One missed call could mean one missed life-saving appointment.
In the current state of healthcare, every patient interaction counts, and many of them begin with a phone call.
Healthcare continues to bear the highest cost per data breach of any industry. In 2024, the average cost of a healthcare data breach was approximately $9.77 million,
To address the communication overload and growing security threats, many clinics and hospitals are turning to AI voice agents. These intelligent systems can automate routine tasks, such as appointment scheduling, follow-up reminders, and insurance inquiries, thereby freeing up staff time and enhancing patient access. But with increased automation comes increased responsibility, especially when sensitive patient data is involved.
This is where HIPAA compliance becomes critical. Without proper safeguards, AI voice agents could unintentionally expose protected health information (PHI), putting both patients and healthcare providers at risk.
In this blog, we explore why HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents are crucial for delivering secure, efficient, and patient-centered care. We’ll break down the risks, highlight the required safeguards, and show how platforms like Avahi are setting the standard in healthcare voice automation, ensuring every call is secure and every patient protected.
What Is HIPAA and Why Does It Matter for Voice AI?
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a U.S. federal law that was enacted in 1996. It establishes national standards to protect individuals’ medical records and other personal health information. Three essential components of HIPAA directly apply to the use of AI voice agents in healthcare:
1. Privacy Rule
The Privacy Rule regulates how covered entities, like hospitals, clinics, and insurers, can use and disclose patients’ protected health information (PHI). It ensures that patients have control over their personal health data, including the right to access and request corrections.
AI voice agents that handle appointment scheduling, billing inquiries, or health-related conversations must be configured to limit access to PHI and ensure that the data is only used for authorized purposes.
2. Security Rule
The Security Rule sets the standards for safeguarding electronic protected health information (ePHI). It requires administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
Voice AI systems that store or transmit audio recordings, transcripts, or interaction logs must encrypt the data, control access, and maintain secure transmission channels.
3. Breach Notification Rule
The Breach Notification Rule requires healthcare entities to notify affected individuals, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and, in some cases, the media if there is a breach involving unsecured PHI.
If an AI voice system is compromised, such as by unauthorized access to audio files, prompt breach reporting is required under this rule.
Understanding Protected Health Information (PHI): What AI Voice Agents Must Protect
Protected Health Information (PHI) refers to any information about a patient’s health status, healthcare services, or payment history that can be linked to an individual.
In the context of AI voice agents, PHI may include:
- Patient names and dates of birth are spoken during calls.
- Symptoms or medical conditions were discussed verbally.
- Appointment details and medications mentioned.
- Insurance or billing information
- Audio recordings or transcriptions of calls
- Call metadata (e.g., time stamps, caller identity)
Any system that collects, stores, or transmits this type of information must meet HIPAA’s requirements to ensure data confidentiality and security.
Risks of Non‑Compliance
Failing to comply with HIPAA regulations carries serious consequences for healthcare providers and any vendors handling PHI. These include:
Financial Penalties
Civil fines range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with an annual maximum of $1.5 million per type of violation. Fines are scaled based on the severity of the issue and whether it was caused by willful neglect.
Criminal Charges
In cases of intentional misuse or gross negligence, criminal charges may be filed. These can lead to fines of up to $250,000 and imprisonment for up to 10 years, mainly when PHI is obtained under pretenses or used for personal gain.
Reputational Damage
HIPAA violations are often publicized, especially in cases involving significant breaches. This can erode public trust and damage a healthcare provider’s reputation, leading to patient attrition and lost partnerships.
Operational Impact
Breach investigations and legal processes can disrupt day-to-day operations, result in the temporary suspension of systems, and create long-term operational strain due to increased oversight and mandatory audits.
