TL;DR
|
Medication non-adherence is one of the most pressing challenges in healthcare today. According to the World Health Organization, only about 50% of patients with chronic illnesses adhere to their prescribed treatments. This means millions of people are missing doses, taking the wrong amounts, or stopping treatment prematurely, often without realizing the risks.
The result is alarming. Non-adherence contributes to 125,000 preventable deaths annually in the U.S. alone and drives an estimated $100–300 billion in avoidable healthcare costs each year. Poor adherence leads to disease progression, more hospital visits, and lower quality of life for patients.
Conventional reminder tools, such as pillboxes, mobile apps, and text alerts, have not been effective in solving the problem. They often fail to engage patients in a meaningful way, lack personalization, and cannot adapt to individual routines. This is where AI-powered voice agents are emerging as a game-changer, offering interactive, adaptive, and human-like support to help patients stay on track with their treatments.
This blog examines how AI voice agents for medication management can enhance medication adherence, increase adherence rates, and yield improved outcomes for both patients and healthcare providers.
Medication Non-Adherence: What’s at Stake for Patients and Providers
Medication adherence refers to the extent to which a patient takes their medications as prescribed, including the correct dose, timing, and frequency of administration. It includes both starting a prescribed therapy and continuing it without missed doses or early discontinuation.
Non-adherence leads to poor disease control, progression of illness, and a higher risk of complications. For example, missed antihypertensive doses can result in uncontrolled blood pressure, increasing the risk of stroke or heart attack.
Non-adherence is a major contributor to preventable healthcare costs. It often results in additional doctor visits, emergency room use, and hospital admissions. At the individual level, patients who do not adhere to their medication regimens may experience worsening symptoms, reduced daily functioning, and lower quality of life. In some cases, it can lead to irreversible health deterioration or premature death.
Standard Medication Adherence Solutions: The Limitations of Current Medication Reminder Systems
Several traditional interventions are used to support medication adherence; however, each has its own limitations.
| Intervention | Summary |
| Pillboxes | Organize doses by day/time, but rely on patient action and offer no tracking. |
| Mobile Apps | Send reminders and basic tracking, but need manual input and lack engagement. |
| SMS Reminders | Low-cost alerts are one-way, easy to ignore, and offer no confirmation. |
| Nurse Call Follow-Ups | Provide personal check-ins, but they are costly, time-consuming, and challenging to scale. |
1. One-Way Communication (No Patient Input)
Most traditional solutions only send reminders without allowing patients to respond or ask questions. There is no confirmation of whether the medication was taken or missed.
2. Lack of Personalization/Context
Reminders are usually generic and do not adapt to the patient’s lifestyle, language, or health condition. They are often scheduled at fixed times without considering the patient’s daily routine or medication history.
3. Alert Fatigue
When reminders are repetitive or poorly timed, patients may begin to ignore them. Over time, constant alerts lose their effectiveness and become background noise.
4. No Educational or Motivational Component
Conventional tools do not explain why a medication is essential, how it works, or what could happen if doses are missed. They also do not motivate the patient to stay consistent with their regimen.
5. Poor Adaptability Across Age, Language, and Tech Literacy
Older adults or those with limited experience using smartphones may struggle with digital apps. Many tools lack multi-language support, voice accessibility, or features designed for users with low health literacy.
AI Voice Agents for Medication Management: Core Architecture and Capabilities
An AI voice agent for medication management is a software system designed to carry out spoken conversations with users using artificial intelligence. These agents can understand human speech, process its meaning, and respond with spoken output.
Unlike regular automated phone systems, AI voice agents use natural language processing to interpret a wide range of inputs and provide contextually appropriate responses. Here is a list of the core components of these AI voice agents:
- Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR): ASR converts spoken words into text, allowing the system to process what the user is saying. It must handle variations in accents, speech speed, and background noise.
- Natural Language Processing/Understanding (NLP/NLU): NLP and NLU enable the system to comprehend the meaning and intent behind the user’s words. This includes identifying commands, answering questions, or recognizing when a patient needs help.
- Text-to-Speech (TTS): TTS technology enables the agent to respond by converting text-based output into natural-sounding speech. This makes the interaction feel conversational and accessible.
- Decision Logic: This refers to the rule-based or AI-driven logic that determines how the system responds based on the user’s input. It decides whether to confirm a dose, escalate a concern, or provide additional information.
