TL;DR
|
Healthcare is the only industry where the customer waits while the service provider types.
In clinics and hospitals around the world, physicians are spending more time documenting care than actually delivering it.
While patients talk about their symptoms, doctors are often typing notes, navigating digital records, and toggling between systems, creating a disconnected experience on both sides of the table. Up to 50% of a doctor’s workday is spent entering or managing data in Electronic Health Records (EHRs). Physician burnout has reached 63%, with administrative burden cited as a top cause.
These challenges impact patient safety, clinician well-being, and the financial sustainability of healthcare systems. The pressure to “do more with less” is growing, and conventional tools are no longer enough. That’s where AI-powered clinical voice agents are starting to make a difference.
By utilizing natural language processing to capture, process, and act on clinical information, these systems are helping to reduce documentation time, streamline patient interactions, and support informed decision-making. And most importantly, put the human connection back at the center of care.
In this blog, we’ll explore how these AI clinical voice agents work, why they are essential in today’s healthcare environment, and how you can successfully implement them in real-world clinical workflows.
Understanding AI Clinical Voice Agents: Types and Functions
Clinical voice agents are AI-powered systems made to understand and respond to spoken language in healthcare settings. These tools help doctors, nurses, and patients communicate more efficiently by converting spoken conversations into structured digital actions. There are two main types of clinical voice agents:
Passive (Ambient) Voice Agents
These agents listen in the background during doctor–patient conversations and automatically transcribe and summarize the interaction. For example, they can generate clinical notes while a doctor is examining a patient, reducing the need for manual data entry.
Interactive Voice Agents
These agents actively engage with patients or staff by asking and answering questions. They are used for tasks like pre-visit intake, symptom triage, appointment reminders, and post-visit follow-ups.
Patients speak to the agent, and it responds with relevant prompts or information. These systems rely on a combination of technologies to ensure accuracy, context awareness, and medical relevance.
Essential Components of Clinical Voice Agents
| Component | Purpose | How It Works |
| Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) | Converts speech to text | When a patient or doctor speaks, ASR captures the audio and transcribes it into written text in real-time. Modern ASR systems are trained to handle medical terminology, different accents, and background noise. |
| Natural Language Understanding (NLU) | Interprets the meaning of speech | NLU analyzes the transcribed text to identify key details such as symptoms, conditions, medications, and intent (e.g., “I need to reschedule my appointment”). It enables the system to understand medical context, not just words. |
| Language Model / Rule-Based Logic | Determines the correct response or action | NLU analyzes the transcribed text to identify key details such as symptoms, conditions, medications, and intent (e.g., “I need to reschedule my appointment”). It enables the system to understand medical context, not just words. |
Current Challenges Driving the Adoption of Voice AI in Healthcare

Below are the operational and clinical challenges prompting healthcare organizations to explore AI-driven voice technologies.
1. EHR Overload for Physicians
Most doctors today spend a significant portion of their workday entering data into EHR systems, often more than the time they spend directly with patients. This reduces face-to-face interaction during appointments, which can lead to patients feeling unheard or disconnected from their healthcare providers.
The constant need to type, click through forms, and update records not only slows down the clinical workflow but also impacts the quality of doctor–patient communication. It creates a transactional environment where the clinician is focused on documentation rather than care delivery.
2. Rising Clinician Burnout Rates
Physicians and nurses are experiencing increasing levels of burnout, with administrative tasks being a major contributor. In addition to direct patient care, healthcare staff must handle billing codes, clinical summaries, appointment scheduling, and regulatory documentation.
This overload leads to mental fatigue, reduced job satisfaction, and lower retention rates among skilled professionals. In turn, it increases recruitment and training costs for healthcare organizations. Over time, this also compromises patient safety and continuity of care.
3. Gaps in Follow-Up and Triage
Timely follow-ups are essential for managing chronic conditions, ensuring medication adherence, and preventing complications. However, in many practices, follow-ups rely on manual phone calls or incomplete reminder systems.