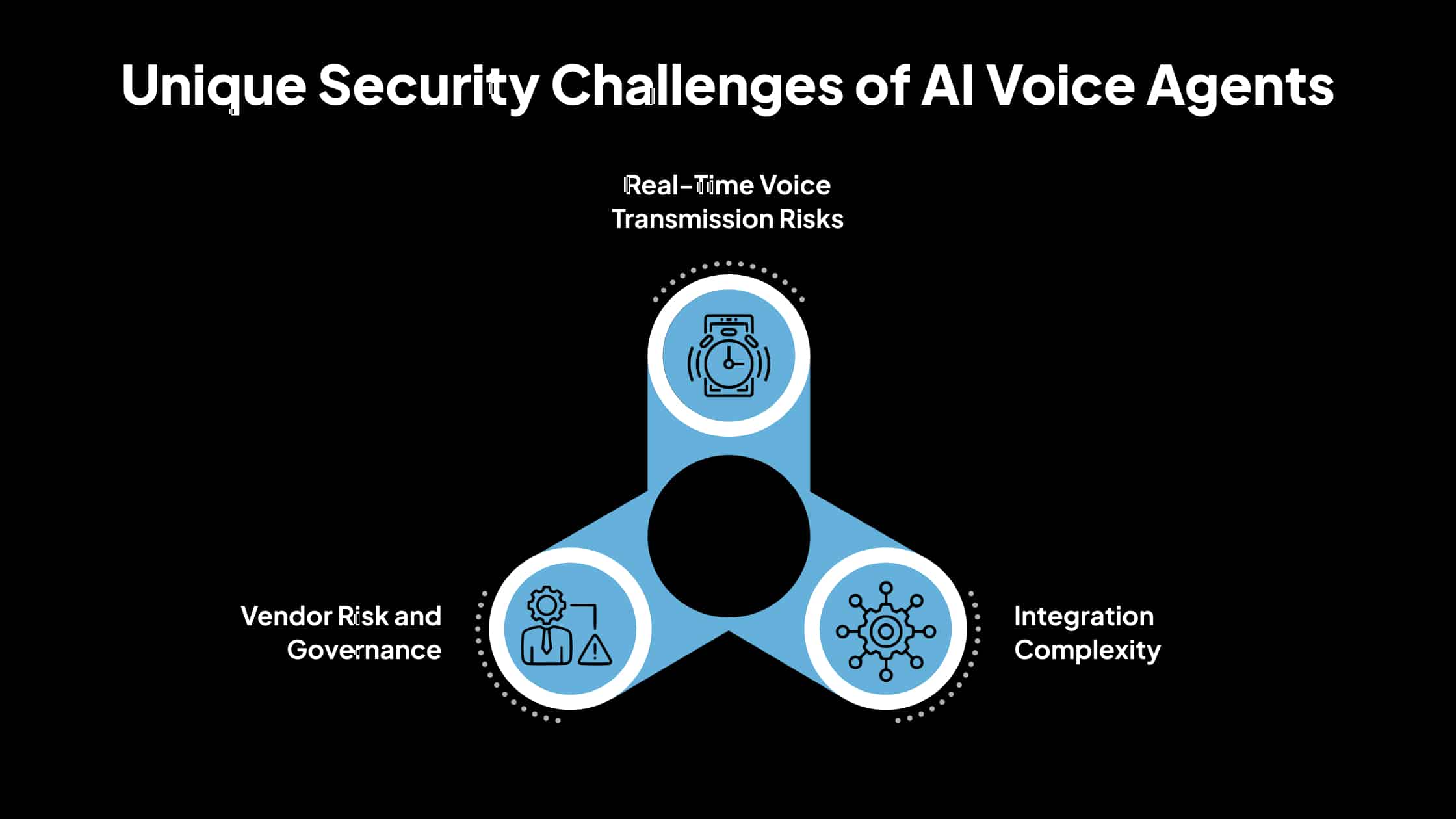
Unique Security Challenges of AI Voice Agents
AI voice agents can improve efficiency in healthcare, but they also introduce specific security concerns. Understanding these challenges is crucial for ensuring compliance with HIPAA and safeguarding patient data.
1. Real-Time Voice Transmission Risks
When patients interact with voice agents, their information is captured and transmitted instantly. This real-time exchange makes the data vulnerable at several points: during voice capture by microphones, during transmission over networks, and when stored temporarily or permanently.
If proper safeguards such as encryption and secure channels are not in place, sensitive patient information can be intercepted, altered, or accessed by unauthorized parties.