The Workflow of AI Voice Agents in Medication Management
AI voice agents follow a structured workflow to deliver reminders, engage patients in real-time, and support consistent medication adherence.
1. Schedule-Based Reminders via Phone, Speaker, or App
AI voice agents are configured to send medication reminders at specific times tailored to each patient’s prescription schedule. These reminders can be delivered through various devices, such as landline telephones, mobile phones, or smart speakers like Amazon Echo or Google Home.
Using familiar communication channels ensures the reminders are accessible, especially for elderly patients or those with limited technical skills.
2. Real-Time Interaction: Ask About Dose Taken, Follow-Up Questions
Unlike static alerts, AI voice agents initiate a two-way conversation. After delivering a reminder, the agent asks if the medication was taken.
Suppose the patient responds negatively or does not respond at all. In that case, the system can follow up with additional questions, such as whether the patient forgot to take the medication, experienced side effects, or chose not to take it. This interaction helps uncover barriers to adherence in real time.
3. Intelligent Branching: Escalates if Doses Are Missed or Symptoms Reported
If the patient reports missed doses, adverse effects, or concerning symptoms during the interaction, the AI agent follows predefined rules to take appropriate next steps.
This may include alerting a caregiver, sending a notification to a healthcare provider, or scheduling a follow-up call. The system can differentiate between low-risk and high-risk responses, enabling appropriate escalation without manual intervention.
4. Tracks Adherence Behavior Over Time
Each interaction, whether the medication was taken, missed, or skipped, is recorded securely. Over time, this builds a comprehensive adherence profile for the patient. Healthcare providers can access reports that highlight patterns, such as frequent missed doses or increasing non-compliance, enabling proactive intervention. This historical data also supports informed clinical decision-making and adjustments to care plans.
Core Functional Capabilities of AI Voice Agents in Medication Adherence
