TL;DR
|
AI agents are moving from demos to real work, and they are starting to change how entire teams operate.
McKinsey estimates that generative AI and agents could automate work worth up to $4.4 trillion in annual value across functions such as sales, marketing, operations, and software engineering. In a global CIO survey, around 60% of leaders said they are actively investing in AI to automate workflows, not just answer questions in chat-style tools.
Many companies already report measurable impact, with faster processing times, fewer manual steps, and higher accuracy across sales, finance, HR, operations, and supply chain tasks.
You are no longer looking at AI as a support add-on. You are evaluating it as a core operational tool. AI agents plan tasks, use your systems, coordinate across teams, and complete work that previously required human oversight. This matters because most business processes depend on routine actions, data entry, approvals, and follow-ups that take time away from higher-value work.
This blog helps you understand where AI agents deliver meaningful results beyond customer support.
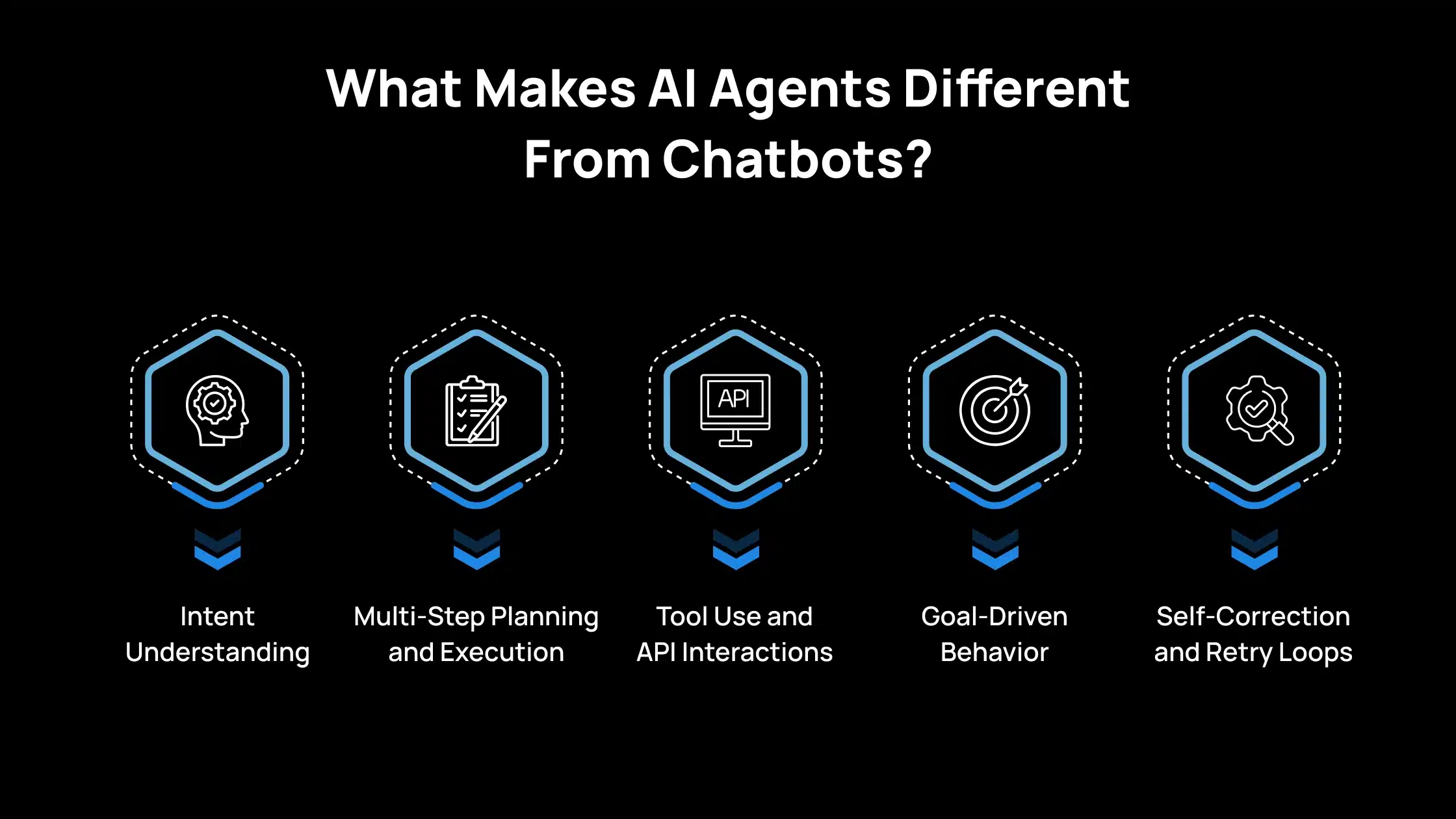
What Makes AI Agents Different From Chatbots?
