TL;DR
|
AI is no longer a future concept; it is becoming the operational backbone of modern enterprises.
Across industries, autonomous AI agents are rapidly moving from experimental tools to core business infrastructure. Organizations are no longer asking if AI should be adopted; they are asking how fast it can be implemented without losing control, security, and trust.
A McKinsey Global Survey reports that around 78% of organizations now use AI in at least one business function, demonstrating widespread AI adoption across enterprises. This shift is not driven solely by innovation; it is driven by survival in highly competitive, data-driven markets.
You are under constant pressure to reduce costs without lowering performance, scale operations without increasing complexity, make faster decisions without increasing risk, and deliver uninterrupted services without expanding manpower. Autonomous AI agents promise to solve these challenges by operating continuously, learning from data, and executing actions at machine speed.
But this transformation is not risk-free. As you move toward AI-driven enterprise systems, you must understand both sides of the equation.
Autonomous AI agents can create a strong competitive advantage, but they also introduce new risks related to security, governance, accountability, workforce stability, and operational control. This blog helps you understand how autonomous AI agents reshape enterprise systems, what they enable, what they expose, and how you can approach adoption with structure, strategy, and long-term resilience.
What Are Autonomous AI Agents?
An autonomous AI agent is built to observe, analyze, and act on real-time data. These agents are equipped with machine learning capabilities, enabling them to learn from previous experiences and make smarter decisions over time. They can operate continuously, handle complex tasks, and optimize processes without direct oversight, which is a significant departure from traditional automated systems. Some of the functionalities of autonomous AI agents include:
- Self-learning: They improve their decision-making and actions based on accumulated data.
- Adaptability: They can adjust to new situations and changing environments without needing a human to recalibrate their actions.
- Efficiency: They optimize processes by quickly analyzing data and executing tasks faster than humans.
High-Impact Business Areas Enabled by Autonomous AI Agents
In enterprise systems, autonomous AI agents are transforming various business operations. Here are some key areas where they are already making a significant impact:
1. Automation
AI agents can handle repetitive tasks, such as inventory management, scheduling, and order processing. For instance, in e-commerce, autonomous AI agents can automatically update stock levels, process customer orders, and trigger restocking alerts.
2. Data Analysis