Below are the core functional capabilities that enable AI voice agents to effectively support and improve medication adherence.
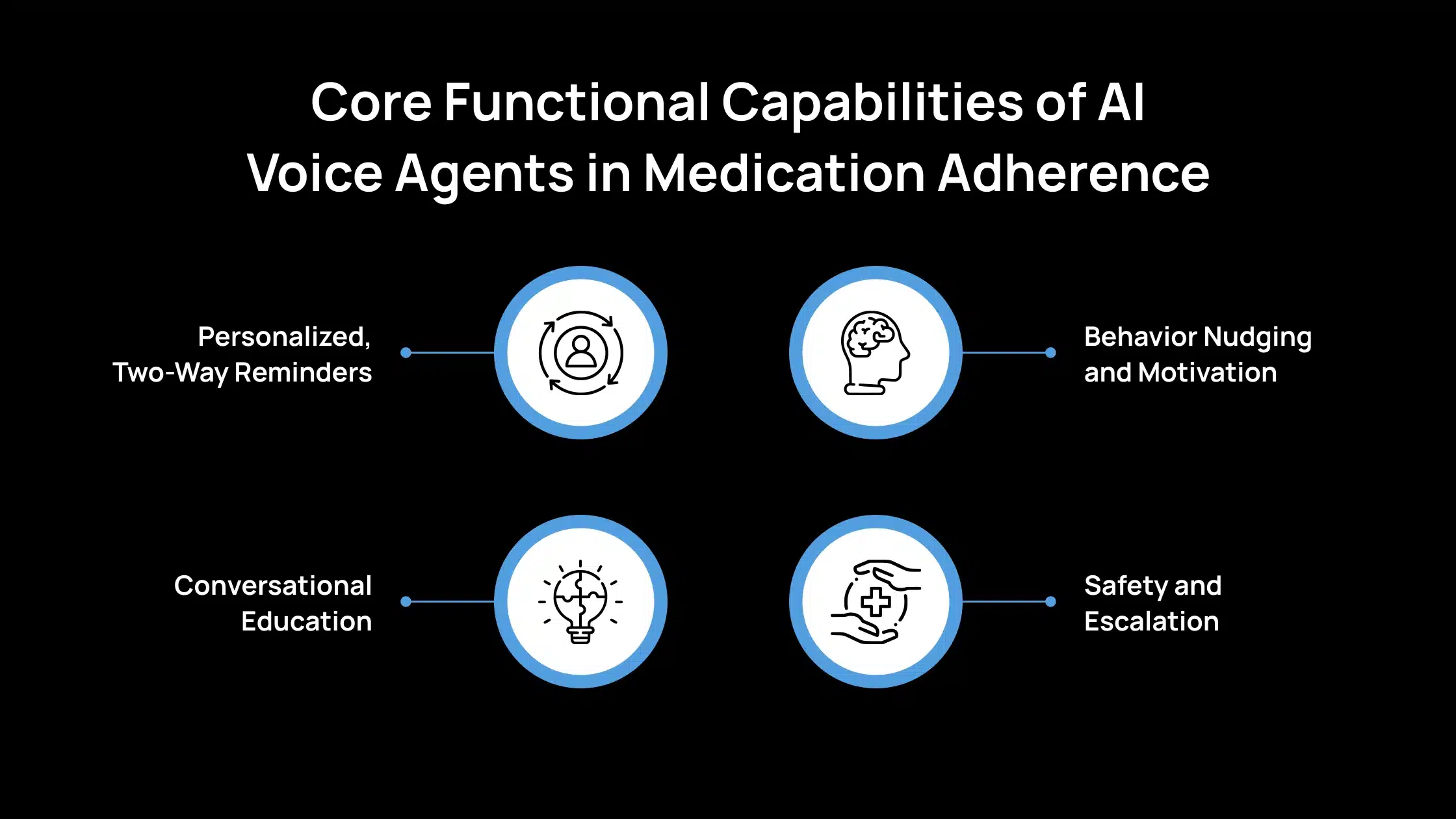
1. Personalized, Two-Way Reminders
AI voice agents can adjust reminder times to fit the patient’s daily schedule rather than relying on fixed times. For example, reminders can be aligned with meal times, sleep schedules, or work shifts, making them more practical and less disruptive.
After delivering a reminder, the system can request verbal confirmation. This creates a two-way interaction, helping to verify whether the medication was taken and allowing the system to log adherence in real-time.
2. Conversational Education
The voice agent can provide simple explanations about why a medication is essential, potential side effects, and how it works. This helps patients understand the value of adherence and reduces fear or confusion.
When patients have questions, such as “What should I do if I miss a dose?”, the agent can respond with contextually relevant, evidence-based answers. Large Language Models (LLMs) enable these systems to provide more accurate and human-like responses.
3. Behavior Nudging and Motivation
The agent can encourage patients by acknowledging progress (e.g., “You’ve taken your medication on time all week”) or by using supportive language to reinforce good habits.
Some systems may incorporate light gamification, such as tracking streaks or setting goals, to keep patients engaged and motivated. Empathetic tone and language can also improve patient motivation and make the experience more human-like.
4. Safety and Escalation
If the system detects repeated missed doses, concerning symptoms, or potential side effects, it can automatically send alerts to healthcare providers or caregivers for timely intervention.
When a patient reports a side effect verbally, the system can record it, categorize its severity, and either provide guidance or escalate to a clinician if necessary. This ensures adverse events are tracked and addressed promptly.
Essential Technical and Design Considerations for Deploying AI Voice Agents
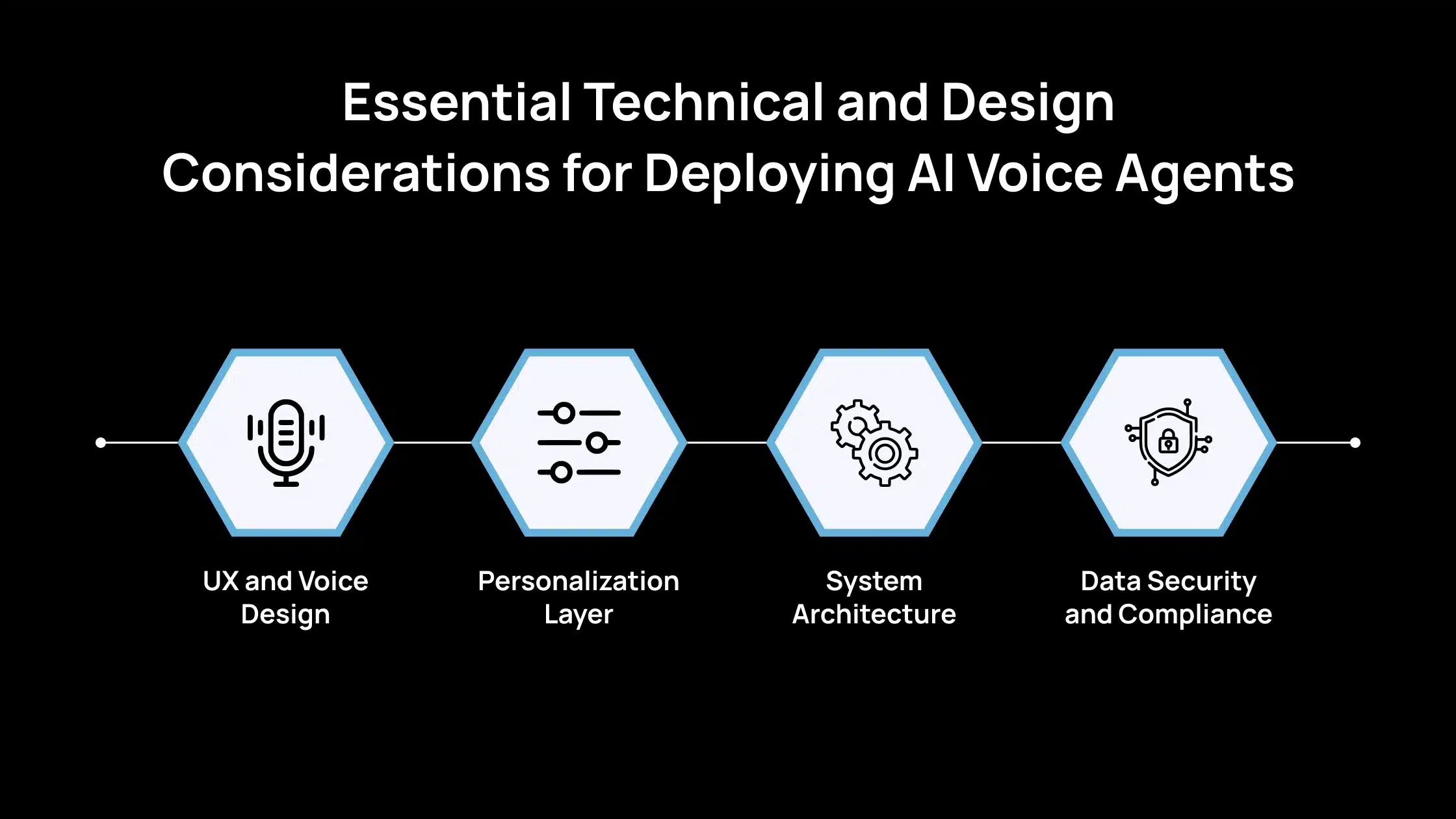