When you evaluate AI solutions for your operations, you need clarity on what an AI agent can do that a chatbot cannot. A chatbot responds to questions. An AI agent completes tasks, follows steps, and works across your systems with a clear objective.
This difference becomes important when you want reliable automation that supports daily work across sales, finance, HR, IT, and other functions. Here is the list of core capabilities you should expect from AI Agents
Intent Understanding
You are not limited to scripted prompts or fixed decision trees. The agent interprets your request and identifies what you want to accomplish, even if the instruction is not perfectly structured.
Multi-Step Planning and Execution
You get more than a single reply. The agent identifies the steps required, organizes them, and carries out each one until the task is complete.
Tool Use and API Interactions
You can connect the agent to your operational systems. It performs actions directly within your CRM, ERP, ticketing tools, email, or databases, rather than just giving you suggestions.
Goal-Driven Behavior
You set the outcome, and the agent determines how to reach it with the resources available. It focuses on completing the workflow, not just explaining the next step.
Self-Correction and Retry Loops
You do not need to monitor every action. If a step fails, the agent reassesses the situation, adjusts the plan, and tries again until it reaches a reliable result or escalates to you.
Practical AI Agents Use Cases Beyond Support Tickets
Below is a clear, organized view of how agents support these tasks and reduce manual effort for your team.
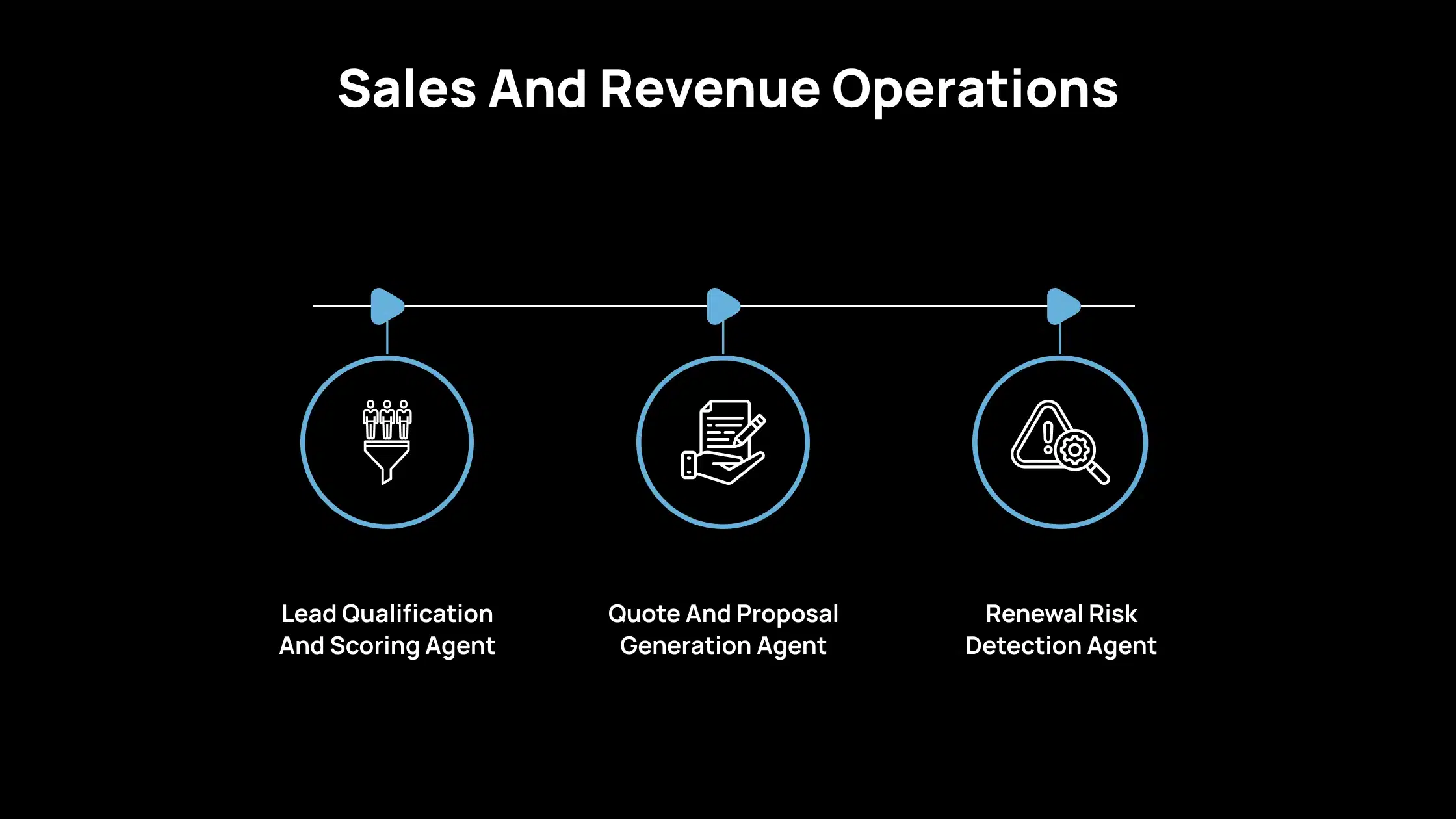
1. Sales And Revenue Operations
Lead Qualification And Scoring Agent
A lead qualification agent helps you assess new leads without manual screening. It enriches profiles with company size, industry, technology stack, or revenue data. It looks at engagement signals such as form submissions, email activity, or website visits. Based on your scoring model, it assigns a score and routes the lead to the right owner.
For example, instead of your sales team reviewing every inbound lead, the agent filters low-fit leads and forwards only qualified ones. This improves speed-to-lead and ensures reps spend more time with prospects who are likely to convert.
Quote And Proposal Generation Agent
A quote generation agent supports your team by identifying the correct pricing rules, product configurations, and contract terms. It combines these inputs to build accurate quotes and keeps versions organized for easy review.
