TL;DR
|
Hiring teams are drowning in volume and losing good candidates in the gaps.
The global average time to hire is about 44 days, meaning roles stay open for weeks while recruiters sift, screen, and schedule interviews. At the same time, the best candidates are usually off the market in roughly 10 days, so slow early-stage screening directly costs you talent.
This is the problem an AI recruiter agent is built to solve. It handles the high-volume, repeatable steps between a job post and an interview, sorting applicants, running first screens, answering candidate questions, and scheduling so that recruiters can focus on judgment calls instead of admin. The goal is to shorten the time from posting to shortlist without cutting corners on fit or fairness.
This blog will explore how an AI recruiter agent moves hiring from job post to interview, step by step, and what that means for speed, fit, and candidate experience.
AI Recruiter Agent Explained for Modern Hiring Teams
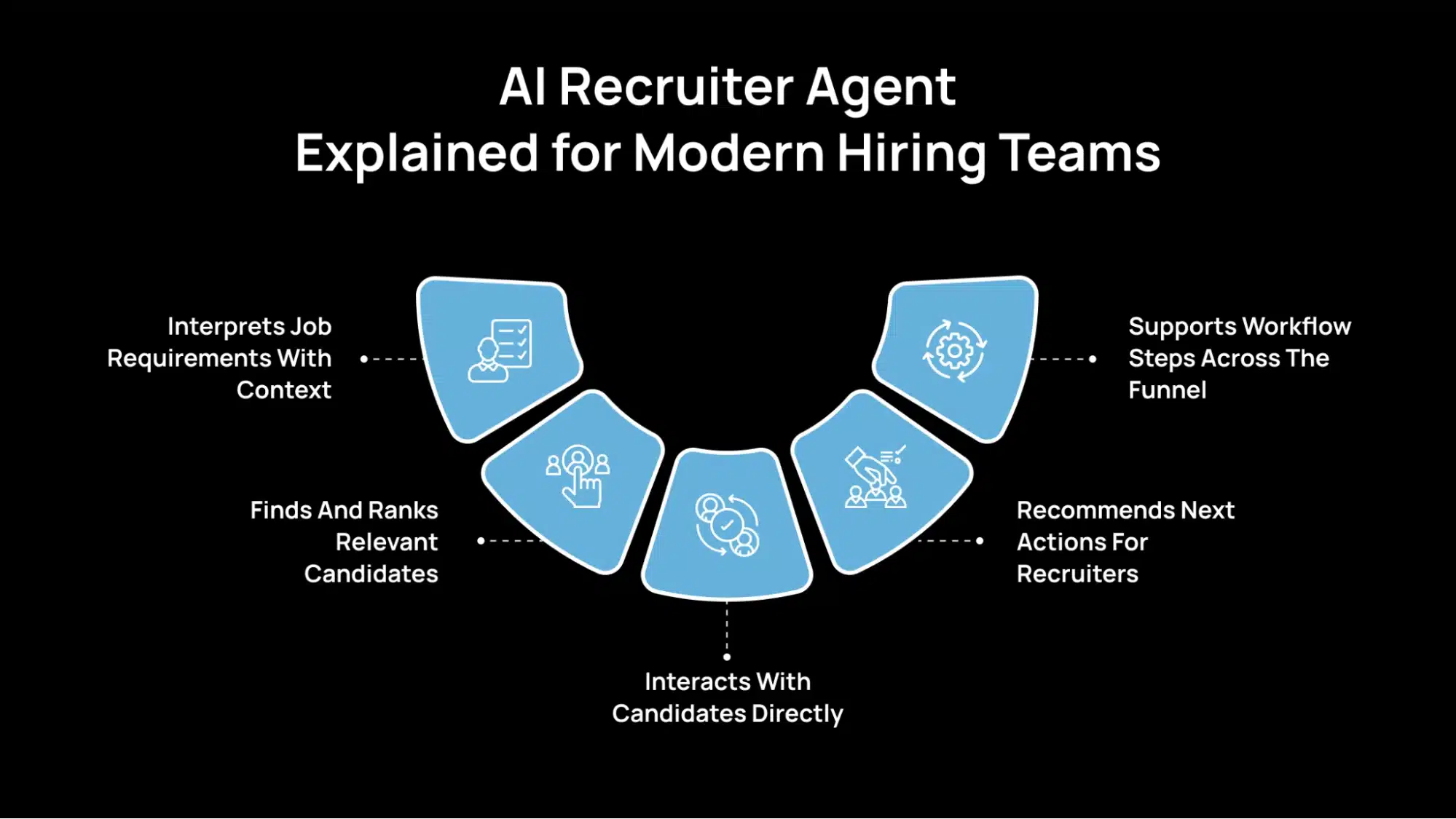
An AI recruiter agent is a hiring-focused AI system that does the work, not just stores information. Unlike a standard ATS, which primarily stores resumes and filters them by predefined rules, this agent can read a job requirement, understand its meaning, and act on it. It helps move candidates through the pipeline with less manual effort from your side. Here’s what that means in practice:
Interprets Job Requirements With Context
The agent reads the whole job post, not just keywords. It separates must-have from nice-to-have skills and recognizes related skills that still fit, so strong candidates are not missed due to different wording.