Below are the essential technical and design considerations that ensure AI voice agents function reliably, remain user-friendly, and align with healthcare standards.
1. UX and Voice Design
The voice agent must use a tone that is clear, calm, and professional to ensure users feel comfortable and respected. Support for multiple languages and dialects is crucial for reaching diverse patient populations. Conversational branching should be carefully designed to guide users naturally, offering relevant follow-up questions and options without overwhelming them.
The system should use slower, well-articulated speech and simple language for older adults or users with cognitive limitations. It must work with devices that do not require screen interaction, making it inclusive for visually impaired users. Features such as repeat or “slow mode” commands can enhance usability.
2. Personalization Layer
AI voice agents can improve over time by learning user preferences, such as ideal reminder times, preferred levels of detail, and communication styles. This adaptive approach makes reminders more effective and less intrusive.
Each patient’s profile can store information about their medication schedule, literacy level, and preferred language. This enables the system to adjust its messaging complexity and tone, ensuring that the information is both understandable and relevant.
3. System Architecture
On-device processing offers better privacy and offline functionality but may have limited computing power. Cloud-based agents enable more advanced AI capabilities and real-time updates, but they require secure and reliable internet connectivity. The choice depends on deployment needs, patient population, and regulatory constraints.
Integration with electronic health records and pharmacy systems allows the voice agent to stay updated with prescription changes, refill data, and clinical notes. Wearable sensors or smart pill bottles can provide additional adherence data, making the system more accurate and comprehensive.
4. Data Security and Compliance
Voice agents handling patient information must comply with healthcare privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. This ensures that patient data is collected, stored, and shared securely and in accordance with legal requirements.
