Voice, not clicks, could be the future of healthcare documentation. This simple truth highlights one of the most significant challenges in modern clinical practice: the growing disparity between technology and the human aspect of care.
Physicians are spending more time on screens than with patients, and administrative tasks are taking a toll on their time, energy, and focus.
According to a study published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, doctors spend nearly two hours on EHR tasks for every one hour of direct patient care. Another report by the American Medical Association found that 63% of physicians experience burnout, with EHR-related workload being a leading contributor.
This is where AI-powered voice agents are beginning to transform the conversation, literally.
These intelligent systems are designed to bridge the gap between clinical intent and digital execution. By allowing clinicians to speak naturally and interact with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) through voice, these agents can dramatically reduce typing, streamline documentation, automate routine tasks, and improve both provider and patient experiences.
However, while the potential is enormous, integrating voice AI with complex EHR systems presents its own set of technical, operational, and safety challenges, including data accuracy, system latency, interoperability, and compliance.
In this blog, we’ll explore the key opportunities, benefits, and challenges of integrating AI voice agents with EHRs, and what healthcare organizations need to succeed.
TL;DR
|
Understanding Voice AI Agents in Healthcare
A Voice AI Agent in healthcare is an advanced system that allows users and clinicians to interact with digital systems using natural spoken language. Unlike traditional voice tools that simply convert speech into text (speech-to-text or dictation), modern AI voice agents are conversational and context-aware.
These agents are capable of understanding intent, which means they can recognize what the user wants to achieve, such as ordering a lab test or updating a patient’s medication. They also utilize contextual memory, enabling them to track what has been said during an interaction and maintain a coherent conversation.
Finally, they can take actions based on voice commands, such as scheduling follow-ups, updating records, or retrieving patient history, often through integration with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems.
EHR and EMR Systems: The Backbone of Modern Healthcare
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Electronic Medical Records (EMRs) are the digital foundation of modern healthcare. They serve as centralized systems that store and organize a patient’s complete medical information, ranging from medical history and diagnoses to medications, lab results, imaging, and treatment plans. These platforms help clinicians access accurate and up-to-date data, ensuring continuity of care, better coordination among healthcare providers, and data-driven clinical decisions.
The Role and Importance of EHR/EMR Systems
EHR and EMR systems have transformed the way healthcare operates. By digitizing patient records, they eliminate the need for paper documentation, enable remote access to patient data, and support clinical analytics. They are essential tools for tracking patient outcomes, identifying health trends, and improving population health management.
However, despite their significance, traditional EHR systems have certain limitations. Many are complex, time-consuming, and not optimized for clinical workflows. Physicians often find themselves spending more time entering data than engaging with patients—a trend that directly affects productivity and satisfaction. These challenges have created a need for smarter, more intuitive systems that work with clinicians rather than against them.
Integrating AI with EHR Systems
This is where AI-powered automation, particularly AI voice agents, is reshaping the EHR landscape. By integrating AI with EHR systems, healthcare providers can unlock new levels of efficiency and accuracy.
- Automation of Documentation: AI voice agents can listen during consultations, capture key clinical details, and enter structured data into the EHR automatically—reducing manual typing.
- Faster Data Retrieval: Clinicians can use natural voice commands to instantly access patient history, lab results, or treatment plans without navigating multiple screens.
- Improved Decision Support: AI models can analyze EHR data in real time, flag anomalies, and provide clinical insights, supporting more informed decisions.
In essence, EHR systems integrated with AI transform static record-keeping tools into intelligent clinical assistants. They not only improve workflow efficiency but also help restore the human connection in healthcare by giving clinicians more time to focus on patients rather than paperwork.