Finds And Ranks Relevant Candidates
It scans resumes and profiles, pulls out key details like skills, experience level, and role history, then ranks candidates against your criteria. You set the rules; the agent sorts at scale.
Interacts With Candidates Directly
The agent can contact candidates, answer basic questions, collect missing information, and guide them to the next step through chat or voice. This reduces delays and keeps candidates engaged.
Recommends Next Actions For Recruiters
After screening, it generates a shortlist with clear reasons for each match and flags areas that may need follow-up. This gives recruiters a faster, more structured decision starting point.
Supports Workflow Steps Across The Funnel
It can handle scheduling, reminders, and status updates once a candidate is ready to move forward. This eliminates manual coordination and helps keep the process on track.
How Does an AI Recruiter Agent Differ From ATS and Basic Automation?
| Aspect | ATS (Applicant Tracking System) | Basic automation (rule-based tools) | AI recruiter agent |
| Primary role | Stores, tracks, and organizes applicants. | Automates single tasks like emails or status updates. | Runs multiple hiring steps end-to-end within defined limits. |
| How it works | Uses fixed workflows and filters chosen by the recruiter. | Uses “if-this-then-that” rules set in advance. | Uses AI models to understand context and make recommendations. |
| Matching approach | Mostly keyword and rule-based filtering. | No matching logic; only executes preset actions. | Reads job needs and resumes semantically to find skill fit beyond keywords. |
| Decision support | Shows pipeline status and filtered lists. | Doesn’t support decisions; only reduces manual steps. | Ranks candidates, explains fit, and flags gaps or risks for review. |
| Candidate interaction | Limited; it often depends on the recruiter’s actions. | Sends templated messages triggered by rules. | Holds two-way chat or voice conversations to screen, clarify, and guide candidates. |