For example, if a customer requests pricing for three product tiers with specific contract lengths, the agent pulls the latest price list, applies discounts or exceptions based on rules you define, and prepares a draft quote for approval. This helps you avoid pricing errors and reduces the back-and-forth often seen in proposal workflows.
Renewal Risk Detection Agent
A renewal risk agent monitors customer activity and highlights accounts that require attention. It tracks usage patterns, open support tickets, delayed payments, and changes in engagement. It compares these signals with historical churn indicators and alerts your account team when a risk pattern appears.
For example, if a customer’s product usage drops significantly or support tickets increase, the agent creates a renewal risk summary and suggests steps such as scheduling a check-in or reviewing their subscription fit. This helps your team act early and improve retention outcomes.
2. Marketing Operations
Campaign Briefing Agent
A campaign briefing agent helps you pull together the information required to plan a new campaign. It gathers product updates, audience details, competitor insights, and past campaign metrics so you do not have to search through multiple documents or tools. It then organizes these inputs into a structured brief that your team can review.
For example, if you need to prepare a launch campaign for a new feature, the agent collects recent product notes, summarizes customer feedback, and adds performance data from similar past campaigns. This saves time and gives your team a clear starting point.
Content Creation And Compliance Agent
A content agent prepares first drafts for blogs, emails, social posts, and product descriptions based on guidelines you provide. It checks tone requirements, formatting rules, and compliance constraints before sending the draft for review. This gives your writers more time to focus on refining content rather than gathering inputs or performing initial checks.
For example, if your industry requires specific legal disclaimers, the agent automatically inserts them and flags sections that require human approval. This helps you maintain consistency and reduces the chance of missed compliance elements.
SEO And Research Agent
An SEO agent assists you by analyzing competitor pages, clustering keywords, and identifying search intent patterns. It converts this information into easy-to-follow outlines, suggestions, or optimization checklists.
For example, if you want to target a new keyword group, the agent reviews top-ranking pages, identifies content gaps, and recommends structure, headings, and topics worth covering. This speeds up your research process and helps your team create content that aligns with search demand.