2. Integration Complexity
AI voice agents rarely operate in isolation. They often connect with electronic health records (EHRs), customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and telephony platforms. Each integration point increases the potential for security weaknesses.
For example, an improperly configured interface between a voice agent and an EHR could expose patient details or create unauthorized access pathways. The more systems that interact with the agent, the more important it becomes to ensure every connection is secure and continuously monitored.
3. Vendor Risk and Governance
Many healthcare organizations rely on third-party vendors to deploy and maintain AI voice solutions. This creates additional responsibilities to ensure compliance. Under HIPAA, vendors handling protected health information (PHI) are considered business associates and must sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA).
The BAA outlines its obligations to safeguard PHI and specifies accountability in case of a breach. Without proper governance and oversight, organizations risk non-compliance if vendors fail to meet HIPAA standards. Regular audits, vendor due diligence, and clearly defined responsibilities are essential to reduce this risk.
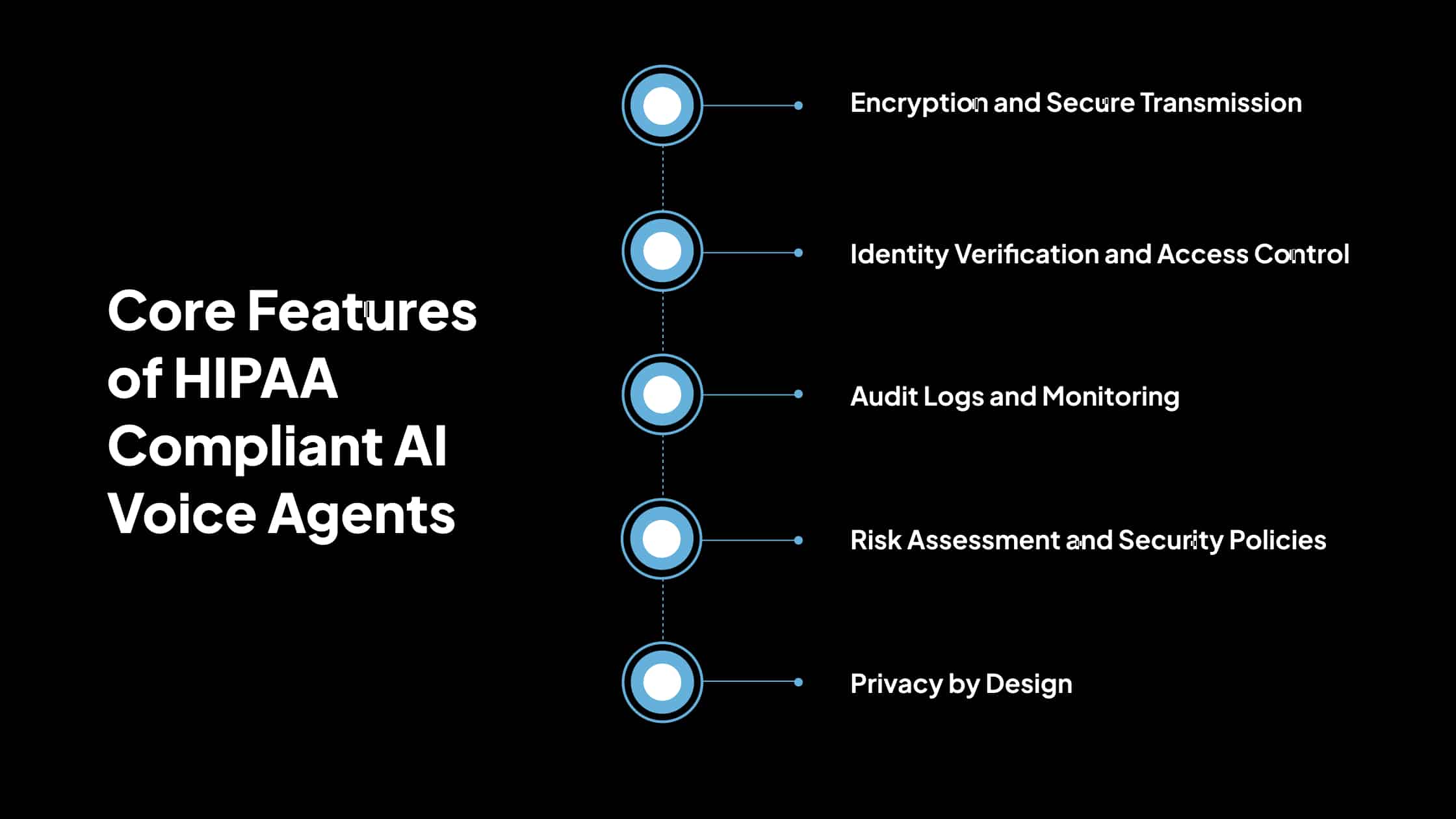
Core Features of HIPAA Compliant AI Voice Agents
To protect patient data and ensure regulatory compliance, AI voice agents used in healthcare must be designed with specific technical and administrative safeguards in place. Below are the essential features that define HIPAA-compliant voice agent systems.