| Proactive actions | Mostly passive; waits for recruiter input. | Acts only when a preset trigger occurs. | Proactively sources, follows up, and moves candidates forward. |
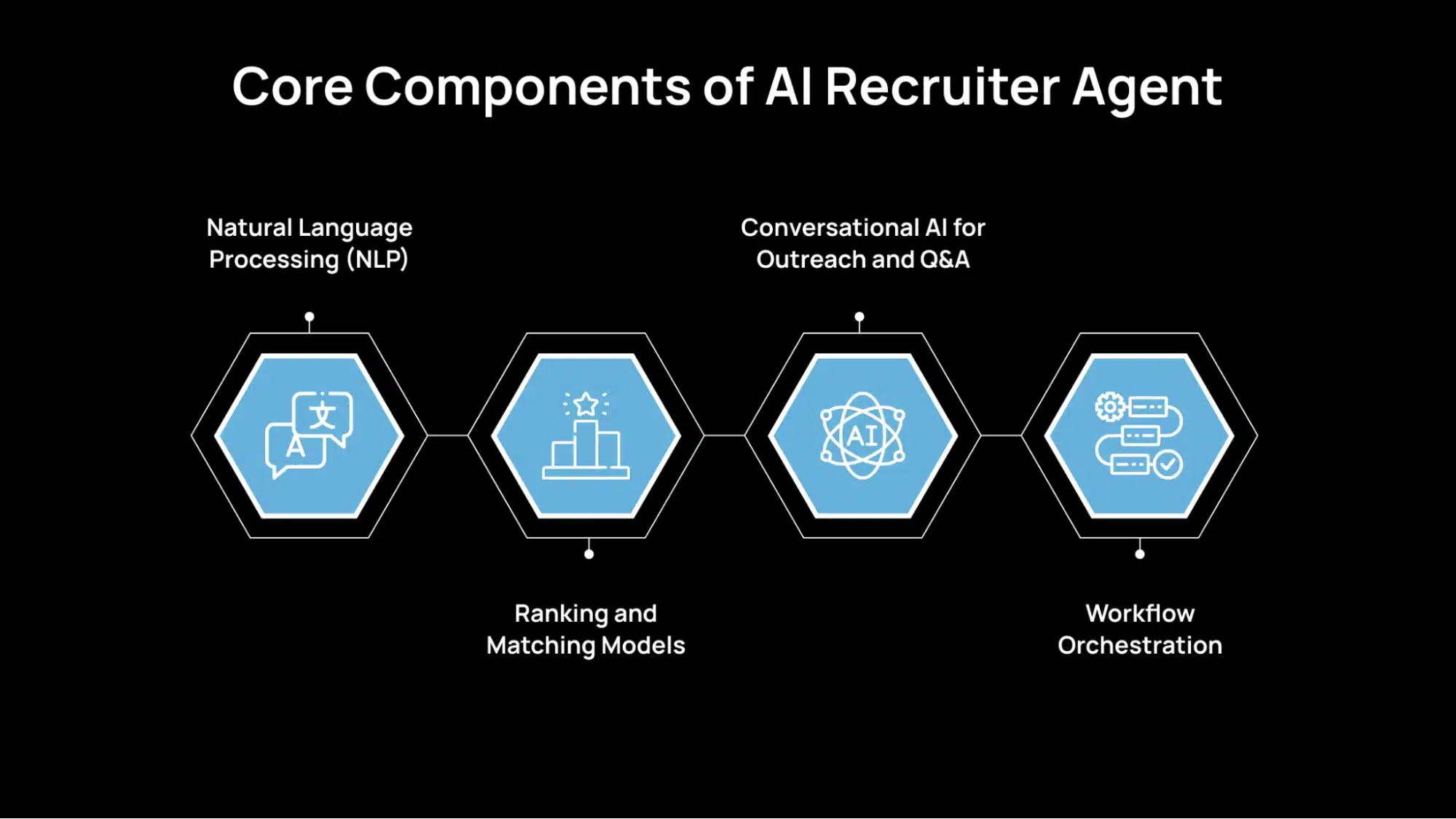
Core Components of AI Recruiter Agent
An AI recruiter agent works because a few specific technologies come together to handle hiring tasks accurately and consistently.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP helps the agent read job descriptions and resumes the way a recruiter would, but in a more robust way. It pulls out skills, experience, role scope, and context, even when the wording is different.
For example, it can recognize that “client onboarding” and “customer implementation” may describe similar work. This reduces missed matches caused by simple keyword gaps and improves early screening accuracy.
Ranking and Matching Models
These models compare a candidate profile to the job requirements and calculate a fit score or rank. They consider factors such as skill overlap, seniority, industry relevance, role progression, and, sometimes, stated preferences.
The output is not a final decision. It is a prioritized shortlist with clear signals on why each candidate appears relevant, so recruiters spend time on the right profiles first.
Conversational AI for Outreach and Q&A
Conversational AI enables the agent to interact with candidates via chat or voice. It can send tailored outreach, answer common questions about the role, collect missing details, and run basic screening conversations.
This keeps candidates engaged without waiting for the recruiter’s availability and ensures the agent gathers structured information before passing the candidate forward.
Workflow Orchestration
Workflow orchestration is the layer that connects actions into a usable hiring flow. It decides which step to take next based on rules and candidate responses, such as moving a qualified person to a screening call, sending a reminder if they do not respond, or proposing interview slots once they clear the first stage. This keeps the pipeline moving smoothly and reduces manual follow-ups and coordination work.