Practical Applications and Growth Opportunities of AI Voice Agents EHR Integration
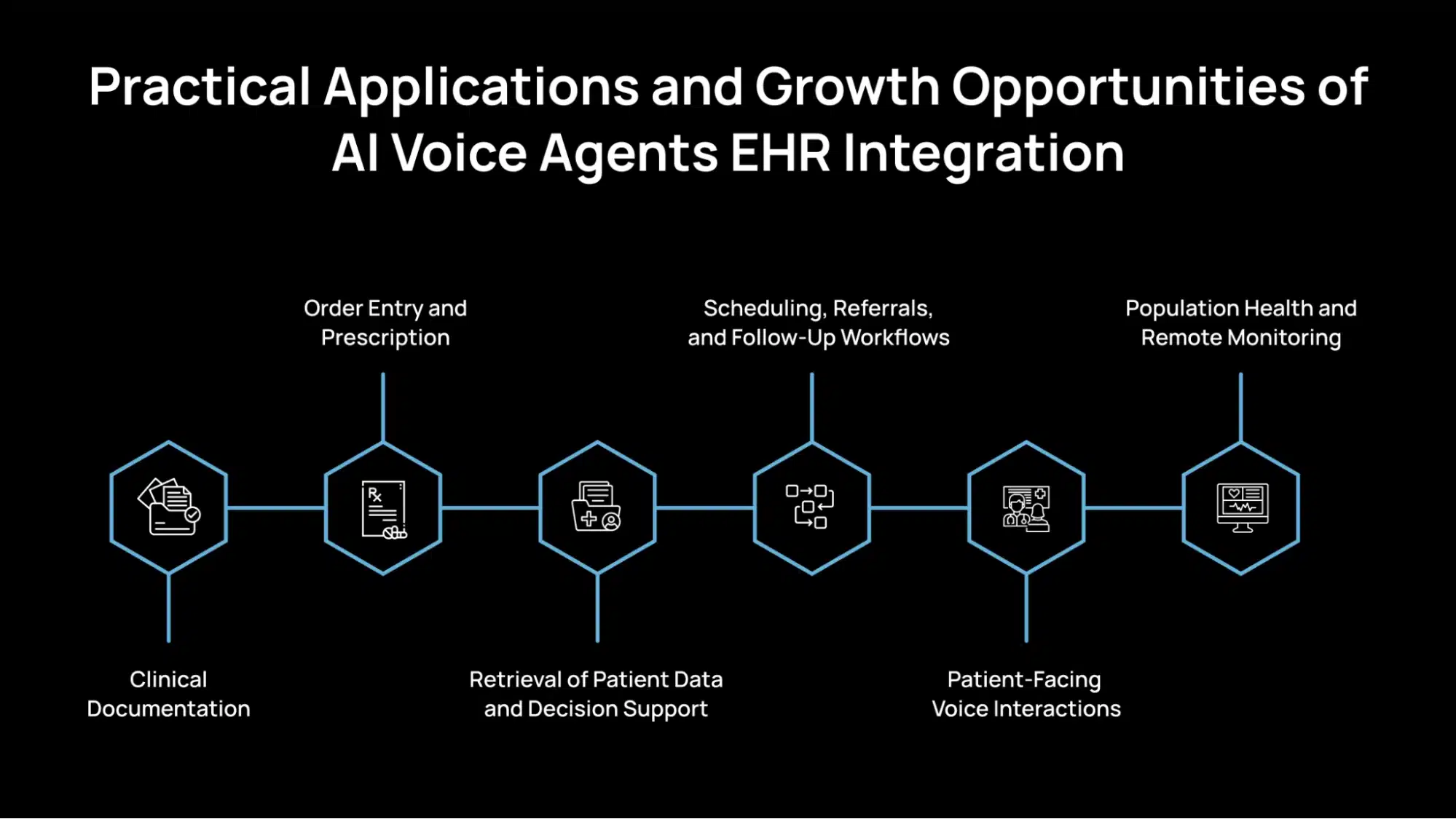
Integrating AI voice agents with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems opens up several practical use cases that can directly improve efficiency, reduce administrative burden, and support better clinical outcomes. Below are the primary domains where this integration creates meaningful value.