1. Encryption and Secure Transmission
AI voice agents must use strong encryption protocols to protect data during transmission and storage. All voice data, whether it’s live audio, recorded conversations, or transcriptions, must be encrypted in transit (e.g., using TLS 1.2 or higher) and at rest (e.g., using AES-256 encryption).
This ensures that even if the data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it cannot be read or misused. Secure communication channels must also be maintained between the AI agent and other systems, such as EHRs and telephony platforms.
2. Identity Verification and Access Control
Controlling who can access the voice agent system is essential for preventing unauthorized use.
HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents should include strong identity verification methods such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) for administrators and authorized users.
Role-based access control (RBAC) must be implemented to ensure users can only view or modify data necessary for their role. In patient-facing scenarios, the agent may also need to verify the caller’s identity before discussing PHI.
3. Audit Logs and Monitoring
Tracking system activity is necessary to detect, investigate, and respond to potential security issues. Compliant systems must maintain detailed audit trails of all voice agent interactions, including access attempts, data retrievals, changes, and transmissions.
These logs should be immutable, time-stamped, and regularly reviewed. Audit logs also play a critical role during internal reviews and external investigations following a suspected breach.
4. Risk Assessment and Security Policies
Healthcare organizations and vendors must regularly evaluate system risks and adjust policies accordingly.HIPAA requires routine Security Risk Assessments (SRAs) to identify potential threats and weaknesses in systems that handle PHI.
Voice agent vendors and healthcare providers must document and implement clear security policies that cover data handling, user access, system updates, and incident response. Risk mitigation plans must be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in technology or regulation.
5. Privacy by Design
The system must be built with patient privacy as a foundational requirement, not as an afterthought. HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents should minimize data collection, limit data retention, and obtain explicit consent where necessary. Features like anonymization of non-essential identifiers, clear consent prompts before sharing sensitive details, and opt-out options for patients contribute to stronger compliance and patient trust. All user-facing interactions must clearly state how data will be used and stored.
Real-World Benefits of HIPAA Compliant AI Voice Agents
Below are the benefits of using HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents in healthcare settings, which ensure secure communication, improved efficiency, and enhanced patient care.
1. Improved Patient Experience
Patients often struggle with long wait times and limited access to healthcare staff. AI voice agents help solve this by providing 24/7 assistance. For example, a HIPAA-compliant voice assistant can automatically handle appointment bookings, prescription refill requests, and common inquiries, without involving a human agent.
According to a report by Accenture, 64% of patients said they would be willing to use AI tools for health-related questions if their data is kept secure. This reduces patient frustration and enables faster responses, especially during high call volumes or after clinic hours.
2. Increased Operational Efficiency
Healthcare providers save time and resources by automating routine tasks. Healthcare facilities using AI voice agents have reduced call handling time by up to 40% and have successfully redirected over 60% of non-critical inquiries to automated systems. This allows front desk staff and medical professionals to focus more on critical patient care, rather than administrative follow-ups.
Voice agents can also integrate with calendars, patient records, and billing systems—automating confirmations, reminders, and payment-related queries.
3. Enhanced Security and Risk Management
By adhering to HIPAA standards, voice agents significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and penalties for non-compliance. Ensuring encryption, access control, and audit logging reduces the chances of unauthorized access and helps healthcare providers avoid these severe financial consequences.
