patient expressions. Ensure the system integrates smoothly with your existing RPM platforms, Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and care coordination tools, utilizing standards such as HL7 or FHIR.
Verify that the vendor adheres to relevant industry regulations, such as HIPAA (U.S.) or GDPR (EU), or local equivalents. Look for built-in encryption, secure data storage, and access control.
Select solutions that allow you to configure workflows, script content, escalation rules, and languages based on your organization’s needs and patient demographics.
2. Patient Segmentation
Many older adults find voice interfaces easier to use than mobile apps or touchscreens. Voice agents can improve adherence and reduce confusion in this group.
Individuals managing conditions like diabetes, heart failure, or COPD require regular check-ins. Voice agents can reduce the burden on care teams while keeping patients engaged.
Patients recently discharged from the hospital often require close follow-up. Voice agents can provide daily wellness checks and monitor for early signs of complications.
3. Integration with Existing Systems
Voice agents should not operate in isolation. The agent must send data back to your Electronic Health Record system in real time to maintain continuity of care.
Integrate voice-collected data into the same dashboards used for vitals, lab results, and other remote metrics. Set up real-time alerts that notify care teams when a patient reports worsening symptoms or fails to respond to scheduled prompts.
Utilizing open standards such as FHIR or HL7 can simplify these integrations and ensure future interoperability.
4. Training and Onboarding
Educate staff on how the voice agent fits into the RPM workflow, how to access patient data collected via voice, and how to respond to alerts.
Introduce patients to the voice agent during the enrollment process. Provide simple instructions, address common concerns, and offer support channels in case of issues.
5. Monitoring and Optimization
Review key metrics, including response rates, symptom trends, and patient drop-offs. Identify where improvements are needed. Refine dialogue flows based on patient behavior and feedback. Adjust prompts to be clearer or more engaging if necessary. Gather input from patients and clinicians regularly. Use surveys or interviews to understand how the system is performing in real-world use.
Avahi AI Voice Agents: Enhancing Operational Efficiency Through Smart Voice Automation
Managing patient calls can consume a significant amount of time and resources in healthcare settings. Avahi AI Healthcare Voice Agents are designed to streamline call handling, allowing providers to focus more on delivering care while ensuring patients receive timely support.
Here is what Avahi’s AI voice agents can handle:
- Answer Routine Questions: The system responds to common patient inquiries about appointments, office hours, directions, and other relevant information.
- Book, Reschedule, and Cancel Appointments: Patients can manage their appointments in real time without waiting for office staff.
- Send Reminders and Follow-Ups: Automated alerts reduce no-shows and keep patients informed about upcoming visits.
- Route Urgent Calls: Important issues are flagged and directed to staff immediately, ensuring quick response when needed.
- Handle Insurance and Referrals: The AI assists with insurance-related questions, referrals, and call triage, thereby improving the patient experience and reducing confusion.
Built on AWS’s healthcare-ready cloud infrastructure, Avahi is HIPAA-compliant, SOC 2, and GDPR-compliant, ensuring patient data is handled safely and responsibly. The system can be implemented in practices of all sizes and integrates easily with existing scheduling tools and Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Explicitly designed for high-demand environments like dental, specialty, primary, and urgent care, Avahi helps reduce wait times and improve patient satisfaction.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency?Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are AI voice agents in remote monitoring effective for chronic disease management?
Yes, AI voice agents in remote monitoring are highly effective for managing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart failure, and COPD. They facilitate regular symptom check-ins, medication reminders, and health education through voice interactions. This consistent engagement helps detect issues early, enhances treatment adherence, and reduces the need for in-person follow-ups.
2. Do AI voice agents in remote monitoring support real-time data sharing with healthcare providers?
Yes, AI voice agents in remote monitoring are designed to collect patient responses and transmit them securely and in real time to care teams. The data can be integrated with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems and RPM dashboards, enabling timely clinical review and faster decision-making based on both qualitative and quantitative inputs.
3. Can AI voice agents improve patient engagement in remote care programs?
Absolutely. AI voice agents use natural, conversational language to interact with patients, making it easier for them to report symptoms and follow care instructions. This human-like interface helps reduce communication barriers, particularly for elderly or non-tech-savvy individuals, resulting in higher response rates and improved adherence to remote care plans.
4. Are AI voice agents secure and compliant with healthcare data regulations?
Yes, most AI voice agents used in healthcare are built to comply with major data privacy and security standards, including HIPAA and GDPR. They employ encrypted communication channels, secure cloud storage, and strict access controls to ensure patient information remains confidential and protected at all times.
5. How do AI voice agents integrate with existing remote patient monitoring systems?
AI voice agents can be integrated into existing remote patient monitoring systems using APIs and healthcare interoperability standards such as HL7 and FHIR. This enables patient-reported voice data to be integrated directly into clinical platforms, ensuring seamless coordination between patient interactions and provider workflows.