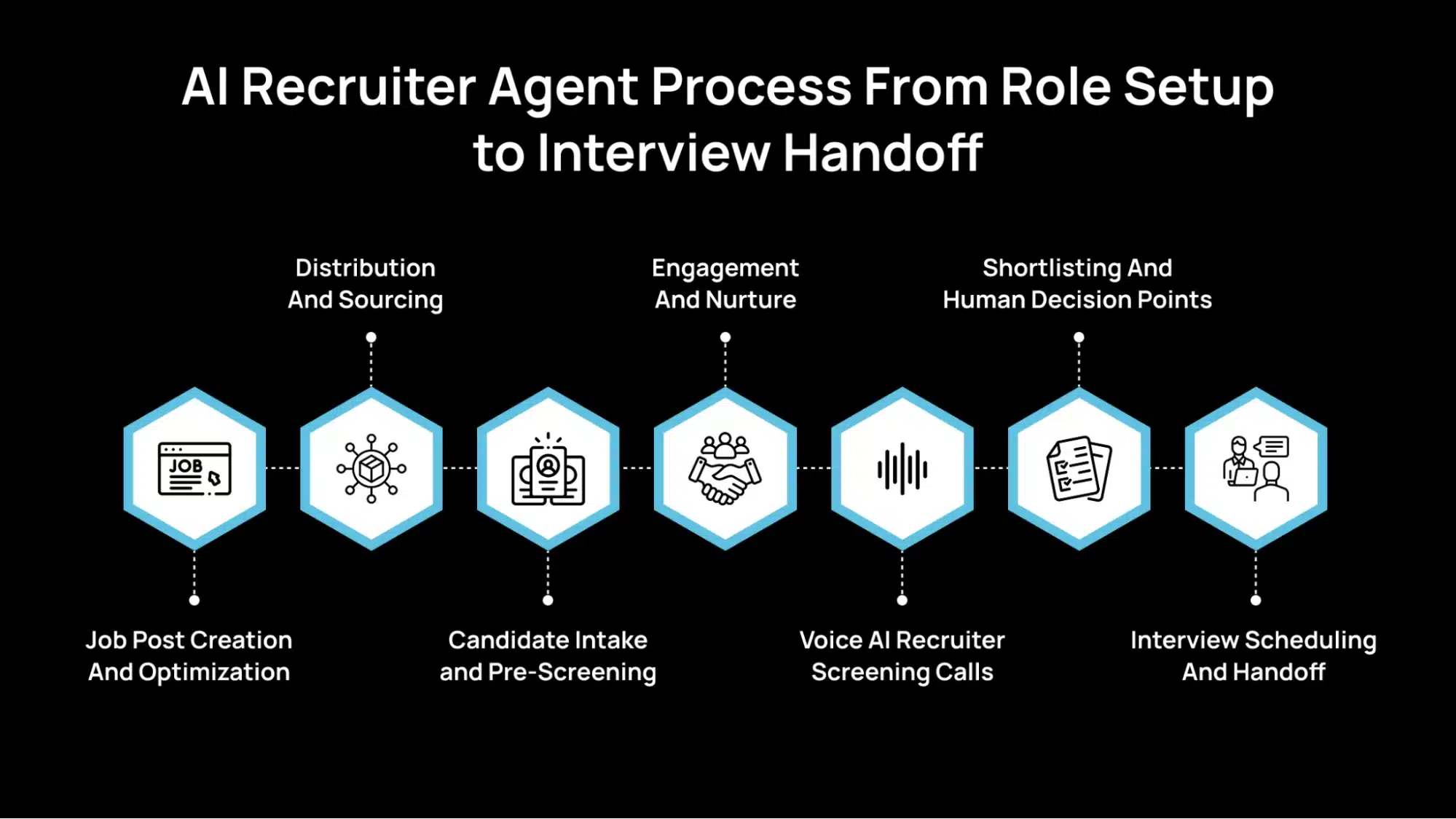
AI Recruiter Agent Process From Role Setup to Interview Handoff
Below is how an AI recruiter agent typically moves a role from “we need to hire” to “candidate is ready for interview,” :
Step 1: Job Post Creation And Optimization
You start with raw inputs from the hiring manager, role goals, key responsibilities, must-have skills, and team context.
- The agent turns that into a structured, specific, and easy-to-understand job description.