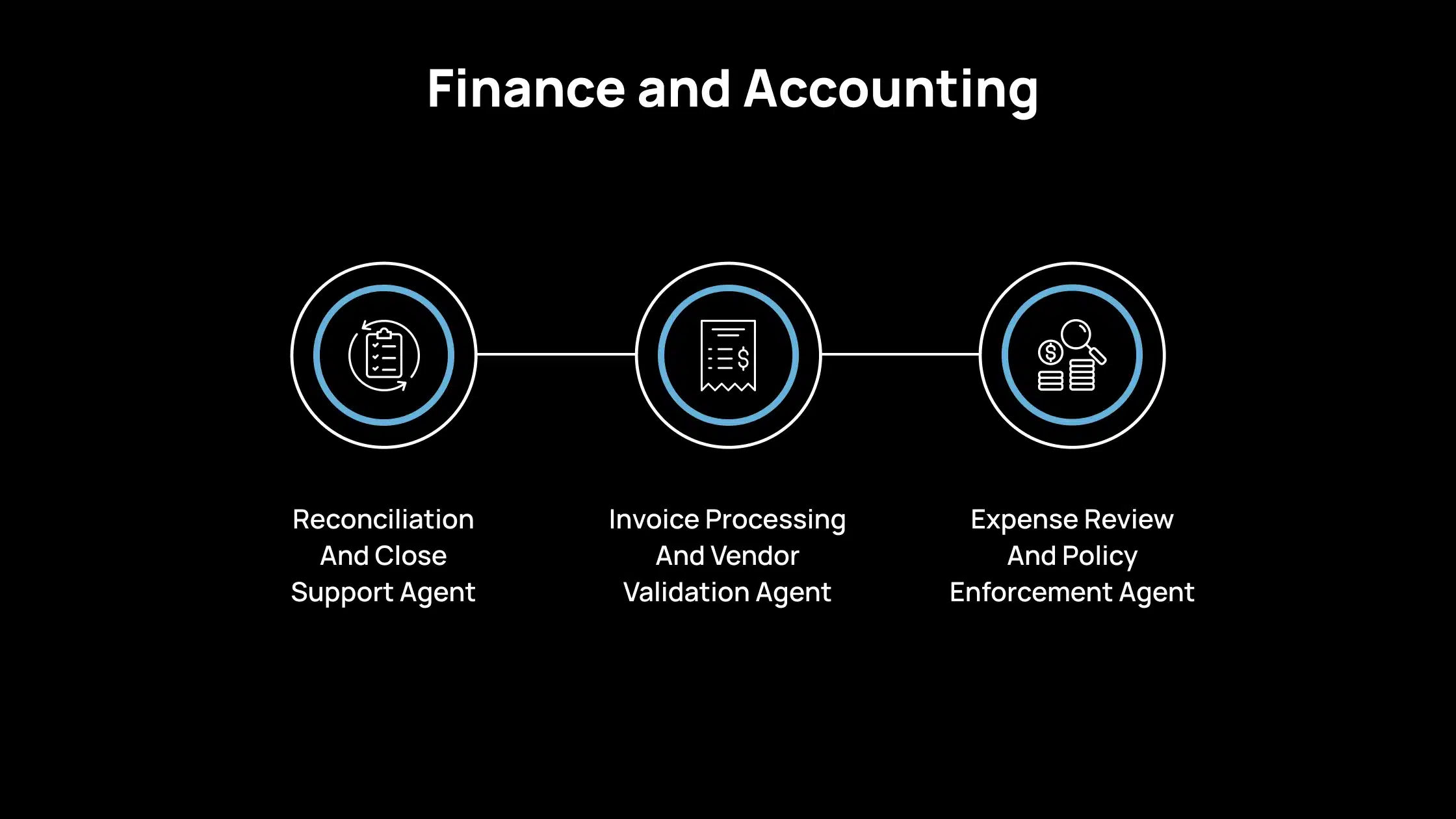
3. Finance And Accounting
Reconciliation And Close Support Agent
A reconciliation agent helps you match transactions across different systems and identify items that need attention. It reviews bank feeds, ledger entries, invoices, and receipts. When something does not align, it flags the mismatch and prepares a summary for your review. It also suggests potential journal entries based on your rules.
For example, if a payment appears in your bank statement but not in your accounting system, the agent highlights the discrepancy, provides possible reasons, and prepares a draft entry for your approval. This reduces manual checking and helps you shorten your month-end close.