1. Clinical Documentation
AI voice agents can listen during patient consultations and extract crucial clinical information in real time. Instead of a physician manually typing notes, the agent identifies and records relevant data into structured fields or suggests pre-filled draft notes.
After the visit, the agent can generate summaries in clinical formats, such as SOAP (Subjective, Objective, Assessment, Plan) notes or HPI/Plan (History of Present Illness and Treatment Plan) drafts. This reduces documentation time and helps ensure essential details are not missed.
2. Order Entry and Prescription
Clinicians can use voice commands to initiate orders for lab tests, imaging, or prescriptions. For example, saying “Order a CBC and chest X-ray” allows the agent to process the request and update the EHR accordingly.
Additionally, the voice agent can cross-check orders against patient history, allergies, and known contraindications, thereby helping to prevent errors and enhancing patient safety.
3. Retrieval of Patient Data and Decision Support
Voice agents enable clinicians to retrieve patient information using natural language quickly. For instance, a doctor might ask, “What were the last three creatinine levels?” or “Does the patient have any drug allergies?” and receive a spoken or visual response based on EHR data.
These agents can also assist in clinical decision support by automatically flagging risks or generating alerts, such as “The patient is at high risk for acute kidney injury based on recent lab trends.”
4. Scheduling, Referrals, and Follow-Up Workflows
Voice AI can simplify appointment scheduling and referrals by enabling commands like “Schedule a follow-up in two weeks” or “Refer to cardiology.” The agent then updates the calendar or referral system accordingly.
It can also automate reminders for follow-ups, ensuring that patients receive notifications and reducing the risk of missed appointments or delays in care.
5. Patient-Facing Voice Interactions
AI voice agents can be used in patient-facing settings such as phone triage or front-desk automation. For example, when a patient calls and describes their symptoms, the voice agent can capture the details, update the EHR, and triage the case based on urgency.
In post-discharge care, voice agents can handle routine follow-up calls, medication reminders, and wellness check-ins, helping providers stay connected with patients between visits.