Similarly, initial triage, determining the urgency of a patient’s symptoms, is often handled by overburdened staff or delayed due to a lack of availability. These inefficiencies can lead to missed appointments, delayed interventions, and lower patient satisfaction.
4. Access Barriers in Vulnerable Populations
Patients in rural areas or older individuals with mobility issues often struggle to access timely care. Many healthcare systems have the staff or resources to consistently monitor these populations, particularly for routine or preventive care.
As a result, health issues may go unreported or untreated until they become severe. This creates disparities in health outcomes and contributes to increased emergency room visits and hospitalizations that could have been avoided with better outreach and monitoring.
Practical Applications of AI Clinical Voice Agents
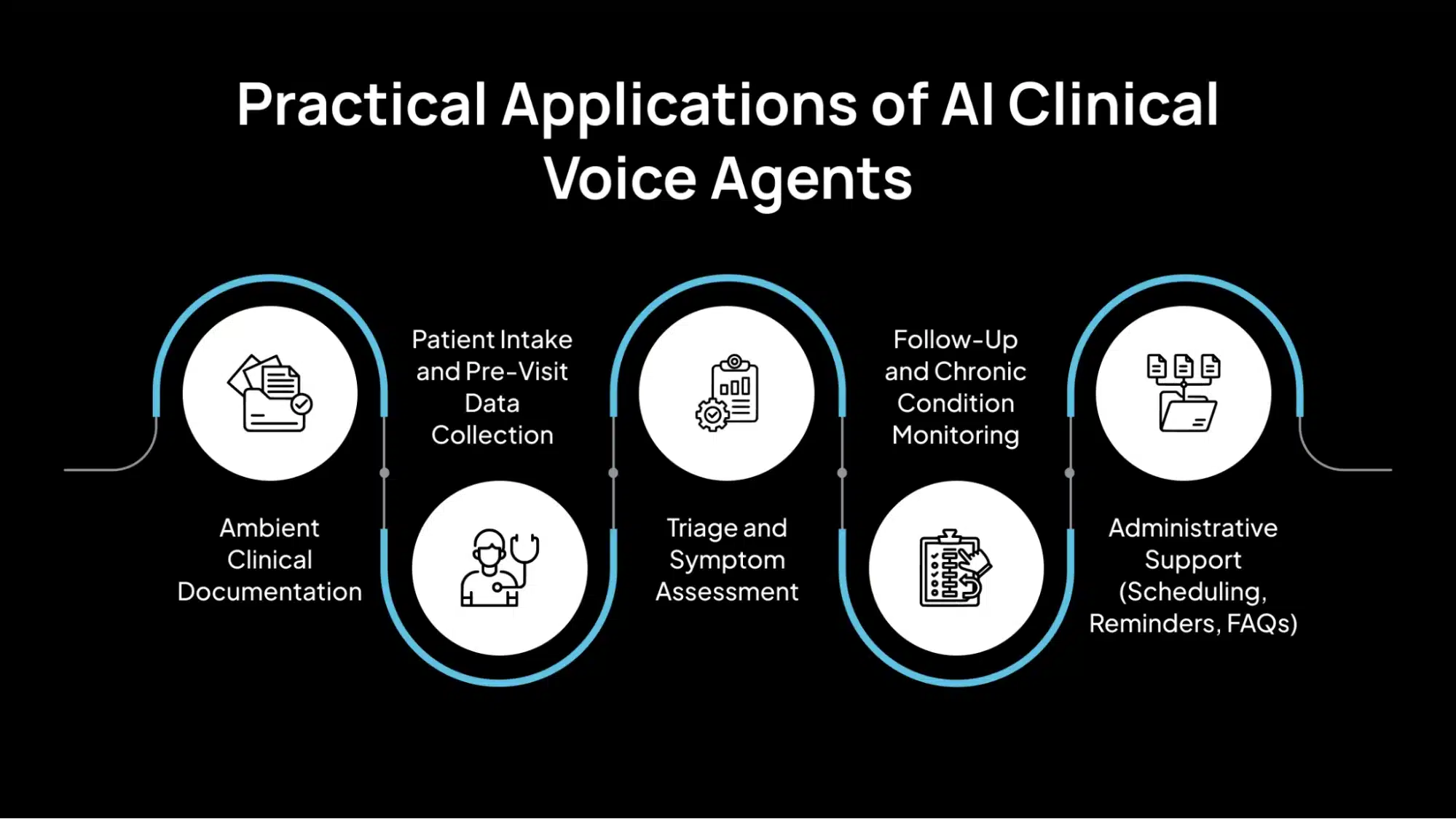
Below are the most impactful use cases where clinical voice agents are actively improving operational efficiency, clinical accuracy, and patient engagement.