Invoice Processing And Vendor Validation Agent
An invoice processing agent reads invoices, extracts important fields such as amounts, dates, vendor details, and line items, and compares them to purchase orders or contracts. When amounts match and meet your policy requirements, the agent marks them as ready for approval. If something looks incorrect, it escalates the issue.
For example, if an invoice shows a quantity higher than the originally ordered quantity, the agent flags the difference and notifies the responsible team. This helps you maintain accuracy and reduce payment risks.
Expense Review And Policy Enforcement Agent
An expense review agent checks each submission against your company’s policy. It looks for missing receipts, unusual amounts, out-of-policy categories, or duplicate entries. Based on its findings, it either approves the expense or routes it to a reviewer.
For example, if an employee submits a travel expense without a receipt or exceeds the allowed limit, the agent creates a note explaining the issue and sends it to the approver. This helps ensure consistent policy enforcement without requiring your finance team to manually inspect every item.
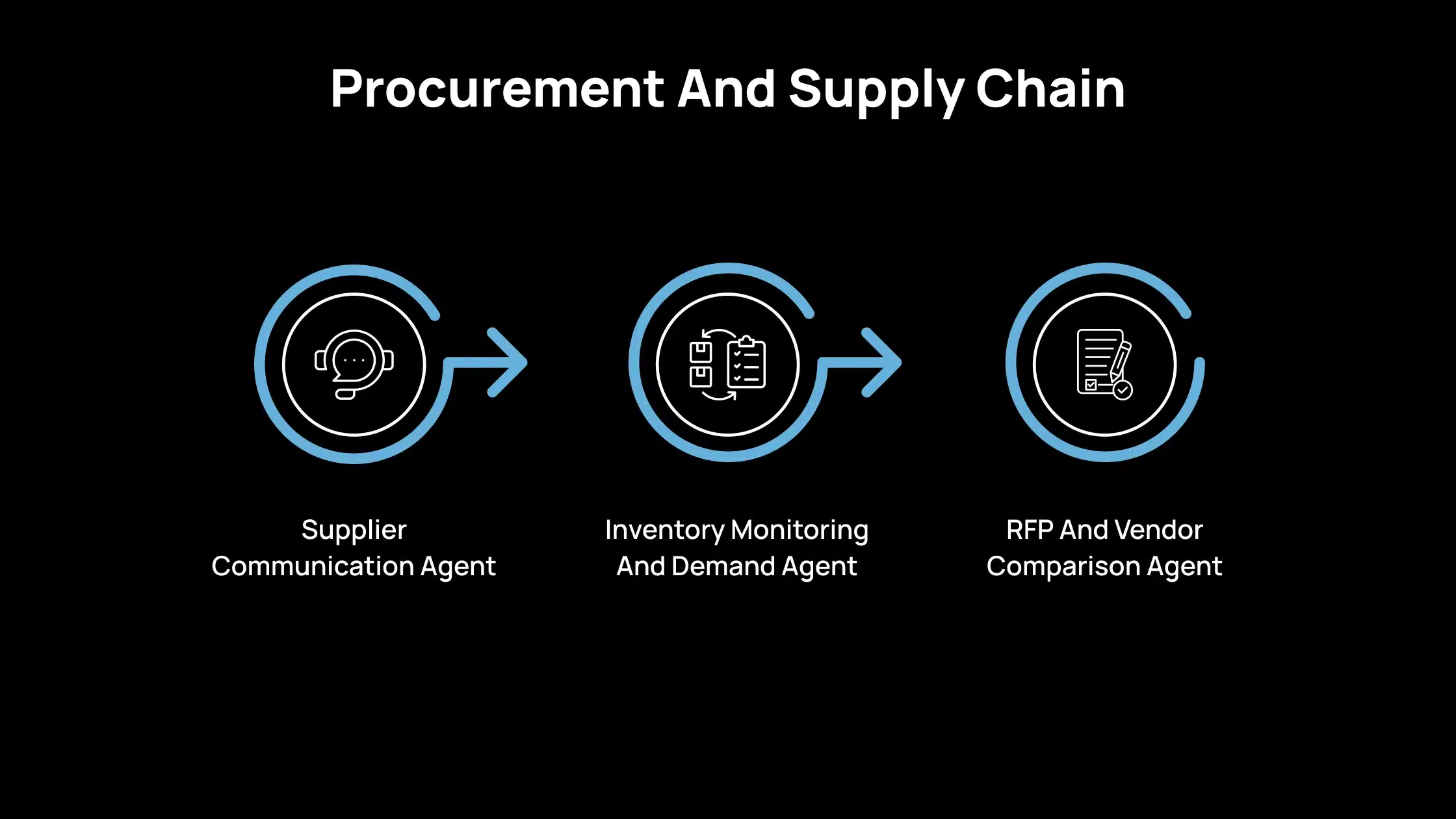
4. Procurement And Supply Chain
Supplier Communication Agent
A supplier communication agent helps you manage routine coordination with vendors. It requests order confirmations, expected delivery dates, and quantity approvals without waiting for manual follow-ups. When a supplier indicates a delay or changes an order detail, the agent alerts the right person immediately so you can respond before it affects downstream work.