Autonomous AI agents analyze large volumes of data at high speeds, identifying patterns and generating insights that would be too complex for manual processes. For example, AI tools in finance can scan historical market data, predict trends, and make investment decisions autonomously.
3. Decision-Making
These agents support decision-making by providing real-time insights. In supply chain management, AI can predict demand fluctuations, adjust procurement strategies, and manage logistics, all without human intervention. Autonomous agents are also used in HR for candidate screening, matching applicants to job descriptions based on skills and experience.
By integrating autonomous AI agents into these operations, businesses can reduce human error, enhance efficiency, and streamline complex processes, while allowing their teams to focus on higher-level strategic tasks.
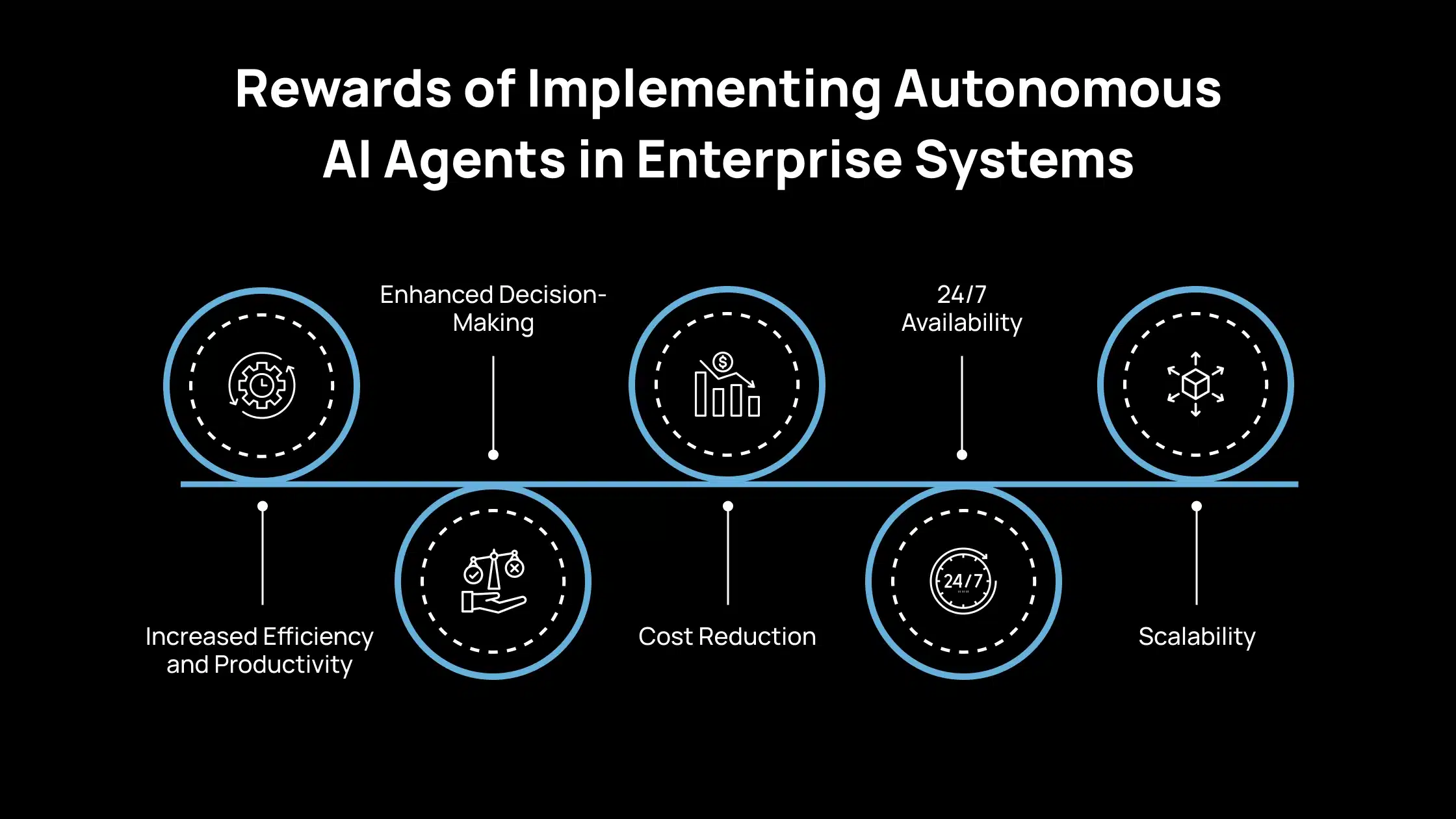
Rewards of Implementing Autonomous AI Agents in Enterprise Systems
When you integrate autonomous AI agents into your enterprise systems, you directly improve how your business operates, decides, and scales. These systems are not just automation tools; they become active operational assets that work continuously to support your goals.
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity
You reduce manual workload by allowing AI agents to handle repetitive, rule-based, and time-consuming tasks. This improves speed, accuracy, and process consistency across operations. You free your teams to focus on higher-value strategic and creative work.
For instance, this helps automate inventory management and customer service workflows, reducing delays and human error.
2. Enhanced Decision-Making
You gain real-time access to data-driven insights, rather than relying on delayed reports or assumptions. AI agents analyze large datasets continuously and highlight patterns you would otherwise miss.
You make faster, more informed business decisions based on live operational intelligence. AI agents use predictive analytics to improve sales forecasting and demand planning.
3. Cost Reduction
You lower operational costs by reducing dependency on manual labor for routine tasks. You minimize errors, rework, and inefficiencies that increase long-term expenses. You create leaner workflows without sacrificing accuracy or speed.
For example, AI agents replace manual data entry with AI systems that autonomously learn, validate, and update databases.
4. 24/7 Availability
You maintain continuous operations without downtime or staffing limitations. AI agents work without breaks, delays, or fatigue. You provide consistent service quality at all times. For example, AI-powered chatbots and help desk assistants that operate around the clock.
5. Scalability
You scale operations without increasing costs at the same rate as growth. AI agents handle higher volumes of data, transactions, and workflows without performance loss. You expand capacity without restructuring your workforce. For instance, AI agents are used in e-commerce order processing during high-demand periods to manage traffic spikes efficiently.