1. Ambient Clinical Documentation
Ambient clinical documentation systems are designed to listen passively during doctor–patient conversations. They automatically transcribe the interactions, identify relevant clinical details, and generate structured notes, such as SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan) summaries. These notes are then synced with the clinic’s Electronic Health Record (EHR) system, reducing the need for manual data entry.
This reduces the administrative workload on physicians by saving 4–6 hours per week. It enhances documentation consistency and accuracy, which is crucial for clinical decision-making, billing, and compliance. Most importantly, it frees doctors to focus more on patient interaction rather than typing into a computer during the appointment.
The system uses an always-on microphone to capture audio, which is then processed through an Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) engine. The transcribed text is passed to a medical language model, which summarizes the relevant clinical points and formats them for the EHR. Integration tools then upload the final note into the patient’s chart.
2. Patient Intake and Pre-Visit Data Collection
Before a patient visits the clinic, a voice-enabled system can reach out via phone or app to ask a series of structured questions. These may include inquiries about current symptoms, vital signs, medications, or medical history. The data collected is then pre-filled into the patient intake forms in the EHR.
Automating this intake process reduces the time spent during the actual appointment, ensures standardized data collection, and helps identify high-risk patients earlier based on their responses. It also improves front-desk efficiency by reducing manual data entry.
The process begins with an outbound interactive voice response (IVR) call or app-based voice assistant. The system uses a conversational flow or medical LLM to guide the interaction, extract relevant information, and populate predefined fields in the EHR or practice management software.
3. Triage and Symptom Assessment
Voice-based triage agents conduct real-time interviews with patients to assess their symptoms and determine the severity of the issue. Based on the responses, the system decides whether the patient should be directed to emergency care, scheduled for a telehealth visit, or advised to manage symptoms at home.
This solution helps reduce unnecessary emergency room visits, improves routing for telehealth services, and enables early detection of critical issues that might otherwise go unnoticed. It also ensures faster and more consistent triage compared to manual methods.
Patients speak to the agent via phone or app. The voice is transcribed and analyzed by a symptom classification model, which maps the information to known clinical pathways. The system then applies decision rules or machine learning logic to determine the next step in care and routes the patient accordingly.
4. Follow-Up and Chronic Condition Monitoring
Voice AI tools can schedule automated follow-up calls to check in with patients, especially those managing chronic illnesses. These systems can ask questions such as “Have you taken your medication today?” or “Are you experiencing any new symptoms?” Based on the answers, the system can log patient data and escalate any issues to the care team for further attention.
Automated follow-ups help improve treatment adherence, identify complications early, and reduce hospital readmissions. It also ensures that patients feel supported without requiring constant manual outreach from staff.
Voice agents call or message patients on a scheduled basis. The patient’s spoken responses are logged and analyzed for any red flags. If the system detects a concern, such as worsening symptoms, it sends an alert to a nurse or doctor for further evaluation.
5. Administrative Support (Scheduling, Reminders, FAQs)
Voice assistants are increasingly used to automate everyday administrative tasks, such as booking or rescheduling appointments, answering insurance-related questions, handling medication refill requests, and providing information on clinic policies.
This offloads routine tasks from the front-desk staff, provides 24/7 patient access, and helps reduce call wait times, no-shows, and patient confusion about their appointments or care process.