6. Population Health and Remote Monitoring
For high-risk or chronic care populations, voice agents can conduct routine check-ins via phone or smart devices. Patients can report symptoms or health status verbally, and the data is automatically logged into the EHR.
This enables proactive monitoring, timely interventions, and data aggregation for population health analytics, supporting better long-term care planning.
Transforming Care Delivery: Benefits of AI Voice Agents EHR Integration
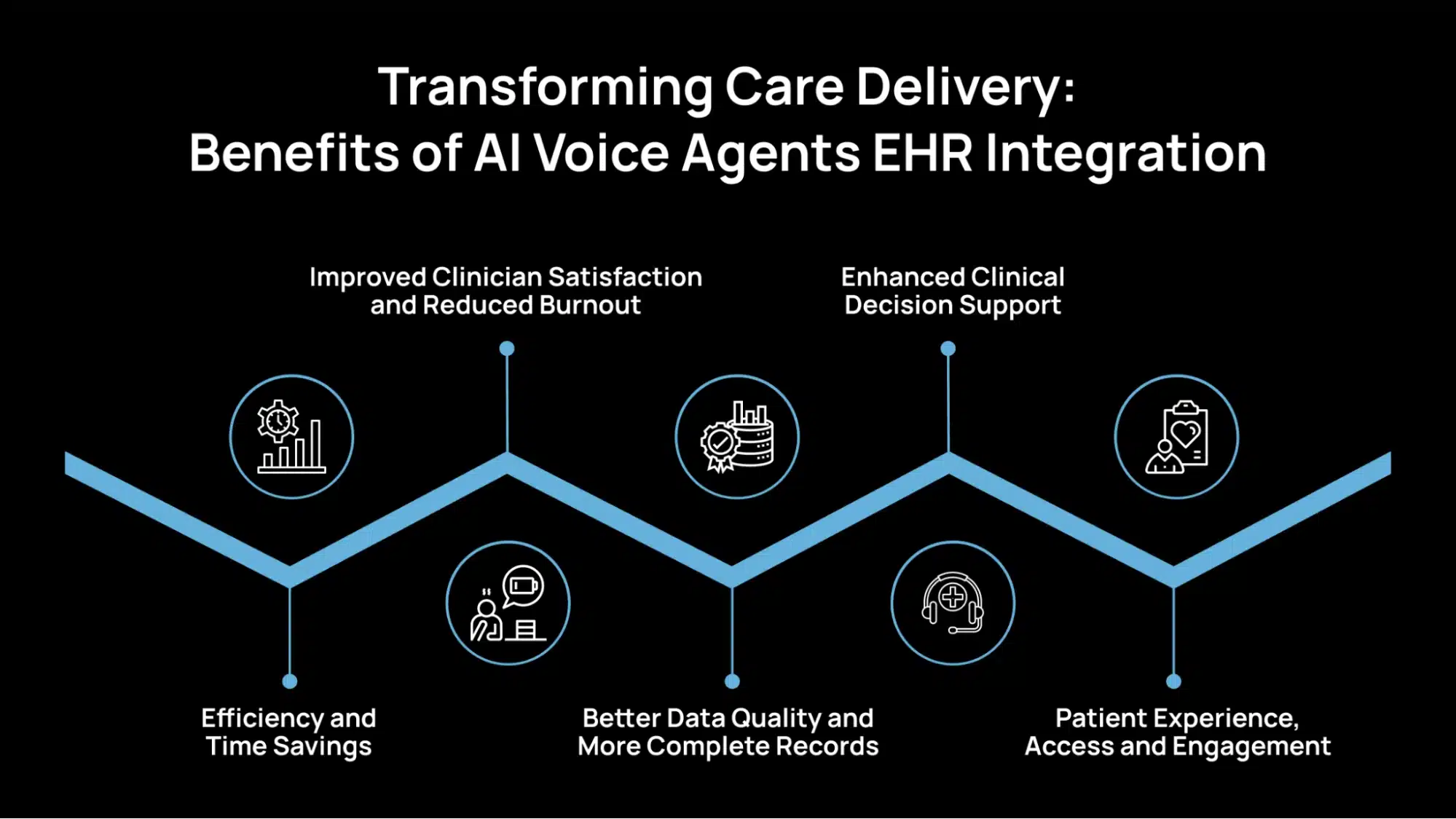
Integrating AI voice agents with EHR systems offers tangible improvements across clinical workflows, patient care, and system-wide efficiency. Below are the essential value areas supported by early research and industry observations.
1. Efficiency and Time Savings
AI voice agents reduce the need for manual data entry and screen navigation, enabling clinicians to complete documentation tasks more efficiently. Instead of typing out notes or searching through menus, providers can use natural speech to perform actions like entering vitals or ordering labs.
Physicians spend an average of 16 minutes and 14 seconds per patient encounter using EHRs.Voice-based automation can significantly lower this overhead by enabling real-time data capture during the patient encounter.
2. Improved Clinician Satisfaction and Reduced Burnout
Administrative workload is a leading cause of physician burnout. Physicians report signs of burnout, much of which is linked to time-consuming EHR use.
By offloading repetitive documentation tasks, voice AI enables providers to focus more on direct patient care. This enhances job satisfaction and contributes to a more balanced workday.
3. Better Data Quality and More Complete Records
Voice agents can promote structured and consistent data entry by guiding providers through standardized templates or extracting key clinical information during conversations.
This leads to fewer missing fields, reduced copy-paste errors, and more timely updates in the EHR. Structured data is also easier to use for analytics, billing, and population health initiatives.
Research from Stanford Medicine’s 2020 Health Trends Report noted that data fragmentation and quality issues continue to be a barrier to fully realizing the value of digital records. AI-assisted documentation helps address these gaps.