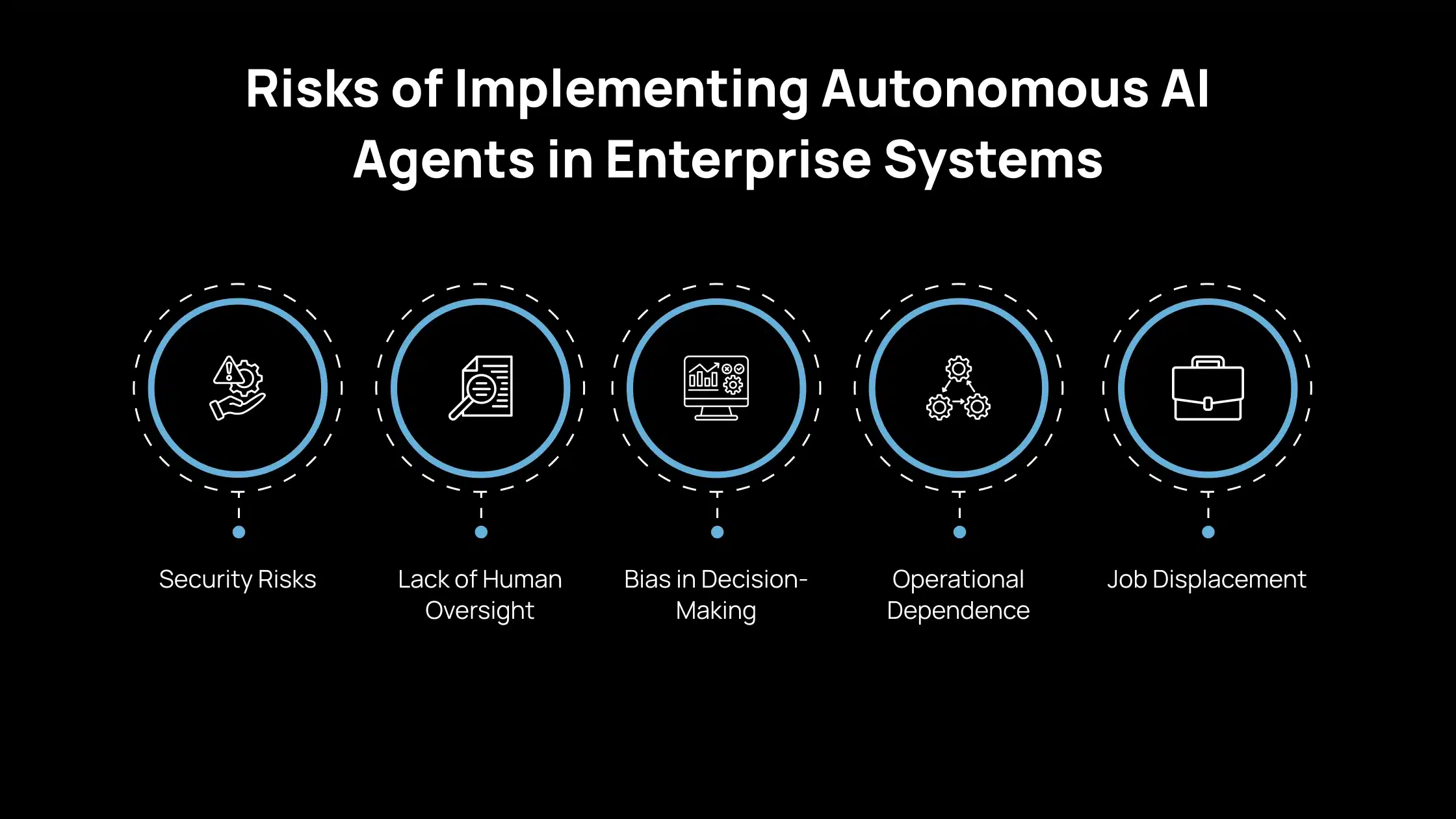
Risks of Implementing Autonomous AI Agents in Enterprise Systems
As you integrate autonomous AI agents into enterprise environments, you introduce not only technological change but also new layers of operational, ethical, and strategic risk. Below are the major risks associated with deploying autonomous AI agents in enterprise systems.
1. Security Risks
Autonomous AI systems expand the digital attack surface of your enterprise infrastructure. Without enterprise-grade security architectures, these systems can introduce new vulnerabilities that expose sensitive business and customer data.