For example, if a supplier updates the delivery date for a critical component, the agent surfaces the change, provides context, and recommends next steps such as adjusting production schedules or requesting an alternative source. This lets you address issues earlier and reduce the chance of supply chain disruptions.
Inventory Monitoring And Demand Agent
An inventory monitoring agent analyzes SKU performance, stock levels, sales velocity, and seasonal trends. It identifies which items are approaching a stockout or which products are overstocked. Based on your reorder rules, it recommends reorder points or prepares draft purchase orders for your review.
For example, if a fast-moving item consistently drops below its safety stock level, the agent notifies you and generates a draft order with the suggested quantity. This helps maintain availability while avoiding unnecessary inventory costs.
RFP And Vendor Comparison Agent
An RFP agent reviews vendor proposals, extracts important information, and organizes it into a clear comparison. It highlights pricing differences, delivery timelines, service capabilities, and contract risks. This reduces the time you spend manually summarizing each proposal.
For example, if three vendors submit bids for the same service, the agent creates a side-by-side summary showing strengths, limitations, and risk considerations. This allows your team to make a more informed decision without sorting through lengthy documents.
5. Human Resources And People Ops
Candidate Screening Agent
A candidate screening agent evaluates resumes against your hiring criteria. It checks skills, experience, certifications, and relevant keywords based on the role rubric. It can also send structured screening questions and gather responses. After reviewing all inputs, it prepares a summary with notes and a preliminary recommendation for the recruiter or hiring manager.
For example, if you are hiring for a technical role, the agent checks for required programming languages, years of experience, and relevant project work. It then compiles the findings into a clean report so you can quickly determine who should move forward.
Interview Scheduling Agent
An interview scheduling agent searches for mutual availability across calendars, suggests ideal time slots, and sends meeting invitations. It manages conflicts automatically and shares reminders with both candidates and interviewers. This removes the coordination workload that often slows hiring.
For example, if a panel interview requires three internal stakeholders, the agent scans their calendars, finds the earliest shared slot, schedules the meeting, and communicates the details. This helps you speed up the interview process without back-and-forth emails.
Onboarding And Access Provisioning Agent
An onboarding agent handles the setup steps for a new employee. It creates system accounts, assigns permissions based on role, requests devices, and collects necessary documents. It also ensures that tasks are completed in the correct order, so nothing is missed.
For example, if a new hire needs access to HR software, CRM tools, and an internal knowledge base, the agent creates those accounts and confirms access status. It then compiles an onboarding checklist to track progress. This ensures your new hire is ready on day one with minimal manual effort from your team.
Choosing The Right Workflow For Your First AI Agent
When you plan your first AI agent rollout, you want a workflow that is stable, measurable, and safe to automate. This helps you build confidence, prove value, and prepare your team for broader adoption. The sections below guide you through the factors to assess before choosing your first use case.
1. Internal Maturity Assessment
- You need clean, accessible data for an agent to perform well. If the workflow depends on missing records or inconsistent formats, the agent will struggle. Start with a process where data is already structured and easy to retrieve.
- Your systems must allow the agent to take actions. If your CRM, ERP, or ticketing system has open APIs or connectors, the agent can read and write information reliably. This reduces friction during integration.
- Agents work best when the steps are mostly consistent. If a workflow follows a defined sequence, even with occasional variations, it is a suitable candidate for automation.
2. Pilot Requirements
- You need measurable outcomes such as reduced processing time, fewer manual steps, or improved accuracy. These metrics help you evaluate effectiveness and justify expansion.
- Choose a task where errors are unlikely to cause significant financial or compliance issues. For example, generating drafts or running analyses is safer than approving payments.