Additionally, detailed audit logs and secure data handling protocols facilitate a prompt response to potential threats and enable compliance demonstration during audits.
4. Greater Patient Trust and Transparency
When patients know secure systems protect their data, they are more likely to engage and disclose accurate information. Studies have shown that patients are 2.5 times more likely to share sensitive information with digital tools when security protocols are made visible upfront.
By clearly informing patients that the AI agent is HIPAA-compliant, uses encrypted communication, and does not share their data without consent, healthcare providers can strengthen the relationship between patient and technology.
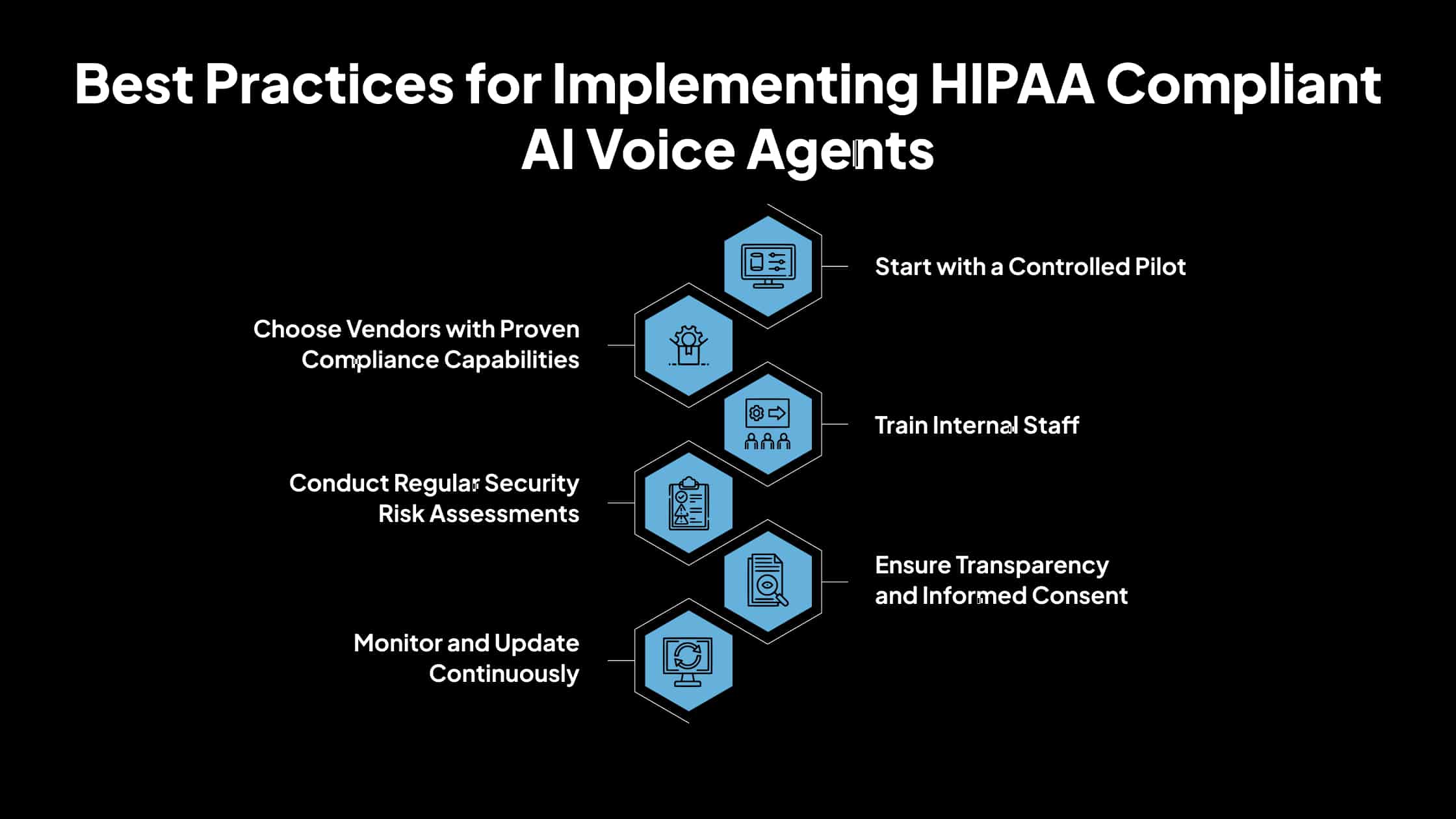
Best Practices for Implementing HIPAA Compliant AI Voice Agents
Deploying AI voice agents in a healthcare setting requires more than just choosing the right software; it involves strategic planning, regulatory diligence, and continuous monitoring. Below are the best practices organizations should follow to ensure safe and effective implementation.