- It also checks for wording that may unintentionally narrow the talent pool, such as unclear requirements or overly restrictive phrasing, and suggests cleaner alternatives.
- Once the basics are in place, the agent identifies the skill set implied by the role. It recommends skills that often appear in strong candidates and separates essential requirements from optional requirements.
- It also adjusts seniority cues, for example, whether the role is closer to a mid-level executor or a strategic leader. This helps you avoid unrealistic job posts and improves match quality later.
Step 2: Distribution And Sourcing
After the post is ready, the agent can push it to selected job boards, career pages, and talent communities.
- It also checks internal databases, past applicants, silver-medalist candidates, and employee referral pools, so you reuse warm leads before starting from scratch.
- Beyond inbound applicants, the agent runs semantic searches to find passive candidates who may be a good fit even if their titles differ.
It looks for transferable skills and adjacent roles, for example, matching a “customer success manager” profile to an “implementation lead” role when there is substantial overlap. This expands the pool without reducing relevance.
Step 3: Candidate Intake and Pre-Screening
As applications arrive, the agent reads resumes and profiles and pulls out structured details.
- It identifies core skills, years of experience in each area, project types, industry exposure, and role progression. This is the same information a recruiter scans for, but done consistently across every applicant.
- Next, the agent compares each profile to the job requirements and assigns a fit score or ranking.
- Importantly, it records why the candidate scored the way they did, such as substantial skill overlap, relevant domain experience, or gaps in a key requirement. This gives recruiters a quick, explainable view instead of a black-box grade.
For clear deal-breakers (like missing a required license or location constraint), the agent can auto-reject based on rules you define. For borderline cases, it routes candidates to recruiters rather than automatically rejecting them.
Step 4: Engagement And Nurture
Qualified candidates receive tailored outreach that references the role and their relevant experience. The agent uses job context and candidate signals to keep messages aligned with why they might be a fit. This improves response rates compared to generic templates.
- Candidates can ask questions and share missing details through chat.
- The agent handles common queries (role scope, shifts, location, and salary range, if provided) and collects inputs such as notice period and availability. This keeps the momentum without requiring the recruiter to spend time on every interaction.
- If a candidate doesn’t respond or complete a step, the agent sends short reminders at set intervals. This reduces early-stage drop-offs, especially in high-volume roles where delays usually cost you strong applicants.
Step 5: Voice AI Recruiter Screening Calls
For roles that need a phone screen, the voice AI recruiter runs the first-round call. It asks a fixed set of questions tied to your screening rubric, captures responses, and tags signals such as work eligibility, role interest, salary expectations, and basic communication fit. The questions remain consistent across candidates, improving comparability.
Because the agent is always available, multiple candidates can complete screening in parallel.
- Candidates pick a time that works for them, and you avoid waiting days just to run first calls. This is especially useful when volume is high, and speed affects who stays in the process.
- The agent scores candidates on clear early-stage criteria, such as alignment with the role, communication basics, and any non-negotiables you define.
- After the call, you receive a transcript, structured answers, and follow-up flags. Some systems also add confidence or sentiment markers to help recruiters quickly spot strong signals or concerns. You can review everything before moving a candidate forward.
Step 6: Shortlisting And Human Decision Points
Based on screening and scoring, the agent produces a shortlist ordered by fit. Each candidate comes with a short explanation of what matches, what may be missing, and why they are recommended. This reduces the time recruiters spend rebuilding context from scratch.
Recruiters then validate the list, review borderline candidates, and confirm that all decisions are job-related and fair. This human checkpoint is a key requirement in responsible AI hiring guidance, mainly when systems are used for screening decisions.
Step 7: Interview Scheduling And Handoff
Once a candidate is approved for an interview, the agent shares available slots pulled from the recruiter’s or panel’s calendars. Candidates choose a time, and the system automatically confirms it. This cuts down the longest delay in most hiring funnels: manual coordination.
Before the interview, the agent sends hiring managers a clean handoff pack: screening notes, call transcript or recording, and suggested areas to probe based on gaps or signals.
Risks and Responsible Use of an AI Recruiter Agent
AI recruiter agents can save time, but only if you control the risks. Below are the main ones and the practical ways to reduce them.