All audio recordings and transcripts should be encrypted during transmission and storage. Identifiable patient information must be anonymized whenever possible, and access should be restricted to authorized personnel only to maintain confidentiality.
Deploying AI Voice Agents in Healthcare: A Practical Roadmap
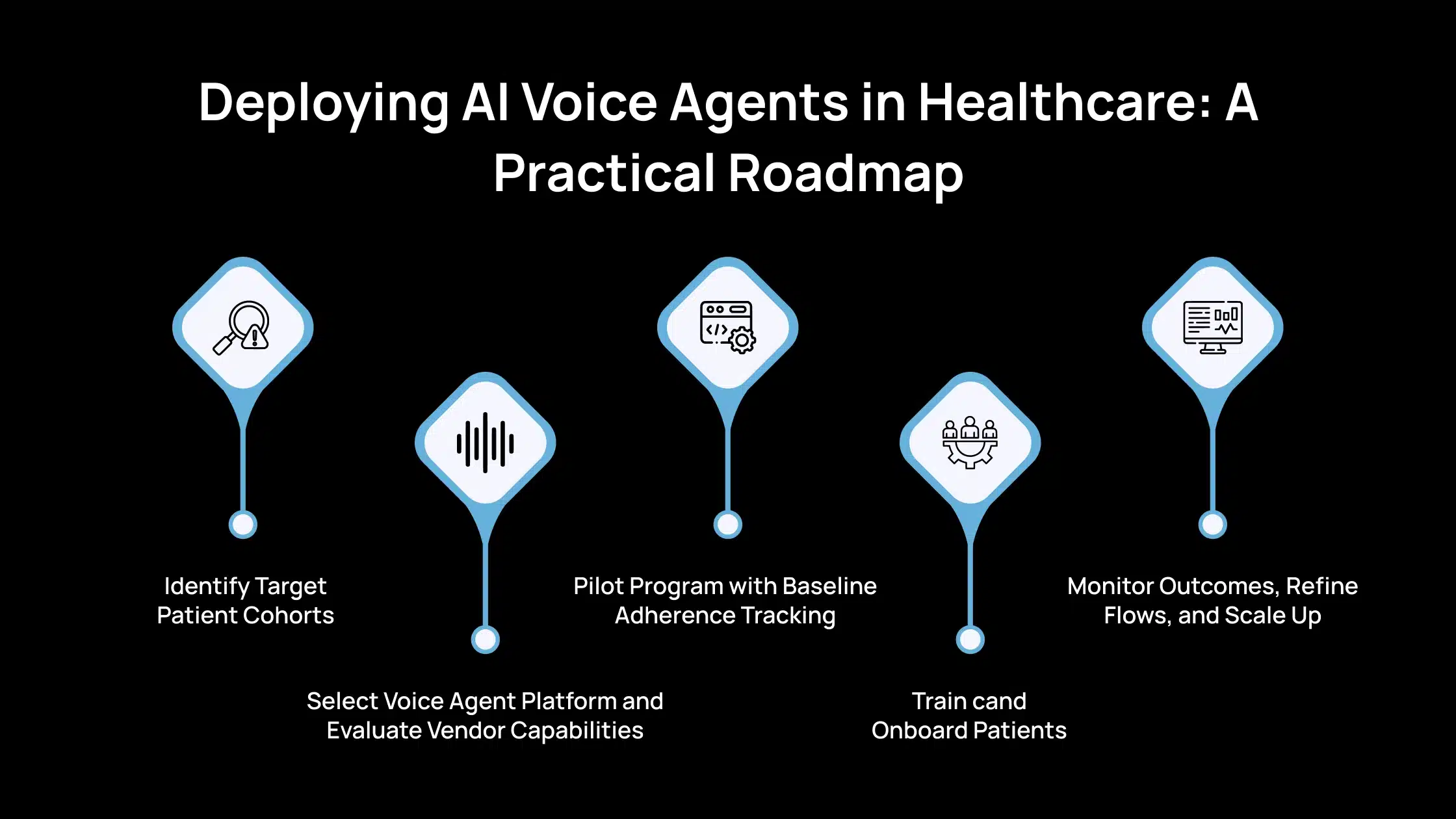
Here’s what your healthcare organization must do to successfully implement AI voice agents for medication management, from planning to scale-up.