The system listens to a patient’s request, such as “I’d like to move my appointment to next Tuesday” and uses an intent recognition engine to understand the request. It then engages in a short dialogue to confirm details and executes the action by interfacing with the practice’s calendar or patient management system (PMS).
How to Successfully Implement AI Clinical Voice Agents into Your Healthcare Organization
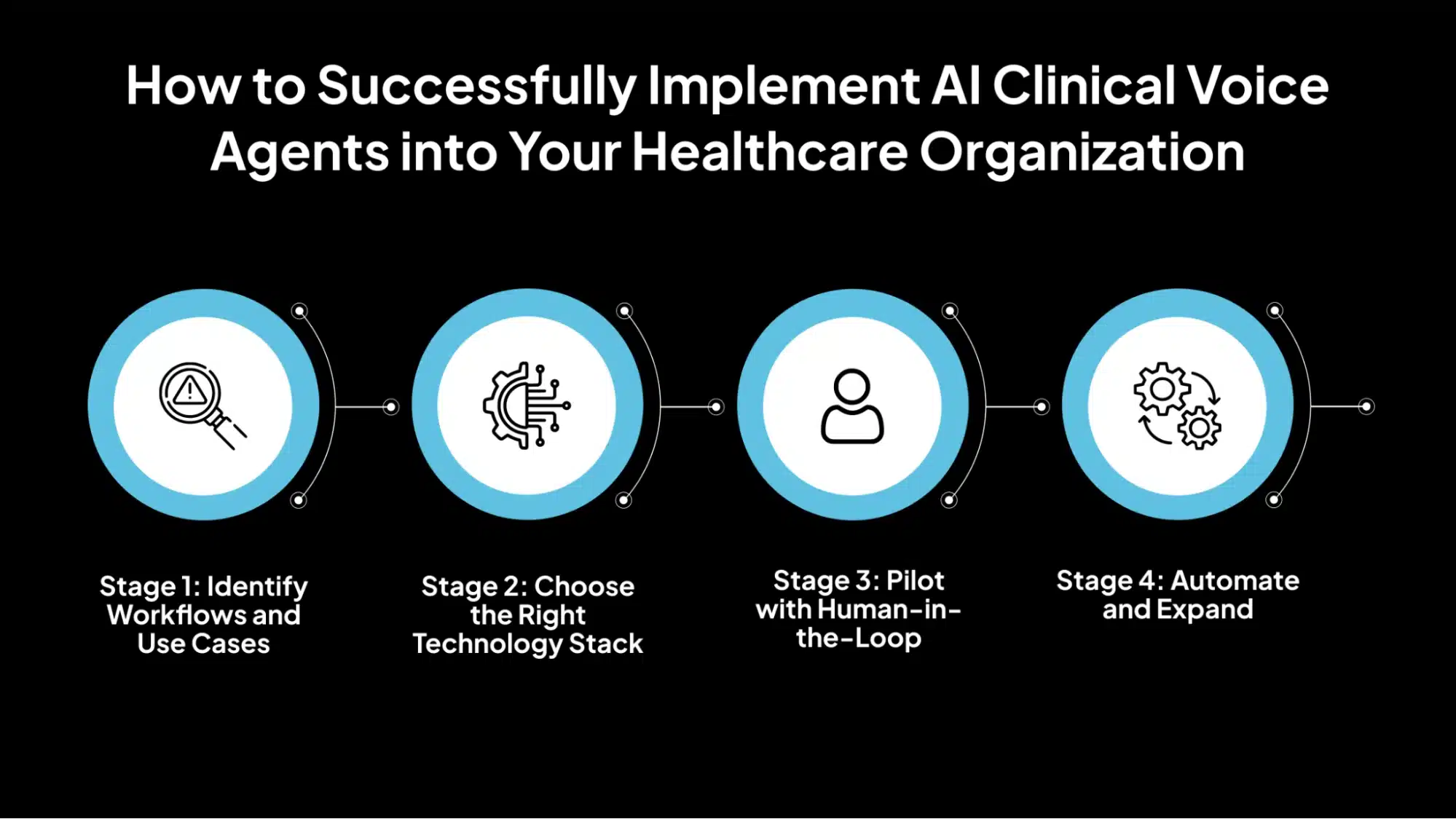
Successfully integrating voice AI into clinical workflows requires a structured, phased approach. This ensures the technology aligns with operational needs, minimizes risk, and builds trust among clinicians and patients. Below is a four-stage roadmap for the practical deployment of voice AI in healthcare settings.