1. Bias And Discrimination
If the system is trained on past hiring data that reflects unfair patterns, it may learn those patterns as “success signals.” Bias can also creep in when the model relies on proxy signals that link to protected traits, such as certain schools, gaps in employment, location, or language style.
Use job-related criteria only, and document those criteria clearly. Bias checks on shortlists and rejection rates to spot uneven outcomes across groups. Keep a human override path for edge cases, rather than letting the system make final decisions on its own.
2. Privacy And Consent
Screening bots process resumes, contact details, work history, and sometimes audio or video. If data is stored too long, shared too widely, or used beyond hiring, you risk violating data protection laws.
Collect only what you need for hiring. Set clear retention limits, restrict access to hiring teams, and ensure vendors follow the same rules. Candidates should be told what data is collected, how long it’s kept, and who can see it.
3. Transparency And Candidate Trust
If people cannot tell they are interacting with AI or do not understand what is being assessed, trust drops, and disputes rise. Lack of clarity also makes it hard to give meaningful feedback to rejected candidates.
Tell candidates when AI is used, what stage it supports, and what inputs affect outcomes. Provide simple explanations of why someone moved forward or did not, and ensure a human can review contested cases.
4. Voice-Specific Risks
Accent, dialect, speech speed, or disabilities can reduce transcription accuracy. When the system mishears people, they may score lower for reasons unrelated to the job. Studies and reporting have flagged higher error rates for non-native speakers and accent groups.
Use multilingual, accent-robust models, and test them on local speech patterns before full rollout. Track transcription confidence; when it drops, route the candidate to a human screen instead of auto-scoring. This keeps voice screening helpful without becoming a hidden filter.
What to Look for When Choosing an AI Recruiter Agent?
Below are the important things to check before you commit to a platform:
- The agent should understand role intent and related skills so it surfaces strong candidates even when titles or wording differ.
- Look for smooth two-way chat, an optional voice AI recruiter for screening, and clear transitions to a human recruiter when needed.
- The vendor should provide audit logs, consent workflows, and tools to test and document fairness in screening outcomes.
- The agent must plug into your existing stack so data flows cleanly and scheduling or outreach does not sit in a silo.
- You should be able to set role-level scoring rules, non-negotiables, and screening questions, rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach.
Why Avahi’s AI Voice Agent Works for Modern Talent Acquisition Teams?
For talent acquisition teams, speed, consistency, and secure handling of candidate data matter at every stage. Avahi’s AI Voice Agent helps HR teams keep hiring moving without adding compliance risk.
- Always-on candidate support: Candidates get instant answers and scheduling help, reducing missed calls and slow follow-ups.
- Secure data flow: Conversations and candidate details are imported into your ATS or CRM in a controlled, compliant manner.
- Less admin work: Screening, scheduling, reminders, and FAQs are automated so that recruiters can focus on decision-making.
- Audit-ready records: Every interaction is logged and traceable, making compliance reviews easier.
- Stronger candidate experience: Candidates stay informed and engaged, while your team avoids repetitive coordination.
With Avahi, teams can scale hiring faster while maintaining trust and compliance.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI
Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does an AI recruiter agent do in high-volume hiring?
An AI recruiter agent manages early hiring steps like job post setup, resume screening, candidate outreach, voice or chat pre-screens, shortlisting, and interview scheduling so recruiters can focus on final evaluation.
2. How is an AI recruiter agent different from an ATS?
An ATS mainly tracks applicants and applies rule-based filters, while an AI recruiter agent understands job intent, matches candidates semantically, engages them through chat or voice, and recommends next steps.
3. Can an AI recruiter agent run voice screening calls on its own?
Yes, a voice AI recruiter can conduct first-round screening calls, ask structured questions, capture responses, and share transcripts and signals for recruiter review before any interview decision is made.
4. Is using an AI recruiter agent safe and compliant for hiring?
It can be, if you use job-related criteria, audit outcomes for bias, collect only required candidate data, get clear consent, and keep human review for edge cases and final decisions.
5. What should I look for before choosing an AI recruiter agent?
Check for strong semantic matching, good candidate experience (chat, voice, fast handoff), clear compliance tools (audit logs, bias testing, consent flows), smooth ATS/HRMS integrations, and role-level customization.