1. Identify Target Patient Cohorts
Start by selecting the patient groups that are most likely to benefit from AI voice agent support. Examples include patients with chronic illnesses, those on multiple medications (polypharmacy), or individuals with a history of missed doses. Focusing on high-risk groups helps maximize clinical and financial impact.
2. Select Voice Agent Platform and Evaluate Vendor Capabilities
Assess available solutions based on critical factors, including speech recognition accuracy, multi-language support, data privacy compliance (HIPAA/GDPR), integration options with EHR and pharmacy systems, and scalability. Select a platform that aligns with your IT infrastructure and the needs of your patient population.
3. Pilot Program with Baseline Adherence Tracking
Conduct a small-scale pilot before rolling out the complete solution. Collect baseline adherence data to measure improvement after implementation. The pilot should include a diverse sample of patients to test usability, technical reliability, and patient engagement across demographics.
4. Train Staff and Onboard Patients
Educate clinicians, pharmacists, and support staff on how the voice agent works, what data it collects, and how to respond to alerts or escalations. Provide patients with clear instructions on how to interact with the agent, respond to reminders, and report side effects.
5. Monitor Outcomes, Refine Flows, and Scale Up
Track key metrics such as adherence rates, missed-dose alerts, and patient satisfaction. Analyze data to identify areas for improvement and adjust reminder frequency, language, or escalation protocols as needed. Once the process is optimized, expand the program to larger patient populations and additional therapeutic areas.
Why Healthcare Organizations Should Choose Avahi AI Voice Agents?

Managing patient communication efficiently is critical for healthcare providers. Avahi AI Voice Agents provide a dependable and scalable solution designed to handle the high volume and complexity of routine patient calls, freeing up clinical teams to focus on delivering care.
1. Designed Specifically for Healthcare Needs
Avahi’s AI voice agents are built with healthcare workflows in mind. From appointment scheduling to handling insurance queries, the system is trained to manage the various types of interactions that occur daily in medical, dental, specialty, and urgent care settings.
2. Real-Time Call Management and Scheduling
The system can book, reschedule, or cancel appointments instantly, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring patients receive timely assistance without waiting on hold.
3. Reduces No-Shows with Automated Follow-Ups
By sending out reminders and follow-up messages, the AI agent helps reduce missed appointments, improving patient attendance and maintaining a consistent schedule for providers.
4. Prioritizes Urgent Cases
The voice agent identifies and escalates urgent issues directly to human staff, ensuring that critical patient needs are not delayed or overlooked.
5. Alleviates Staff Workload and Strain
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, such as answering routine questions and verifying referrals, Avahi reduces the burden on front-desk teams, allowing them to focus on higher-priority tasks.
6. Supports High-Demand Care Environments
Whether it’s a busy dental office, behavioral health clinic, or urgent care center, Avahi adapts to fast-paced environments where timely and accurate communication is essential.
Avahi AI Healthcare Voice Agents are strategic enablers that help healthcare providers deliver better patient experiences while managing operations more efficiently.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Utilize Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are AI voice agents for medication management?
AI voice agents for medication management are intelligent systems that use speech recognition and natural language processing to remind patients about their medications, confirm adherence, and provide educational support. These agents help bridge the gap between patients and healthcare providers by offering real-time, two-way communication.
2. How do AI voice agents improve medication adherence?
AI voice agents for medication management enhance adherence by delivering personalized reminders, requesting confirmation when a dose is taken, and escalating alerts if multiple doses are missed. They adapt to patient routines, provide clear instructions, and reduce the chances of missed or incorrect doses.
3. Are AI voice agents suitable for elderly patients or those with low tech literacy?
Yes. AI voice agents for medication management are designed to be intuitive and straightforward, using natural conversation rather than complex app interfaces. They are particularly effective for elderly patients, as they can be used with regular phones or smart speakers, making them accessible without the need for smartphones.
4. Can AI voice agents integrate with existing healthcare systems?
Most AI voice agents for medication management can integrate with electronic health records (EHRs), pharmacy systems, and remote monitoring platforms. This ensures that medication schedules are accurate and up-to-date, and allows providers to receive timely alerts about adherence issues.
5. Is patient data safe when using AI voice agents for medication management?
Yes. AI voice agents for medication management adhere to strict data security protocols, including encryption, anonymization, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR. This ensures that sensitive patient information remains secure while enabling adequate adherence support.