AI models, APIs, and automated workflows can become entry points for cyberattacks if they are not properly monitored, secured, and updated. This creates risks of data breaches, regulatory violations, and reputational damage.
For instance, AI agents handling sensitive customer information become high-value targets for cybercriminals seeking unauthorized access to enterprise systems.
2. Lack of Human Oversight
When AI agents operate with high levels of autonomy, decisions may occur without human validation or contextual understanding.
Autonomous systems rely on data patterns, not judgment, which can lead to unintended outcomes when inputs are flawed, incomplete, or misleading. Over-automation can reduce accountability and weaken governance structures, making it difficult to trace responsibility for errors.
AI-driven supply chain systems execute purchasing decisions based on incorrect demand data, leading to inventory misallocation and financial losses.
3. Bias in Decision-Making
Autonomous AI agents learn from historical datasets, and if those datasets contain bias, the system will replicate and scale those biases.
This can result in discriminatory outcomes, unfair treatment, and ethical violations across hiring, lending, customer segmentation, and service delivery. Biased AI decisions damage trust, create legal risk, and undermine brand credibility.
For instance, hiring algorithms produce discriminatory outcomes due to biased training data, affecting fairness and organizational diversity.
4. Operational Dependence
Over-reliance on autonomous AI agents creates systemic risk within enterprise operations. When critical processes depend entirely on AI systems, any technical failure, model error, or system malfunction can disrupt entire business functions.
Without redundancy, fallback processes, or human intervention mechanisms, organizations become highly vulnerable to downtime and operational paralysis. Fully automated production environments experience large-scale disruptions when AI systems fail, causing costly delays and halted operations.
5. Job Displacement
Automation through autonomous AI agents changes workforce structures by replacing human-driven tasks with machine-driven processes. This creates ethical, cultural, and organizational challenges, including job displacement, workforce resistance, and a decline in morale.
Without structured reskilling and transition programs, businesses risk long-term talent disengagement and internal instability.
Replacing customer service teams with AI-driven bots leads to job losses, reduced employee trust, and organizational dissatisfaction.
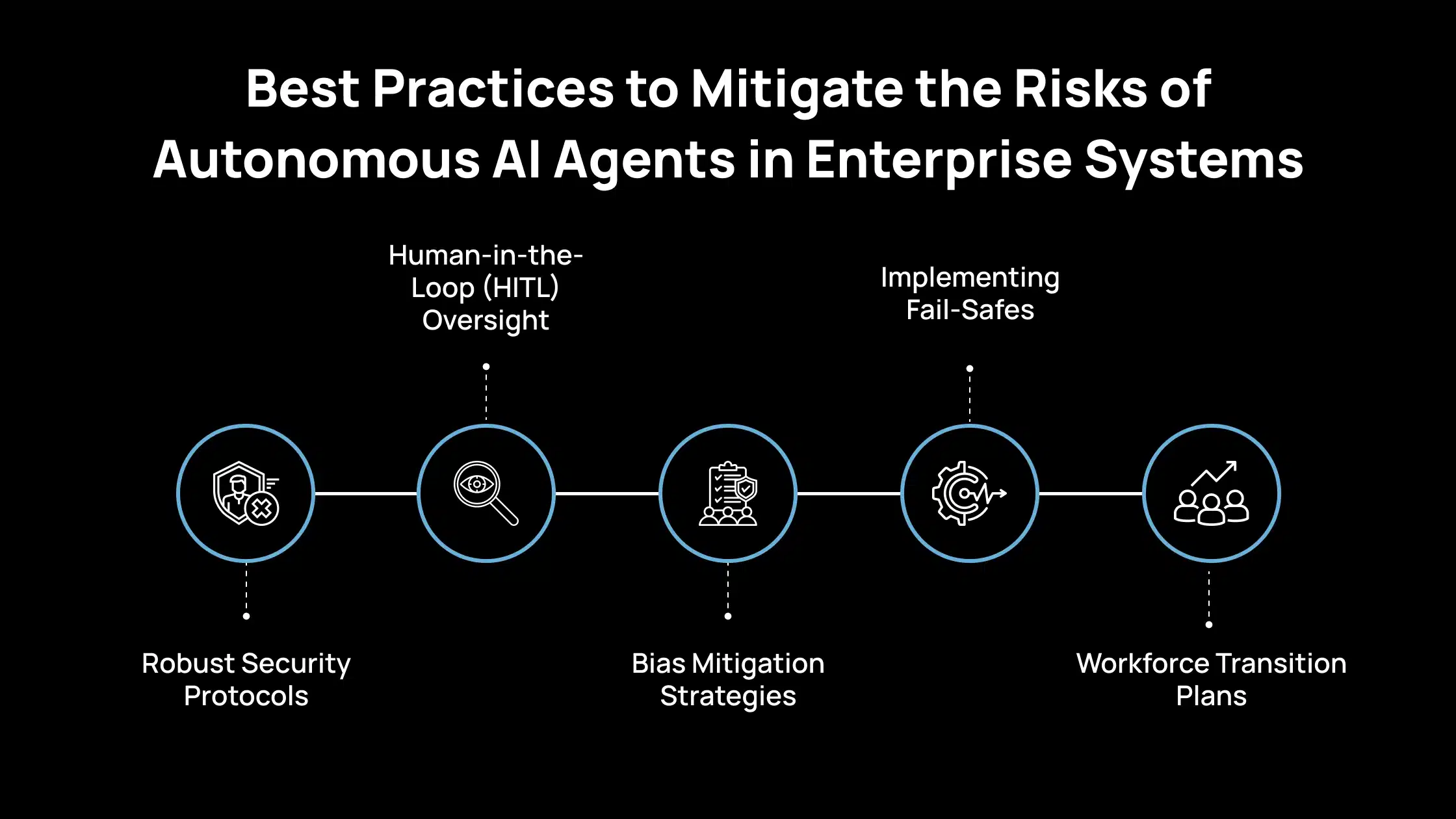
Best Practices to Mitigate the Risks of Autonomous AI Agents in Enterprise Systems
While autonomous AI agents offer significant advantages, they also present certain risks that must be carefully managed. To harness their full potential while safeguarding your organization, consider the following strategies for risk mitigation:
1. Robust Security Protocols
AI systems are susceptible to a range of security threats, including data breaches and cyberattacks. To protect these systems, it is essential to implement strong cybersecurity protocols. Measures include:
- Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use MFA to secure access to critical AI systems, ensuring that only authorized personnel can make system changes.
- Regular Audits: Conduct routine audits of AI systems to identify vulnerabilities, ensure compliance, and address any potential weaknesses before they are exploited.
Implementing encrypted communications for AI systems that handle sensitive customer data and establishing regular cybersecurity audits to identify and address vulnerabilities.
2. Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Oversight
AI agents can make decisions autonomously, but it is vital to include human oversight at key decision points. This ensures that AI-driven processes remain aligned with company goals and ethical standards. Some of the measures are:
- Decision Flagging: Set up systems that allow AI to flag certain actions for human review before execution. This minimizes the risk of errors or harmful outcomes.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly assess the AI system’s decision-making processes and outcomes to ensure they are accurate and aligned with business objectives.
In financial systems, AI may flag large or unusual transactions for human verification before processing, helping catch potential fraud before any financial loss occurs.
3. Bias Mitigation Strategies
AI systems learn from historical data, and if that data is biased, the AI can inadvertently perpetuate these biases. It is crucial to implement strategies to regularly audit and correct any biases in the system. Some of the measures include:
- Regular Audits: Conduct routine audits of AI models to identify biases in decision-making and rectify them.
- Diverse Datasets: Ensure the datasets used for training AI models are diverse, reflecting a wide range of perspectives and demographic groups to avoid systemic biases.
When training AI models for hiring, ensure that the data used does not inadvertently favor one gender, race, or age group over others, thus promoting fair and unbiased hiring decisions.
4. Implementing Fail-Safes
AI systems are powerful, but they are not infallible. Fail-safes are essential to ensure that if an AI system malfunctions or makes an incorrect decision, there is a backup plan to mitigate any negative impact. Here are some of the measures:
- Manual Override: Design systems that allow human operators to intervene when an AI decision may lead to a critical error.
- Backup Systems: Set up systems that can take over in the event of a system failure, ensuring business continuity.
In manufacturing, an AI system that controls the production line can be equipped with a manual override that allows human operators to stop the line in case of an unexpected malfunction or safety risk.