4. Enhanced Clinical Decision Support
With real-time integration, voice agents can serve as a bridge between the clinician and decision support tools. For example, they can surface alerts for potential drug interactions, abnormal lab trends, or missed preventive care.
This integration enhances patient safety and supports timely clinical decisions. When combined with AI analytics, it also enables risk flagging and personalized care suggestions based on historical data.
5. Patient Experience, Access and Engagement
From scheduling to follow-ups, voice agents enable faster response times and automation of routine interactions. This improves service levels and reduces delays in patient communication.
Voice interfaces also benefit populations that may struggle with mobile apps, such as older adults, individuals with low literacy, or those without smartphones.
Technical Barriers and Integration Challenges in AI Voice Agents EHR Integration
Integrating AI voice agents with Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems presents several technical and operational challenges. These issues stem from the complexity of healthcare data, the sensitivity of patient information, and the strict regulatory environment in which these systems operate. Here is a list of some of the main challenges and considerations in integrating AI voice agents with EHRs.
1. Interoperability and Data Standards
One of the most significant challenges is interoperability, which refers to the ability of different EHR systems and AI platforms to communicate effectively. Healthcare organizations use a variety of EHR vendors, each with unique data structures, interfaces, and custom configurations. Many of these systems are closed or partially open, making integration difficult.
A related issue is the lack of standardized APIs and consistent adoption of frameworks like FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). Without common standards, mapping unstructured data from voice outputs (such as transcripts) into structured EHR fields becomes complex and error-prone. Achieving smooth interoperability requires adherence to data exchange standards, middleware solutions, and close coordination with EHR vendors.
2. Latency and Bandwidth Constraints
Voice interactions demand real-time responsiveness. Even a short delay can disrupt the natural flow of conversation and reduce usability. However, AI inference models, huge language models, require substantial computational resources, which can lead to potential latency during processing.
Network speed and bandwidth constraints can also impact performance, especially in clinical settings with high data traffic or limited connectivity. Organizations must carefully balance edge computing (processing data locally for speed) versus cloud processing (for scalability and model accuracy). Optimizing this trade-off is crucial for maintaining reliability in real-world healthcare environments.
3. Accuracy, Error, and “Hallucination” Risk
Accuracy is essential in healthcare communication. Voice AI systems can misinterpret medical terms, particularly when encountering diverse accents, background noise, or overlapping speech. Even minor transcription errors can have profound clinical implications.
There’s also a risk of AI “hallucination”, where a model generates incorrect or fabricated responses. To mitigate this, systems should include confidence thresholds that execute commands only when the model’s confidence is high, and implement human review mechanisms for uncertain outputs. Continuous testing with diverse voice samples and domain-specific vocabularies helps improve reliability.
4. Interruption Management and Dialog Design
Effective communication requires the AI system to understand when a speaker has finished talking and how to manage interruptions. In a clinical environment, conversations are often fast-paced and involve multiple participants, making this especially challenging.
Voice agents must be trained to handle overlapping speech, accurately identify speaker intent, and use confirmation prompts when ambiguity arises. Well-designed dialog management systems can minimize errors by verifying commands (“Did you mean order CBC test?”) and supporting seamless back-and-forth interaction.
5. Clinical Safety, Escalation and Risk Management
Voice AI agents must be built with safety guardrails to prevent unintended actions. When uncertainty is detected, for example, if the agent is unsure about a medication dosage, the system should escalate to a human clinician rather than proceed automatically.
Establishing clear clinical escalation protocols, maintaining audit trails, and enforcing action logging are essential for accountability and traceability. These measures ensure compliance with healthcare safety standards and reduce the risk of automation-related errors.