Stage 1: Identify Workflows and Use Cases
The first step is to determine where voice AI can provide immediate value without disrupting critical care functions. It’s essential to start with high-frequency, low-risk tasks that are repetitive and well-defined.
For example, administrative tasks, including appointment scheduling, reminders, and policy inquiries.Clinical documentation, where ambient voice tools can transcribe and summarize conversations. Chronic care check-ins, where patients are asked routine follow-up questions via voice bots.
Focusing on these areas helps reduce complexity and allows teams to validate performance in a controlled environment before expanding.
Stage 2: Choose the Right Technology Stack
Once use cases are selected, the next step is to choose the appropriate technology infrastructure that fits your organization’s requirements and compliance standards. Essential considerations include:
- Deployment Model: Decide between on-premises (more control, but higher setup cost) and cloud-based solutions (faster deployment, more effortless scalability).
- HIPAA-Compliant ASR: Ensure the speech recognition engine meets data privacy and security standards required for handling patient information.
- Medical LLMs: Utilize large language models that are either trained or fine-tuned on medical data to ensure accuracy in clinical contexts.
- System Integration: Verify that the AI solution can integrate with your EHR and other tools using industry standards, such as HL7 or FHIR APIs.
Selecting the right stack is crucial for long-term scalability and regulatory compliance.
Stage 3: Pilot with Human-in-the-Loop
Before going fully live, run a pilot program with human oversight to validate performance, build clinician confidence, and gather feedback. In this stage, AI systems are used to assist, not make final decisions.
A human reviewer, such as a physician, nurse, or admin, verifies all AI outputs before they are submitted or acted upon. Failure points and edge cases are documented to enhance model performance and identify areas where manual intervention may still be necessary.
This human-in-the-loop model helps prevent errors, ensures accountability, and creates a safer learning environment for both staff and AI systems.
Stage 4: Automate and Expand
Once the pilot demonstrates consistent and accurate performance, the next step is to automate tasks and gradually expand usage. This includes increasing the AI confidence threshold so that the system can make decisions or complete actions without human review in routine scenarios, growing to more complex use cases, such as triage conversations or multi-turn patient interactions, and integrating feedback loops to continually retrain and improve the system based on real-world performance data.
As the system matures, it can take on a larger share of the workload, enabling broader automation and long-term operational efficiency.
The Future of Clinical Voice Technology: What’s Next for Voice AI in Healthcare
As voice AI continues to evolve in healthcare, several emerging trends are shaping its next phase. These developments aim to enhance precision, safety, and personalization while ensuring data privacy and maintaining regulatory compliance.
1. Multimodal Agents for Elderly Care (Voice + Visual + Sensors)
Future clinical voice agents will integrate voice input, visual monitoring (e.g., camera or avatar interface), and sensor data (such as wearable devices or home devices) to support elderly patients more effectively.
These systems can detect non-verbal cues, such as facial expressions, posture changes, or fluctuations in heart rate, enabling more comprehensive remote care, particularly for patients with limited mobility or chronic conditions.
2. Real-Time Clinical Decision Support via Conversational Agents
Voice AI will be integrated with clinical decision support tools to provide real-time guidance during consultations.
For instance, while the doctor speaks with the patient, the AI could suggest differential diagnoses, flag missing lab tests, or recommend treatment guidelines, all based on the latest evidence and patient data. This can help improve clinical accuracy and reduce the chances of oversight.