1. Start with a Controlled Pilot
Before rolling out AI voice agents across all operations, start with a small-scale pilot focused on a single use case.
For example, a clinic might deploy a voice assistant to handle only appointment scheduling. This limited use helps the team test system accuracy, monitor data handling, and troubleshoot errors without risking large-scale disruption. Pilots provide a foundation for feedback and compliance evaluation before full deployment.
2. Choose Vendors with Proven Compliance Capabilities
Third-party vendors play a major role in data handling and must demonstrate their ability to meet HIPAA requirements. Before entering into a partnership, healthcare organizations should request:
- Proof of HIPAA training for the vendor’s staff
- Documentation of technical safeguards (e.g., encryption protocols, access controls)
- A signed Business Associate Agreement (BAA)
- Incident response policies and historical breach handling reports
3. Train Internal Staff
Even with advanced technology, human error remains a common cause of HIPAA violations.
Staff must be trained on how to use the AI voice agent securely, recognizing phishing or social engineering attempts, incident reporting procedures, and proper verification steps before discussing PHI over the phone. Training should be repeated periodically and updated with new security protocols.
4. Conduct Regular Security Risk Assessments
HIPAA requires ongoing risk assessments to identify and fix vulnerabilities in systems that process protected health information.
Risk assessments should cover data transmission methods, storage practices, access permissions, backup and recovery plans, and integration points with other systems (e.g., EHR, CRM). Utilize tools such as penetration testing and simulated breach drills to validate your defenses.
5. Ensure Transparency and Informed Consent
Patients must be aware that they are interacting with an AI system and must understand how their data will be used. Always inform the caller at the beginning of the interaction that they are speaking with a voice assistant.
If the conversation involves collecting or sharing PHI, ensure explicit consent is received and logged. Clear, concise privacy statements must be provided when applicable.
6. Monitor and Update Continuously
HIPAA compliance is not a one-time task; it requires ongoing monitoring and adaptation.
Stay informed about updates to HIPAA regulations, new cybersecurity threats, and industry best practices to ensure compliance and protection. Audit system logs regularly, track performance metrics (such as call completion rates and error reports), and patch any identified vulnerabilities.
AI Voice Agents in Healthcare: Compliance Trends to Watch
As AI voice agents become more embedded in healthcare, regulatory demands are accelerating. Here’s what organizations need to know to stay compliant and future-ready.
1. Heightened HIPAA Enforcement and Updated Security Standards
Recent cybersecurity threats are prompting regulators to act. In 2024, ransomware incidents surged by 264%, pushing the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) to adopt stricter enforcement measures.
This includes in-depth Security Risk Analyses (SRAs) and a proposed modernization of the HIPAA Security Rule, mandating encryption, multifactor authentication, patching, and social engineering training. Healthcare organizations must proactively update their security controls, conduct thorough risk assessments, and train staff to defend against evolving threats.
2. Responsible Use of PHI and Scrutiny of Emerging Technologies
AI tools, voice agents included, are under growing scrutiny. Regulators are increasingly focused on how Protected Health Information (PHI) is used, especially by AI systems and tracking technologies. Even deviations in authenticated web tracking are coming under fire.
Healthcare providers and vendors must ensure that AI systems use PHI only for authorized purposes, carefully audit third-party tools, and enforce strict limits on data usage and disclosure.
3. State-Level Privacy Laws Add Complexity
Beyond HIPAA, states are enacting their own data protection laws. For instance, California’s CMIA, Washington’s My Health My Data Act, and Florida’s Digital Bill of Rights introduce stricter standards and penalties for misuse of health data.