6. Security, Privacy, Compliance, and Governance
Handling patient information introduces strict data security and privacy requirements. All communications must be encrypted during transmission and storage. Systems should support role-based access control, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Compliance with HIPAA (in the U.S.) and GDPR (in the European Union), as well as other regional health data laws, is non-negotiable. Advanced methods, such as data de-identification, federated learning, and privacy-preserving AI, can enhance security while maintaining performance. Transparency and explicit patient consent are equally crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring both legal compliance and patient safety.
Avahi AI Voice Agents: The Future of Intelligent Clinical Workflows
What if your clinic could handle every routine patient call without putting anyone on hold? What if your front-desk team could focus on people, not paperwork? With Avahi AI Voice Agents, that’s not just possible, it’s already happening.
Avahi AI Voice Agents offer a reliable voice automation layer that integrates with core systems to handle routine patient interactions at scale.
- Purpose-Built for Healthcare Workflows
Avahi’s voice agents are engineered with healthcare-specific intent models, allowing accurate handling of appointment scheduling, insurance inquiries, referrals, and intake coordination across medical, dental, and specialty care practices.
- Real-Time Scheduling and Transactional Automation
The system supports live scheduling, cancellations, and rescheduling without human intervention, minimizing hold times and reducing patient drop-offs.
- Integrated No-Show Management
Automated follow-up messages and reminders reduce missed appointments, optimizing provider utilization and ensuring predictable scheduling patterns.
- Priority Triage & Escalation Handling
Urgent issues are identified using contextual intent detection and routed to designated staff in real time, improving care responsiveness.
- Operational Load Redistribution
By automating common front-desk queries and administrative workflows, Avahi frees up staff resources for more value-driven patient support activities.
- High-Throughput Readiness
Whether in fast-paced urgent care centers or multi-location dental practices, Avahi scales to meet communication demands while maintaining SLA compliance and data integrity.
Discover Avahi’s AI Platform in Action
At Avahi, we empower businesses to deploy advanced Generative AI that streamlines operations, enhances decision-making, and accelerates innovation—all with zero complexity.
As your trusted AWS Cloud Consulting Partner, we empower organizations to harness the full potential of AI while ensuring security, scalability, and compliance with industry-leading cloud solutions.
Our AI Solutions Include
- AI Adoption & Integration – Utilize Amazon Bedrock and GenAI to Enhance Automation and Decision-Making.
- Custom AI Development – Build intelligent applications tailored to your business needs.
- AI Model Optimization – Seamlessly switch between AI models with automated cost, accuracy, and performance comparisons.
- AI Automation – Automate repetitive tasks and free up time for strategic growth.
- Advanced Security & AI Governance – Ensure compliance, detect fraud, and deploy secure models.
Want to unlock the power of AI with enterprise-grade security and efficiency? Start Your AI Transformation with Avahi Today!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is AI voice agents’ EHR integration?
AI voice agents’ EHR integration refers to the seamless connection between AI-powered voice assistants and electronic health record systems. This enables clinicians to use voice commands for documentation, order entry, and data retrieval, improving speed and accuracy.
2. How does AI voice agents’ EHR integration benefit healthcare providers?
The integration reduces manual data entry, accelerates clinical workflows, and minimizes burnout. With AI voice agents for EHR integration, providers can focus more on patient care and less on administrative tasks.
3. What challenges come with AI voice agents’ EHR integration?
Key challenges include ensuring data accuracy, meeting HIPAA compliance requirements, managing interoperability across various systems, and maintaining real-time processing capabilities. Overcoming these challenges is essential for the safe and effective integration of AI voice agents with EHRs.
4. Is AI voice agents’ EHR integration secure and HIPAA-compliant?
Yes, when properly implemented. Secure AI voice agents’ EHR integration involves end-to-end encryption, role-based access controls, and strict data governance to comply with HIPAA and other relevant health data regulations.
5. Can small clinics benefit from AI voice agents’ EHR integration?
Absolutely. Even small practices can benefit from AI voice agents’ EHR integration by reducing the time spent on documentation and improving patient interactions, ultimately making healthcare delivery more efficient.