- Everyone involved should understand the pilot’s purpose, scope, and success indicators. Alignment ensures smoother adoption and avoids confusion once the agent goes live.
3. Scaling To Additional Use Cases
- Once you complete the pilot, use the same structure for similar workflows across teams. This reduces development time and ensures consistent behavior across agents.
- Define who can create agents, who approves them, and how updates are handled. A central framework keeps deployments organized as adoption grows.
- Decide which steps require human review. For example, actions involving system updates or customer communication may need approval before execution.
- Track agent activity through logs and dashboards. This helps your team quickly identify issues, measure performance, and refine workflows over time.
Risks And Considerations When Deploying AI Agents
As you expand automation with AI agents, it is important to manage risks related to accuracy, data access, system behavior, and regulatory compliance. Clear safeguards make your deployment more reliable and easier to oversee.
1. Hallucination And Accuracy Concerns
Set minimum confidence levels for the agent’s outputs. When confidence is low, the agent should request human input instead of making assumptions.
Ask the agent to reference the data source it used. This ensures transparency and helps reviewers verify information before approving actions.
2. System Access And Data Permissions
Give the agent only the access it needs for the workflow. Limiting permissions reduces risk if the agent misinterprets a request or encounters unexpected data.
Enable logs that capture the agent’s actions, prompts, and system interactions. These records help you investigate issues and maintain compliance.
3. Workflow Breakage And Escalations
Workflows often fail due to temporary issues such as network delays or unavailable APIs. Agents should retry these steps automatically before escalating.
If a task becomes too complex or unusual, the agent should hand it off with a clear summary. This prevents incorrect actions and keeps the workflow moving.
4. Compliance And Regulatory Constraints
Check whether your organization handles data subject to GDPR, SOC2, and HIPAA regulations. The agent must comply with all requirements regarding privacy, security, and data access.
Make sure the agent stores data only as long as required and in approved locations. Clear traceability supports audits and internal reviews.
How Avahi Helps You Turn AI Into Real Business Results?
If your goal is to apply AI in practical ways that deliver measurable business impact, Avahi offers solutions designed specifically for real-world challenges. Avahi enables organizations to quickly and securely adopt advanced AI capabilities, supported by a strong cloud foundation and deep AWS expertise.
Avahi AI solutions deliver business benefits such as:
- Round-the-Clock Customer Engagement
- Automated Lead Capture and Call Management
- Faster Content Creation
- Quick Conversion of Documents Into Usable Data
- Smarter Planning Through Predictive Insights
- Deeper Understanding of Visual Content
- Effortless Data Access Through Natural Language Queries
- Built-In Data Protection and Regulatory Compliance
- Seamless Global Communication Through Advanced Translation and Localization
By partnering with Avahi, organizations gain access to a team with extensive AI and cloud experience committed to delivering tailored solutions. The focus remains on measurable outcomes, from automation that saves time and reduces costs to analytics that improve strategic decision-making to AI-driven interactions that elevate the customer experience.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Leverage Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency?
Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How are AI agents different from chatbots?
Chatbots reply to questions and follow fixed flows. AI agents work with a specific goal, such as qualifying a lead or reconciling a report. They use APIs, move through multiple steps, adjust when something fails, and hand off to a human when needed.
2. Which teams benefit most from AI agents’ use cases beyond customer support?
Teams with repeatable, rule-based work see the most value. Sales and revenue teams use agents for qualification and renewals. Finance uses them for reconciliation and invoice checks. HR, procurement, and operations use agents for screening, scheduling, approvals, and vendor coordination.
3. How do I choose the right first AI agent use case?
Start with a workflow that has clean data, clear steps, and low risk if a mistake happens. Pick a process with measurable outcomes, such as time saved per request or error reduction. Align stakeholders on goals, then run a limited pilot before rolling out more AI agent use cases.
4. Are AI agents safe to use with sensitive data?
Safety depends on access controls and design. Use a least-privilege model, give the agent only the permissions required, and log every action. Combine this with strong data policies, audit trails, and compliance checks for GDPR, SOC2, HIPAA, or other standards relevant to your organization.
5. Do AI agents replace human roles or support them?
AI agents usually handle routine steps, not entire roles. They handle tasks such as data entry, matching, routing, and basic checks, while people focus on decision-making, relationships, and complex exceptions. The most effective AI agents use cases treat agents as support for teams, not full replacements.