Healthcare organizations operating across state lines must map their technology stacks, audit vendor compliance, and adapt privacy notices to navigate these overlapping laws effectively.
4. AI-Specific Compliance Developments on the Horizon
Emerging frameworks are beginning to define how AI systems, particularly voice agents, should comply with HIPAA. Academic research suggests new methods, such as Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC), hybrid PHI sanitization (combining pattern detection and AI models), and immutable audit logs, for achieving context-aware compliance. Expect future regulation or formal guidelines that require AI systems to embed such advanced controls to ensure PHI isn’t misused or exposed.
5. Expansion of Sensitive Data Protections
In response to societal shifts and new legal decisions, HIPAA’s reach is expanding into sensitive areas like reproductive health.
A final rule issued in December 2024 restricts the use of reproductive health information in legal or administrative investigations, though its legal status is under challenge. Providers must update their privacy policies and internal procedures accordingly, while also monitoring ongoing legal developments to ensure compliance.
Avahi AI Healthcare Voice Agents: Enhancing Patient Engagement Through Smarter Call Handling
Managing incoming and missed patient calls remains one of the most time-consuming and costly aspects of healthcare operations. Unanswered calls can result in missed appointments, reduced patient satisfaction, and added pressure on administrative staff. Avahi AI Healthcare Voice Agents are purpose-built to solve this problem, automating routine interactions so that healthcare teams can focus on delivering high-quality care.
Avahi’s voice agents are tailored for clinics, hospitals, and private practices seeking scalable support for patient communication. They are especially effective in high-traffic specialties such as:
- Primary care and urgent care
- Dental and orthodontic practices
- Behavioral health services
- Specialty care clinics
In these settings, where every call can influence the quality and timeliness of care, automation helps maintain continuity, responsiveness, and professionalism.
What Avahi Agents Can Do
Explicitly trained for healthcare scenarios, Avahi’s AI voice system can handle a wide range of patient communications, including:
- Answering routine questions related to office hours, locations, or services offered
- Booking, rescheduling, and canceling appointments in real time through integration with your scheduling system
- Sending automated reminders and follow-ups to reduce patient no-show rates
- Identifying and escalating urgent calls to the appropriate staff for immediate response
- Managing insurance, referral, and prescription-related inquiries efficiently
This smart call handling reduces average response times, keeps appointment calendars full, and ensures urgent needs don’t fall through the cracks. Avahi is deployed on AWS’s healthcare-ready infrastructure, ensuring all data is managed according to top industry standards. The platform is HIPAA-compliant, SOC 2 compliant, and GDPR-compliant.
It integrates smoothly with existing EHRs and practice management tools and can scale across multiple clinics or locations without disrupting operations.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents?
HIPAA-compliant AI voice agents are automated voice systems designed to handle patient communications while ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations. They protect sensitive health information by utilizing encryption, access controls, audit logs, and secure data handling processes during tasks such as scheduling, billing, and patient inquiries.
2. How do AI voice agents ensure HIPAA compliance in healthcare?
AI voice agents ensure HIPAA compliance by encrypting voice data, verifying user identity, maintaining access controls, recording audit trails, and following strict privacy policies. They are also supported by Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with healthcare providers to clarify compliance responsibilities.
3. What patient data is considered PHI in AI voice interactions?
In AI voice agent interactions, PHI includes patient names, birthdates, medical symptoms, appointment details, insurance information, call recordings, transcriptions, and call metadata. Any system handling this data must comply with HIPAA’s privacy and security rules.
4. Why is HIPAA compliance substantial for AI voice agents in healthcare?
HIPAA compliance is essential because it protects patient privacy, reduces the risk of costly data breaches, and ensures legal accountability. Non-compliant AI voice systems can expose sensitive data, resulting in fines, lawsuits, and a loss of patient trust.
5. What are the penalties for using non-HIPAA-compliant AI tools in healthcare?
Penalties include civil fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, criminal charges with penalties of up to $250,000, and potential prison sentences of up to 10 years, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. Regulatory audits and patient lawsuits can further strain resources.