5. Workforce Transition Plans
As AI automates more repetitive tasks, some employees may find their roles shifting or becoming obsolete. To address this, businesses must have workforce transition plans in place.
Here are some of the measures:
- Reskilling Programs: Develop training initiatives to help employees acquire new skills for roles less likely to be automated by AI.
- Role Evolution: Ensure that employees are prepared for new responsibilities that leverage their unique human abilities, such as creativity, empathy, or strategic thinking.
A company could offer training programs to help customer service representatives transition from answering routine inquiries to focusing on more complex customer issues that require human judgment and empathy
The Future of Autonomous AI Agents in Enterprise Systems
As AI technology continues to evolve, autonomous agents are expected to become more sophisticated and integral to enterprise systems.
AI technology is advancing rapidly, with continuous improvements in machine learning algorithms, data processing power, and natural language processing capabilities. These advancements are making autonomous AI agents more capable and efficient, pushing them to new levels of performance and versatility.
1. Enhanced Learning Capabilities
AI models will become even more proficient at learning from smaller datasets and making real-time predictions, reducing the need for extensive training and enabling quicker adaptation to changing environments.
2. Greater Integration with Other Technologies
AI systems will increasingly integrate with emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), blockchain, and 5G, creating more seamless, efficient workflows across enterprise systems.
3. Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, autonomous agents will increasingly work alongside employees, handling repetitive or data-intensive tasks while allowing humans to focus on more strategic or creative aspects.
4. Data-Driven Insights
Autonomous AI agents can analyze vast amounts of data in seconds, uncovering trends and insights that would otherwise go unnoticed. This can lead to new product innovations, market opportunities, and improved customer experiences.
5. Customized Solutions
AI agents can create personalized recommendations or tailor-made solutions for customers, allowing businesses to offer more targeted services and products.
Companies in industries such as healthcare and finance are already using AI agents to discover patterns in medical research and financial transactions, leading to innovations such as new treatments and better investment strategies.
How Avahi Helps You Operationalize AI Across Your Enterprise?
If your goal is to apply AI in practical ways that deliver measurable business impact, Avahi offers solutions developed specifically for real-world challenges. Avahi enables organizations to quickly and securely adopt advanced AI capabilities, supported by a strong cloud foundation and deep AWS expertise.
Avahi AI solutions deliver business benefits such as:
- Round-the-Clock Customer Engagement
- Automated Lead Capture and Call Management
- Faster Content Creation
- Quick Conversion of Documents Into Usable Data
- Smarter Planning Through Predictive Insights
- Deeper Understanding of Visual Content
- Effortless Data Access Through Natural Language Queries
- Built-In Data Protection and Regulatory Compliance
- Seamless Global Communication Through Advanced Translation and Localization
By partnering with Avahi, organizations gain access to a team with extensive AI and cloud experience committed to delivering tailored solutions. The focus remains on measurable outcomes, from automation that saves time and reduces costs to analytics that improve strategic decision-making to AI-driven interactions that elevate the customer experience.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation, all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Utilize Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency?
Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What makes autonomous AI agents different from conventional automation systems?
Autonomous AI agents do not follow fixed rule-based instructions like traditional automation. They learn from data, adapt to changing environments, and make independent decisions, allowing them to improve performance over time without constant human intervention.
2. Are autonomous AI agents suitable for all enterprise functions?
Not all functions should be fully automated. Autonomous AI agents are most effective in data-heavy, repetitive, and process-driven operations such as analytics, customer support, supply chain management, and operations. Strategic, ethical, and people-centric decisions still require human involvement.
3. How can enterprises maintain control over autonomous AI systems?
You maintain control through governance frameworks, human-in-the-loop oversight, monitoring systems, audit mechanisms, and clearly defined accountability structures. AI should support decisions, not replace responsibility.
4. What industries benefit the most from autonomous AI agents?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, e-commerce, manufacturing, logistics, and enterprise IT operations benefit significantly due to high data volumes, complex workflows, and the need for real-time decision-making.
5. Do autonomous AI agents replace human jobs entirely?
They replace tasks, not human value. While some roles may change or be reduced, new roles emerge in AI management, governance, data strategy, and system oversight. The future model is human–AI collaboration, not full workforce replacement.