3. Voice AI + LLM Copilots for Doctors
Combining voice recognition with large language models (LLMs) will lead to intelligent smart clinical copilots that can summarize patient visits, identify relevant ICD codes, draft prescriptions, and even order lab tests based on spoken commands.
These tfunctions act like digital assistants, helping clinicians work more efficiently while reducing administrative burdens, without disrupting their natural workflow.
4. AI-Powered Simulation for Medical Training
Medical education will benefit from AI-driven voice agents that simulate a virtual patient, enabling more effective training and education.
These agents can interact with students in realistic scenarios, allowing them to practice history-taking, diagnosis, and communication skills in a safe environment. It enables on-demand, scalable, and adaptive training for both clinical reasoning and bedside manner.
5. Federated Learning for Privacy-Preserving Model Improvement
To improve AI systems while protecting sensitive health data, federated learning allows hospitals and clinics to train models locally on their data and share only model updates, not patient records. This approach ensures compliance with privacy regulations (like HIPAA and GDPR) while contributing to global improvements in AI accuracy and reliability.
Why Healthcare Providers Are Choosing Avahi AI Voice Agents to Eliminate Call Center Bottlenecks
Managing high call volumes is one of the most time-consuming and resource-draining tasks in healthcare today. For practices seeking to reduce operational stress and enhance patient experience without increasing staff, Avahi AI Voice Agents provide a practical and scalable solution.
Explicitly designed for high-demand care environments like dental, specialty, primary, and urgent care, Avahi automates patient communication through innovative, conversational voice technology, available 24/7.
Here’s What Avahi AI Voice Agents Can Do for Your Practice:
- Instantly Answer Common Patient Questions
Patients can get immediate answers to frequently asked questions—like office hours, directions, and service availability—without waiting on hold.
- Automate Appointment Scheduling
Let patients book, reschedule, or cancel appointments in real time, without requiring staff involvement. Reduce friction and missed care opportunities.
- Send Reminders and Post-Visit Follow-Ups
Reduce no-shows and maintain care continuity with automated alerts that keep patients informed about their upcoming or recent visits.
- Intelligently Route Urgent Calls
Calls involving time-sensitive or critical symptoms are automatically escalated to the appropriate clinical team, ensuring prompt intervention.
- Support Insurance and Referral Questions
Streamline administrative workflows by automating responses to insurance coverage, referral tracking, and call triage.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are AI clinical voice agents in healthcare?
AI clinical voice agents are voice-enabled systems powered by artificial intelligence that can understand, process, and respond to spoken language in clinical environments. These agents assist with tasks such as documentation, patient intake, appointment scheduling, and follow-ups, helping to reduce administrative workload and improve patient communication.
2. How do AI clinical voice agents improve doctor–patient interactions?
AI clinical voice agents enhance doctor–patient communication by reducing the time doctors spend on manual data entry. By automatically transcribing and summarizing conversations, these agents enable physicians to maintain eye contact and focus more on the patient, resulting in a more connected and personalized experience.
3. Are AI clinical voice agents secure and compliant with healthcare regulations?
Yes, most AI clinical voice agents are designed with healthcare-grade security. Leading platforms are HIPAA, SOC 2, and GDPR compliant, ensuring that patient data is encrypted and handled safely. Always choose solutions that integrate securely with your EHR systems and follow industry compliance standards.
4. What clinical workflows can AI voice agents automate?
AI clinical voice agents can automate several workflows, including ambient clinical documentation, patient intake, triage assessments, appointment management, and post-visit follow-ups. This automation helps clinics reduce wait times, administrative overhead, and human error across daily operations.
5. How can I implement AI clinical voice agents in my practice?
To implement AI clinical voice agents, start by identifying repetitive tasks that can be automated, such as documentation and scheduling. Choose a HIPAA-compliant solution that integrates with your existing EHR system. Begin with a pilot phase that utilizes human oversight, and scale the system gradually as it proves reliable.